
СУБД Oracle / Литература / PowerDesigner 9 / GeneralFeatures
.pdf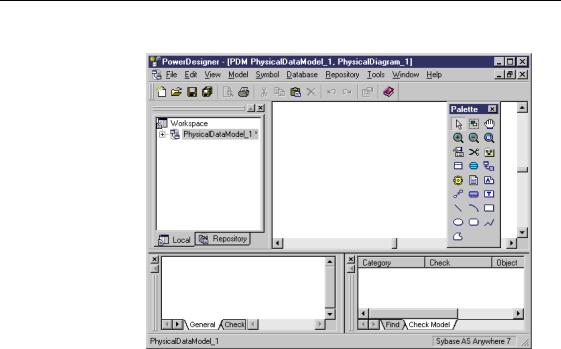
&KDSWHU 3RZHU'HVLJQHU %DVLF &RQFHSWV
The following picture shows the typical PowerDesigner interface:
Browser |
The %URZVHU is a tool for managing information. |
|
In PowerDesigner, the Browser allows you to manage the information items |
|
you use to perform a modeling task. |
|
The Browser displays information in the WUHH YLHZ which is a powerful tool |
|
for navigating among all models existing in the work session. |
Output window |
The 2XWSXW ZLQGRZ shows the progress of any process that you run from |
|
PowerDesigner in the General page. The other pages display messages during |
|
check model, database generation, and reverse engineering operations. |
Repository |
The PowerDesigner UHSRVLWRU\ is a tool for storing versioned documents. In |
|
the repository, a document can be a model, a multi-model report, a MS Word |
|
file, a graphic file, etc. |
Result List |
The 5HVXOW /LVW displays, on separate tabs, the final results of an object |
|
search or a check model operation. |
|
When you check a model, the result list displays the errors and warnings |
|
detected during the verification of the model. |
|
When you perform an object search, the result list displays all objects |
|
matching the search criteria. |
General Features Guide |
|

3RZHU'HVLJQHU LQWHUIDFH
Work area The ZRUN DUHD is the primary window that displays the following types of MDI child windows:
♦The GLDJUDP window is a graphical view displaying the symbols of objects belonging to models or packages
♦The 5HSRUW (GLWRU is a tool for building and editing reports based on your models
♦The 5HSRUW 7HPSODWH (GLWRU is a tool for creating and customizing report templates
|
The ZRUN DUHD is an open work environment that enables you to switch from |
|
one window to another, without having to close the current model diagram |
|
window, or the editor. |
Property sheets |
3URSHUW\ VKHHWV display the properties of a selected object. |
|
Property sheets are modeless and resizable windows; they can remain open |
|
while you open other windows, such as other property sheets or lists. |
Object lists |
2EMHFW OLVWV display all objects of a selected type existing in a package or a |
|
model. |
|
Lists display object properties organized in columns. In a list you can drag |
|
and drop items, sort columns, and define and apply a filter. |
|
Lists are modeless and resizable windows. They can remain open while you |
|
open other windows, such as property sheets or lists. |
|
PowerDesigner |

&KDSWHU 3RZHU'HVLJQHU %DVLF &RQFHSWV
3RZHU'HVLJQHU PRGHOLQJ HQYLURQPHQW
|
The typical hierarchy of objects in PowerDesigner is as follows: |
|
The ZRUNVSDFH is the root of the Browser tree view. When you expand the |
|
workspace, the first optional organization level is the IROGHU Folders are |
|
used to organize the contents of the workspace. Each folder can contain one |
|
or more models. |
|
The PRGHO is the basic design unit in PowerDesigner. |
|
A model can be divided into sub-sets called SDFNDJHV. Each model, or |
|
package, has one or more graphical views called GLDJUDPV, which contain |
|
the symbols of the design REMHFWV. |
|
To document the models you build in PowerDesigner, you can create and |
|
print UHSRUWV in different languages that can be attached to a model or remain |
|
independent. |
Workspace |
A workspace defines the entire set of information you need to perform a |
|
modeling task with PowerDesigner. A workspace is local, it corresponds to |
|
the needs of one user on a given machine. |
|
The workspace allows you to save in a file, a local environment with a |
|
hierarchy of folders and models. It is reusable so the folder structure and data |
|
location information remains on your disk every time you start a session. |
|
You can create several workspace files on your machine, but you can only |
|
work in one workspace at a time in a PowerDesigner session. |
Folders |
A folder is a optional container designed to help you organize the hierarchy |
|
within a workspace. You use folders to structure the contents of the |
|
workspace in your local work environment. |
|
A folder is local to a workspace you cannot share the folder structure you |
|
have created with other users. |
Models |
A model is a container of objects. It is the main design unit. |
|
A model is defined by a name, a type, a file name and a location in the |
|
workspace. |
General Features Guide |
|
3RZHU'HVLJQHU PRGHOLQJ HQYLURQPHQW
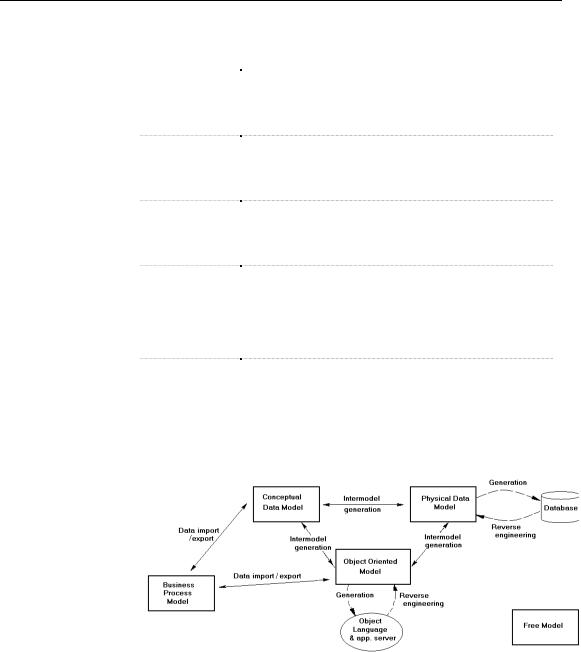
You can build the following types of models:
0RGHO W\SH |
'HILQLWLRQ |
|
Conceptual Data |
Represents the overall logical structure of a system. The |
|
Model |
CDM contains data objects not yet implemented in the |
|
|
physical database. It provides a formal representation of the |
|
|
data needed to run an enterprise or a business activity |
|
Physical Data |
Specifies the physical implementation of a database. With the |
|
Model |
PDM you consider the details of actual physical |
|
|
implementation. It addresses both data access and data |
|
|
storage constraints |
|
Object-Oriented |
Allows you to design object-oriented models using the UML |
|
Model |
notation. With the OOM you can use design classes that |
|
|
interact to perform certain actions that together make up a |
|
|
system of information |
|
Business Process |
Represents a simplified UML activity diagram with Business |
|
Model |
Process extensions. The BPM does not include any |
|
|
implementation details and can be readily used as an input |
|
|
document to do object-oriented analysis. At a conceptual |
|
|
level, it is particularly suitable for analyzing, designing or |
|
|
documenting Business-to-Business exchanges (B2B) |
|
Free Model |
Allows you to create different graphics for your |
|
|
specifications, to explain the architecture of your system and |
|
|
applications, the use-case scenarii of the applications, the |
|
|
flowcharts, or to define your own method |
|
|
|
The following illustration shows the PowerDesigner global software solution:
You can organize a model by dividing it up into packages. You can also divide the display over several diagrams.
|
PowerDesigner |
|
&KDSWHU 3RZHU'HVLJQHU %DVLF &RQFHSWV |
|
|
Packages |
A package is a subdivision of a model. When you are working with large |
|
models, it is useful to split them into smaller subdivisions in order to avoid |
|
manipulating large sets of items. Packages are used to assign different tasks |
|
or subject areas, to different development teams. |
|
A model can contain any number of packages. You can build a hierarchy of |
|
packages, in which there is no limit to the level of decomposition. |
Report |
A report is the association of one or several models, a structure, and a |
|
selection of objects. It represents the structure of one or more models. You |
|
can generate multi-model reports to give a clear overview of all your models |
|
in the same report. You can also generate individual model reports to focus |
|
on a particular model and analyze its contents. Besides, you can choose the |
|
language in which the report is generated. |
Diagram |
A diagram is a graphical view of a model or package, which displays object |
|
symbols. Diagrams allow to split the display of large models and packages in |
|
order to focus on certain objects or subject areas. They can also be used to |
|
view the symbols of the same objects, displayed with different kinds of |
|
information. |
|
You can create several diagrams in a model or in a package. The diagram |
|
window usually appears with a specialized toolbar called 3DOHWWH. In the |
|
palette, you can select tools to create objects in your models and packages. |
Model Objects |
Model objects is a general term used for all items belonging to a model. Each |
|
model includes a series of different object types corresponding to the type of |
|
the model. |
|
Some model objects can have graphical symbols for example a class in the |
|
Object-Oriented Model or a view in the Physical Data Model. Other model |
|
objects, such as business rules, do not appear with symbols in the diagram |
|
window, although they exist in the model. |
General Features Guide |
|

3RZHU'HVLJQHU UHVRXUFHV
3RZHU'HVLJQHU UHVRXUFHV
|
PowerDesigner ships with resources that are available for all models, you can |
|
reuse resources from one model to another. |
DBMS |
A '%06 in PowerDesigner is an object that contains specifications for a |
|
particular DBMS. It provides PowerDesigner with the syntax and guidelines |
|
for generating databases, triggers, and procedures, appropriate for a target |
|
DBMS or ODBC driver. |
|
When you create a new PDM, you choose a target DBMS, which can be |
|
linked to the model from an external file, or copied locally to the model. The |
|
definition for a DBMS can be edited from its property sheet. |
|
Modifications to a linked DBMS are available to all models using that |
|
DBMS, while modifications to a local DBMS are specific to the model |
|
concerned. |
Report templates |
The 5HSRUW 7HPSODWH (GLWRU allows template creation and modification in |
|
different languages. A report template is an independent and reusable file |
|
saved on your hard disk, which gives the overall structure of your report. You |
|
can create this file to generate model reports or PXOWL PRGHO UHSRUWV (several |
|
models in the same report). |
|
You use the Report Editor to define a report structure in order to generate a |
|
multi-model report or a report for a single model. |
|
A report uses one or several templates to associate one or several models, and |
|
a selection of objects. It reflects the contents of one or several models. You |
|
can generate multi-model reports or model reports. |
|
A report can be attached to a model or saved in an independent file. |
Object Languages |
The REMHFW ODQJXDJHV resource contains specifications for a particular |
|
language. It provides PowerDesigner with the syntax and guidelines for |
|
implementing stereotypes, data types, scripts and constants for a target |
|
language. |
|
When you create a new OOM, you choose a target language. The definition |
|
for a target language can be edited from its property sheet. |
|
Modifications to a linked language are available to all models using that |
|
target language. |
Extended Model |
An H[WHQGHG PRGHO GHILQLWLRQ allows you to expand object definitions. To |
Definitions |
do this, an extended model definition is created and saved as a file with the |
|
XEM extension. You can create or attach one or several extended model |
|
definitions to a model. |
|
PowerDesigner |
|
&KDSWHU 3RZHU'HVLJQHU %DVLF &RQFHSWV |
|
|
Profiles |
A profile is an extension mechanism used for customizing a metamodel with |
|
additional semantics. Profiles are used for creating sub-categories of objects |
|
(stereotypes and criteria), customizing the graphics of objects, adding |
|
additional metadata to objects (extended attributes), and defining new or |
|
modified generation capabilities (templates). You create a profile when you |
|
need to design a user-defined methodology, a model with predefined meaning |
|
or for a specific generation target. |
|
Profiles appear in all DBMS, object languages and extended model |
|
definitions delivered with PowerDesigner. By default, each new resource file |
|
has a profile upon creation. |
|
For more information on profiles, see section Managing Profiles in the |
|
$GYDQFHG 8VHU 'RFXPHQWDWLRQ. |
Report Languages |
A UHSRUW ODQJXDJH resource is a file in XML format saved with the .XRL |
|
extension. It contains all the printable texts of a report and their default |
|
values. You use it when you create your report and later generate it whatever |
|
the output. A report language resource file is stored in a central area and can |
|
be shared by any report to guarantee data consistency and save time to the |
|
user. |
Conversion Tables |
&RQYHUVLRQ WDEOHV provide a way to define a correspondence between the |
|
name and the code of an object or the code and the name of an object. |
|
Conversion tables are stored into separate CSV (Comma-Separated Values) |
|
files and are shared by all models. |
General Features Guide |
|

3RZHU'HVLJQHU UHVRXUFHV
|
PowerDesigner |
C H A P T E R 2
8VLQJ WKH 3RZHU'HVLJQHU ,QWHUIDFH
About this chapter |
This chapter describes the PowerDesigner general interface and explains how |
|
|
to use the different components. |
|
Contents |
7RSLF |
3DJH |
|
||
|
Managing windows |
14 |
|
Managing toolbars |
17 |
|
Using property sheets |
28 |
|
Using lists |
43 |
|
Defining global options |
62 |
General Features Guide |
|
0DQDJLQJ ZLQGRZV
0DQDJLQJ ZLQGRZV
The PowerDesigner main window is divided into different windows with independent behavior.
8QGHUVWDQGLQJ WKH PDLQ ZLQGRZ RUJDQL]DWLRQ
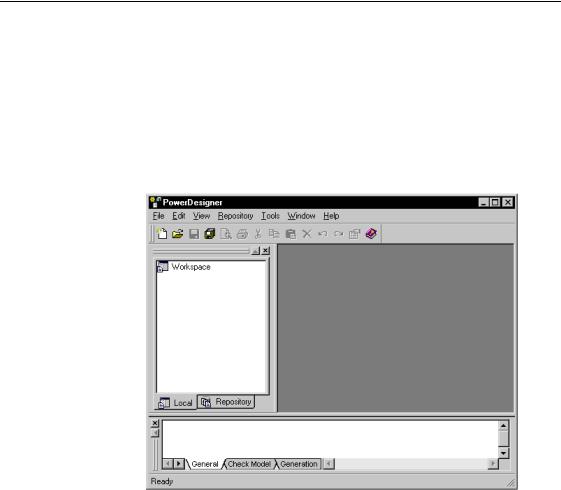
When you open PowerDesigner, the following interface appears:
In the upper part of the window, you can see the PowerDesigner general title bar and the menu bar. Below the general menus, the standard toolbar displays tools for carrying out standard operations such as Open, Save or Undo.
Two dockable windows are displayed by default when you open PowerDesigner: the Browser tree view on the left and the Output window at the bottom.
On the right hand side, the work area is empty upon opening. This area is used to display the different MDI child windows.
|
PowerDesigner |
