
- •Кафедра иностранных языков
- •Contents
- •Conventional Power Generation in Russia ………………………………… 35
- •Modes of Heat Transfer
- •Famous People
- •Hydroelectric Power Plants
- •Famous People
- •Vladimir Grigorievich Shukhov ( 1853 - 1939)
- •Nuclear Power Plants
- •Famous People
- •Fossil-fuel Power Plants
- •Famous People
- •Steam Turbine
- •Famous People
- •Furnace
- •Famous People r obert Boyle (1627-1691)
- •Hydroelectric power
- •Famous People
- •Steam Nozzles
- •Famous people
- •Gas Burners
- •Famous People
- •Old and Modern Theories of Heat
- •Famous People
- •Supplementary texts Part I What do the words ‘Hot’, ‘Cold’ , and ‘Temperature’ mean?
- •Generators
- •Engines
- •Protection Against Environmental Pollution
- •What Is Heat?
- •Evaporation
- •How Can We Use Steam?
- •Electric Current Generation
- •Conventional Power Generation in Russia
- •Amount of Heat Depends on Current and Resistance
- •The Turbine Nozzle
- •Electric Power Plants
- •Chernobyl Accident
- •Part II Renewable energy
- •Steam Generation
- •The Steam-Generating Units
- •Heat Exchangers
- •Direct-Contact Feed-Water Heaters
- •Closed Feed Water Heaters
- •Condensers
- •How a Condenser Works
- •Steam turbine
- •Gas turbine
- •Electricity generation
- •Primary energy sources used in electrical power generation
- •Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydro Systems
- •Automatic Production and Technology Processes
- •Краткий грамматический справочник Страдательный залог
- •Причастие (The Participle)
- •Независимый причастный оборот (The Absolute Participle Construction)
- •Герундий (The Gerund)
- •Сложный герундиальный оборот
- •Инфинитив (The Infinitive)
- •Функции инфинитива
- •Объектный инфинитивный оборот (The Complex Object)
- •Субъектный инфинитивный оборот (The Complex Subject)
- •Инфинитивный оборот с предлогом "for" (Infinitive Construction Introduced by the Preposition "for")
- •Grammar exercises
- •Irregular Verbs Неправильные глаголы
- •Idioms, Prepositional and Conjunctional Phrases
- •Англо-русский словарь
- •Библиографический список
Gas turbine
T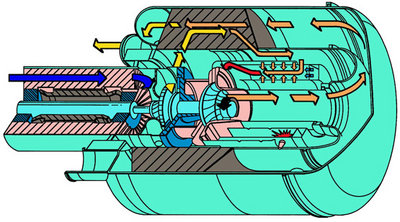 he
world's first commercial, oil-free gas turbine is manufactured by
Capstone. This
machine has a single-stage radial compressor and turbine, a
recuperator, and foil
bearings.
he
world's first commercial, oil-free gas turbine is manufactured by
Capstone. This
machine has a single-stage radial compressor and turbine, a
recuperator, and foil
bearings.
A gas turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a flow of combustion gas. It has an upstream compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between. (Gas turbine may also refer to just the turbine element.)
Energy is added to the gas stream in the combustor, where air is mixed with fuel and ignited. Combustion increases the temperature, velocity and volume of the gas flow. This is directed through a diffuser (nozzle) over the turbine's blades, spinning the turbine and powering the compressor.
Energy is extracted in the form of shaft power, compressed air and thrust, in any combination, and used to power airs\craft, trains, ships and generators.
Industrial gas turbines range in size from truck-mounted mobile plants to enormous , complex systems. The power turbines in the largest industrial gas turbines operate at 3,000 or 3,600 rpm to match AC power grid frequency and to avoid the need for a reduction gearbox. Such engines require a dedicated building. They can be particularly efficient – up to 60% - when waste heat from the gas turbine is recovered by a conventional steam turbine in a combined cycle configuration. They can also be run in a cogeneration configuration, where the exhaust is captured to heat steam which is then used to heat buildings or run air-conditioners through a steam turbine.
Simple cycle gas turbine in the power industry require smaller capital investment than combined cycle gas, coal or nuclear plants and can be designed to generate small or large amounts of power. Also, the actual construction process can take as little as several weeks to a few months, compared to years for base-load plants. Their other main advantage is the ability to be turned on and off within minutes, supplying power during peak demand. Large simple cycle gas turbines may produce several hundred megawatts of power and approach 40%
thermal efficiency. (From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_turbines
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the first process in the delivery of electricity to consumers. The other three processes are electric power transmission, electricity distribution and electricity retailing.
T he
importance of dependable electricity generation, transmission and
distribution
was revealed when it became apparent that electricity was useful for
providing
heat, light and power for human activities. Decentralized power
generation
became possible when it was recognized that alternating current (was
recognized
to be able to transport) electric power lines can transport
electricity at low
cost across great distances by taking advantage of the ability to
transform the voltage using power transformers.
he
importance of dependable electricity generation, transmission and
distribution
was revealed when it became apparent that electricity was useful for
providing
heat, light and power for human activities. Decentralized power
generation
became possible when it was recognized that alternating current (was
recognized
to be able to transport) electric power lines can transport
electricity at low
cost across great distances by taking advantage of the ability to
transform the voltage using power transformers.
Electricity has been generated for the purpose of powering human technologies for at least 120 years from various sources of potential energy. The first power plants were run on wood, while today we rely mainly on oil, natural gas, coal, hydroelectric and nuclear power and a small amount from hydrogen, solar energy, tidal harnesses, and wind generators. The generation and distribution of electricity has mostly been in the hands of either privately owned or state owned public
utilities. In recent years some governments have started to privatise or corporatise these utilities as part of a move to introduce market forces to monopolies. The New Zealand Electricity Market is a typical example.
The demand for electricity can be fed in two different ways. The primary method thus far has been for public utilities to construct large scale projects to generate and transmit the electricity required to fuel growing economies. Many of these projects have unpleasant environmental effects such as air or radiation pollution and the flooding of large areas of land.
Increasingly, distributed generation is seen as a new way to supply the electrical demand close to the users. Smaller, distributed projects can: Protect from blackouts caused by the closure of de-centralized power plants or transmission lines for maintenance, market manipulation or emergency shut downs Reduce pollution Allow smaller players to enter the energy markets
Rotating turbines attached to electrical generators produce most commercially available electricity. Turbines are usually rotated by using steam, water, wind or other fluids as an intermediate energy carrier.
Fuel cells produce electricity using a variety of chemicals and are seen by some people to be the most likely source of power in the long term, especially if hydrogen can be used as the feedstock. However, hydrogen is usually only an energy carrier, and must be formed by some other power source.
Small mobile generators are often driven by diesel engines, especially on ships, remote building sites or for emergency standby. (From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical generation
