
- •Icons Used in This Book
- •Network Security
- •Vulnerabilities
- •Threats
- •Types of Attacks
- •Network Security Policy
- •AVVID and SAFE
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Firewall Technologies
- •Cisco PIX Firewall
- •Foundation Summary
- •The Cisco Secure PIX Firewall
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Overview of the Cisco PIX Firewall
- •Cisco PIX Firewall Models and Features
- •Foundation Summary
- •System Maintenance
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Accessing the Cisco PIX Firewall
- •Installing a New Operating System
- •Upgrading the Cisco PIX OS
- •Creating a Boothelper Diskette Using a Windows PC
- •Auto Update Support
- •Password Recovery
- •Foundation Summary
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •How the PIX Firewall Handles Traffic
- •Address Translation
- •Translation Versus Connection
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Access Modes
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •TurboACL
- •Object Grouping
- •Advanced Protocol Handling
- •Foundation Summary
- •Syslog
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •How Syslog Works
- •How Log Messages Are Organized
- •How to Read System Log Messages
- •Disabling Syslog Messages
- •Foundation Summary
- •Cisco PIX Firewall Failover
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •What Causes a Failover Event
- •What Is Required for a Failover Configuration
- •Failover Monitoring
- •Stateful Failover
- •LAN-Based Failover
- •Foundation Summary
- •Virtual Private Networks
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Overview of VPN Technologies
- •Cisco VPN Client
- •PPPoE Support
- •Foundation Summary
- •Scenario
- •Completed PIX Configurations
- •PIX Device Manager
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •PDM Overview
- •PIX Firewall Requirements to Run PDM
- •Foundation Summary
- •Content Filtering with the Cisco PIX Firewall
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Filtering Java Applets
- •Filtering ActiveX Objects
- •Filtering URLs
- •Foundation Summary
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Overview of AAA and the Cisco PIX Firewall
- •Cisco Secure Access Control Server (CSACS)
- •Foundation Summary
- •How to Best Use This Chapter
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Specifying Your AAA Servers
- •Troubleshooting Your AAA Setup
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Multimedia Support on the Cisco PIX Firewall
- •Attack Guards
- •PIX Firewall’s Intrusion Detection Feature
- •ip verify reverse-path Command
- •Foundation Summary
- •Answers to the “Do I Know This Already?” Quizzes and Q&A Questions
- •Chapter 1
- •Chapter 2
- •Chapter 3
- •Chapter 4
- •Chapter 5
- •Chapter 6
- •Chapter 7
- •Chapter 8
- •Chapter 9
- •Chapter 10
- •Chapter 11
- •Chapter 12
- •Chapter 13
- •Chapter 14
- •Chapter 15
- •Appendix B
- •What’s Wrong with This Picture?
Network Security Policy 7
Network Security Policy
The network security policy is the core of the network security process. Every company should have a written network security policy. At a minimum, that policy should fulfill the following objectives:
•Analyze the threat based on the type of business performed and type of network exposure.
•Determine the organization’s security requirements.
•Document the network infrastructure and identify potential security breach points.
•Identify specific resources that require protection and develop an implementation plan.
NOTE |
An effective network security policy must include physical security to prevent unauthorized |
|
users from gaining local access to equipment. |
|
|
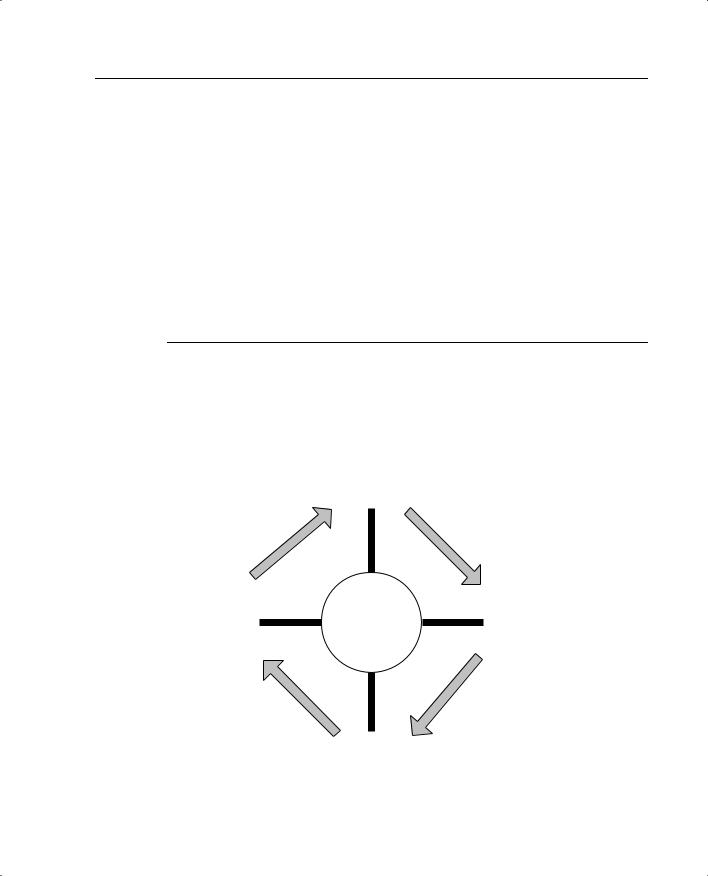
The security process is the implementation of the security policy. It is broken into four steps that run continuously, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Security Process
Secure
Improve
SECURITY
POLICY
Monitor
Test

8 Chapter 1: Network Security
Step 1: Secure
Step 1 is implementing your network security design. This includes hardening your network systems by installing security devices such as firewalls, intrusion detection sensors, and AAA (authentication, authorization, and accounting) servers. Firewalls on the network perimeter prevent unwanted traffic from entering the network. Firewalls within the network verify that only authorized traffic moves from one network segment to another. Restrict access to resources to only authorized users, and implement a strong password convention. Implement data encryption to protect data passing from one network to another across an unsecured connection (via the Internet) or to protect sensitive data within your network. The Cisco PIX Firewall and Cisco Secure IDS are both industry-leading network security devices. The purpose of this step is to prevent unauthorized access to the network and to protect network resources.
Step 2: Monitor
Step 2 is monitoring the network. By installing the Cisco Secure IDS at key points of the network, you can monitor both internal and external traffic. It is important to monitor both internal and external traffic, because you can check for violations of your network security policy from internal sources and attacks from external sources and determine if any external attacks have breached your network. All your perimeter devices, including firewalls and perimeter routers, can provide log data. This log data can and should be filtered to look for specific incidents.
Step 3: Test
Step 3 involves testing the effectiveness of your security design. Verify that the security equipment is properly configured and functioning correctly. The Cisco Secure Scanner is an excellent tool for verifying the capabilities of your design and determining how effective your security devices will be as they are currently configured.
Step 4: Improve
Step 4 involves the data from your intrusion detection sensors and your test data to improve the design. An effective security policy is always a work in progress. It continues to improve with every cycle of the process. This does not necessarily mean implementing new hardware with every cycle. It could be changing certain company procedures or documenting new potential threats and vulnerabilities.
It is very important to remember that security is an ongoing process that is based on the security policy.

AVVID and SAFE 9
AVVID and SAFE
Cisco has two programs in place—AVVID and SAFE—to help network architects design secure network solutions. Both of these programs are based on proven solutions that have been tested for full functionality and interoperability.
What Is AVVID?
AVVID is the Cisco Architecture for Voice, Video, and Integrated Data. AVVID is an open architecture that is used by Cisco partners to develop various solutions. Every Cisco partner solution is rigorously tested for interoperability with Cisco products. AVVID is designed for large enterprise networks requiring an infrastructure that can support emerging applications such as IP telephone, content delivery, and storage. This network of networks concept allows the use of a single network infrastructure to support the concurrent operation of multiple solutions. The Cisco Enterprise Solutions Engineering team creates design guides for use when planning enterprise network infrastructure using Cisco products, software, and features. These solutions provide the following benefits:
•Network performance, measured by the following three metrics rather than just throughput:
—Application response time—This metric measures how well an application responds to changes on a network and how well it responds to network congestion and changes its link speed.
—Device performance—This metric measures the limitations in performance of individual network devices such as switches or routers. A poorly performing device can become a bottleneck to the network, so it is important that devices are not overtaxed. Device performance measures errors, drops, and CPU usage as well as packet-per-second throughput.
—Protocol performance—This metric measures the ability of devices to operate dynamically by verifying that devices and the network can handle the use of routing protocols and the Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP).
•Scalability must allow a network to grow into the future. The network must be designed to allow growth in the following areas:
—Topology—A topology must be selected so that changes do not require major reconfiguration of the entire network.
—Addressing—The addressing scheme should allow for changes with a minimum impact on the addressing scheme and should allow for route summarization.
—Routing protocols—The design should be such that changes in the network are easily handled by the routing protocols.
•Availability is always a major concern to network managers. A network’s ability to overcome outages and adapt to changes is paramount. Three availability issues are incorporated into the AVVID design model:

10Chapter 1: Network Security
—Equipment and link redundancy—This includes not only redundant components and high-availability configurations, but also redundancy within the equipment, such as dual power supplies and other features designed into the modular products.
—Protocol resiliency—The focus here is to use the most resilient protocol. Multiple redundant protocols do not necessarily provide the best solution.
—Network capacity design—A network design that allows for significant expansion in the event of a redundant link failure.
The AVVID network infrastructure design incorporates many different topologies and technologies to provide optimum efficiency and stability.
What Is SAFE?
Cisco’s Secure Blueprint for Enterprise Networks (SAFE) is a guide for network designers focusing on the implementation of secure enterprise networks. It is based on Cisco AVVID. SAFE uses best practices and the interoperability of various Cisco and Cisco Partner products. It uses the following design fundamentals (from the Cisco Systems SAFE white paper, copyright 2000):
•Security and attack mitigation based on policy
•Security implementation throughout the infrastructure (not just specialized security devices)
•Secure management and reporting
•Authentication and authorization of users and administrators to critical network resources
•Intrusion detection for critical resources and subnets
•Support for emerging networked applications
The SAFE Network Security Blueprint is composed of the critical areas of network security:
•Perimeter security—Protects access to the network by controlling access on the network’s entry and exit points
•Secure connectivity—Provides secure communications via virtual private networks (VPNs)
•Application security—Ensures that critical servers and applications are protected
•Identity—Solutions that provide secure authentication and authorization
•Security management and monitoring—Allows for centralized management of security resources and the detection of unauthorized activity on the network
NOTE |
Cisco SAFE Implementation 1.0 (exam 9E0-131) was released on December 31, 2002, and is |
|
a requirement for the CCSP Certification. For more information, refer to www.cisco.com/go/ |
|
certifications |
|
|

Q&A 11
Q&A
The questions in this section are designed to ensure your understanding of the concepts discussed in this chapter.
The answers to these questions can be found in Appendix A.
1True or false: Network security means locking your computer in a filing cabinet.
2What is the goal of a reconnaissance attack?
3True or false: A horizontal scan affects more hosts on a network than a vertical scan.
4True or false: To secure your network, you only need to install a firewall.
5What is the difference between a security policy and a security process?

This chapter covers the following exam topics for the Secure PIX Firewall Advanced Exam (CSPFA 9E0-111):
1.Firewalls
2.PIX Firewall Overview
