
- •М.Г. Кочнева строительные и дорожные машины
- •Рецензенты:
- •I. Read the following words and translate them into Russian:
- •II. Read the following numbers:
- •III. Learn the following information about the Infinitive:
- •IV. Translate into Russian paying attention to the Infinitive.
- •V. Learn the following words.
- •VI. Find the equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •VII. Translate into Russian paying attention to the Participle and the Gerund.
- •VIII. Read the following text.
- •IX. Find the proper function to the following handling equipment mechanisms.
- •X. Complete the sentences using variants (a), (b) or (c).
- •XI. Replace the underlined words by their synonyms given below.
- •XII. Make up sentences according to the scheme:
- •It is interesting to note that a… b
- •XIII. Make up questions according to the models using the words given below:
- •2.What are jacks used for?
- •XV. Read, translate and retell the following text using the introductory phrases:
- •XVI. Translate into English.
- •XVII. Retell the text according to the following scheme.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 2 lesson two
- •I. Read the following words. [au] [qu] - tower, counterweight, thousand, mounted, lower, slower, flow. But: group [grHp]
- •II. Learn the following words.
- •III. Find the equivalents to the following English terms.
- •IV. Find the correct equivalents to the English word combinations.
- •V. Learn the following model and the information about the Infinitive.
- •VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the Infinitive.
- •VII. Read and translate the following text.
- •Tower cranes
- •Fig. 4. Tower cranes
- •IX. Connect the sentences according to the contents.
- •X. Translate into Russian paying attention to the Infinitive.
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XIII. Make up questions with words given below using the models. Answer them.
- •2. How are tower cranes classified ?
- •XIV. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XV. Read, translate and retell the text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVI. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 3 lesson three
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •V. Find the equivalents using variants (a) or (b).
- •VI. Learn the following models and the information about the Complex
- •VII. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the Complex Subject and the Complex Object.
- •VIII. Read and translate the following text.
- •IX. Make up sentences using the scheme. Translate them into Russian.
- •X. Connect the sentences according to the contents.
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XIII. Use the Complex Subject and the Complex Object instead of complex sentences. Translate them into Russian.
- •XIV. Make up questions with the words given below using the models:
- •2. Where are self-powered jib cranes used ?
- •XV. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XVI. Read and retell the text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVII. Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 4 lesson four
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Form nouns from the following verbs by means of the suffix “tion”.
- •III. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the Russian equivalents to the following English terms.
- •V. Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words.
- •VI. Translate the following word combinations into Russian.
- •VII. Learn the following information about the Gerund.
- •VIII. Translate the sentences into Russian paying attention to the Gerund.
- •IX. Read and translate the following text.
- •X. Connect the following parts of sentences using variants a and b.
- •XI. Complete the following sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •XII. Translate into Russian paying attention to the Complex Subject.
- •XIII. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XIV. Fill in the gaps with prepositions. Translate the sentences.
- •XV. Express your doubt using expression: “Is it really so?” (Это на самом деле так?) Ask a general question.
- •XVI. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVII. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Learn the following words:
- •III. Find the correct equivalents to the English terms.
- •IV. Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
- •V. Learn the information about the translation of the verb “to be”.
- •VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the verb “to be”.
- •VII. Read and translate the following text.
- •VIII. Connect the following sentences according to the contents.
- •IX. Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to the
- •Infinitive, the Complex Subject and the Complex Object.
- •X. Insert the verbs in the proper forms. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XI. Fill in the prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XII. Make up questions with the given terms using the model.
- •2. What are the basic elements of a belt conveyor?
- •XIII. Express your agreement or disagreement with following statements.
- •XIV. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XV. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVI. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 6 lesson six
- •I.Read the following words.
- •II. Form adjectives by means of suffix “able”.
- •III. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the equivalents to the following English terms.
- •V. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •VI. Learn the following models and the information about Participle II.
- •VII. Translate the following sentences paying attention to Participle II.
- •VIII. Read and translate the following text.
- •IX. Complete the following sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •X. Translate the sentences paying attention to the Infinitive and the Complex Subject.
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the prepositions. Translate the sentences.
- •XIII. Express agreement or disagreement with the following statements.
- •XIV. Ask questions on the underlined words:
- •XV. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XVI. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVII. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 7 lesson seven
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Mind the stress.
- •III. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the equivalents to he following English terms:
- •V. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms:
- •VI. Translate into Russian using variants.
- •VII. Learn the following information about «that».
- •IX. Read and translate the following text.
- •X. Complete the sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the preposition. Translate the sentences.
- •XIII. Express agreement or disagreement with the following statements. Use the expressions: “I think so”, I don`t think so”.
- •XIV. Make up questions according to the model using the words given below.
- •XV. Ask questions on the underlined words.
- •XVI. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XVII. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVIII. Read and retell the following text using introductory phrases.
- •XIX. Learn the following dialogue.
- •V. Find the equivalents to the following terms.
- •VI. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •VII. Make up sentences according to the scheme.
- •VIII. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the verb “should”.
- •IX. Read and translate the following text.
- •X. Make up sentences according to the scheme using the columns a and b.
- •XI. Complete the sentences using variant (a) or (b).
- •XVIII. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XIX. Learn the following dialogue.
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Form nouns from adjectives by means of suffixes “-ity’и “ability”.
- •III. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the equivalents to the following English terms.
- •V. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the translation of the verbs “to be”, “to have”.
- •VII. Use the Complex Subject and the Complex Object in the following sentences.
- •VIII. Read and translate the following text.
- •IX. Complete the following sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •X. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XI. Fill in the necessary prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XV. Answer the following questions using some of the introductory phrases.
- •XVI. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVII. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Урок 10 lesson ten
- •I. Read the following words.
- •II. Learn the following words.
- •IV. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •V. Learn the information about the word “most”.
- •VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the word “most”.
- •VII. Read and translate the following text.
- •VIII. Define the functions of the shovels.
- •IX. Complete the following sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •X. Use the Gerund instead of the Infinitive.
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the necessary prepositions. Translate the sentences.
- •XVI. Answer the following questions using the introductory phrases.
- •XVII. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVIII. Read and retell the following texts using the introductory phrases.
- •XIX. Learn the following dialogue.
- •II. Read the following words paying attention to the endings.
- •III. Learn the information about Participle I.
- •IV. Translate the following sentences paying attention to Participle I.
- •V. Learn the following words.
- •VI. Find the equivalents to the following word combinations.
- •VII. Read and translate the following text.
- •VIII. Connect sentences according to the contents:
- •IX. Complete the sentences using variants (a) or (b).
- •X. Fill the gaps with prepositions.
- •XI. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences.
- •XIII. Answer the following questions.
- •XIV. Translate into English.
- •XV. Read, translate and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVI. Learn the following dialogue and make up your own dialogue about wheel excavators. Use the scheme of this dialogue.
- •1. Read the following words.
- •III. Form adverbs from the adjectives, translate them.
- •IV. Learn the following words.
- •V. Find the equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •VI. Translate into Russian paying attention to the Participle, the Gerund, the Infinitive, the Complex Subject, the Complex Object.
- •VII. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the Absolute Participle Construction.
- •VIII. Read and translate the following text.
- •IX. Connect the sentences according to the contents. Translate them.
- •X. Insert the verbs in the proper form. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XI. Fill in the necessary prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •XVI. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •XVII. Read and retell the following text using the introductory phrases.
- •XVIII. Learn the following dialogue.
- •Приложение
- •Supplementary reading
- •Суффиксы прилагательных и нареий
- •Cловарь
- •Open, V [`qupqn] открывать
- •Заключение
- •Библиографический список
- •Рекомендуемая литература
- •Оглавление
- •Маргарита григорьевна кочнева строительные и дорожные машины
- •394006 Воронеж, ул. 20-летия Октября, 84
VI. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the word “most”.
1. Most engines operate on the four-stroke cycle.
2. Most commonly in construction electric friction-type winches are used.
3. Pyramidal and conical hoppers are the most common.
4. Forced-discharge is the most reliable although it involves a greater consumption of power.
5. Power graders are most widely used in road construction.
VII. Read and translate the following text.
REVOLVING SHOVELS
The principle of operation subdivides all shovels into revolving shovels and ditchers.
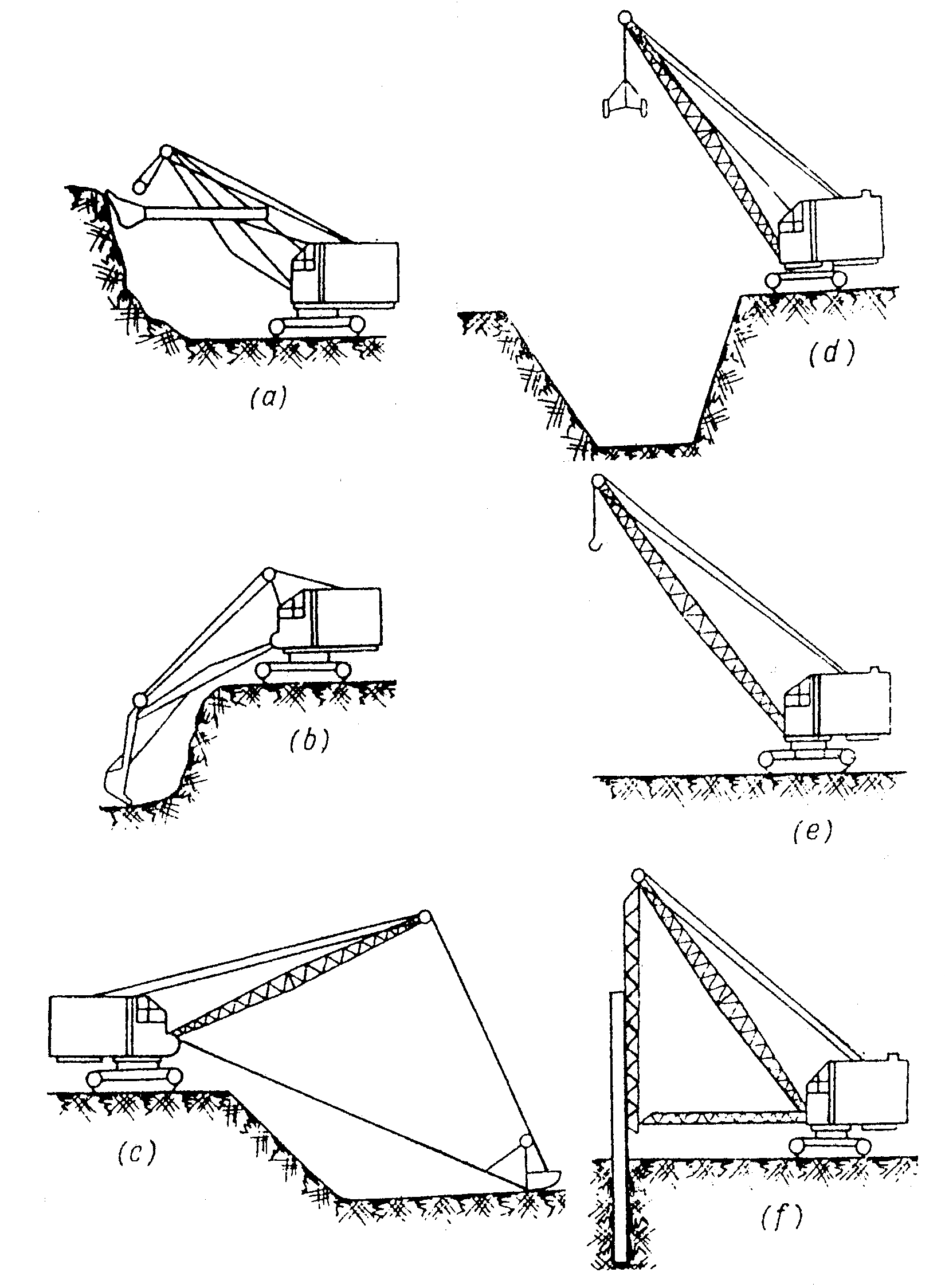
Fig. 6. Front attachments of revolving shovels
A revolving shovel digs soil while standing at one place where as a ditcher moves continuously. Revolving shovels are most widely used in all branches of construction: to drain and irrigate land, extract mineral resources, in mining for baring operations, etc. Revolving shovels can be classified by their purpose, bucket capacity, degree of universality, type of power plant, running gear, and controls. Depending on the bucket capacity and purpose revolving shovels can be divided into the following groups:
Building shovels with bucket capacities of 1.5- 4 cubic meters, used together with various alternative attachments for construction and auxiliary jobs and in small quarries for excavating building materials.
Quarry shovels with bucket capacities of 4-8 cubic meters, intended for extracting raw materials in quarries, for digging very heavy soils.
Stripping shovels with bucket capacities of 4-10 cubic meters, employed for removing the capping and dumping it in piles in open-cast mining,
Walking draglines with bucket capacities from 4 to 50 meters for digging deep cuts in soft soil in hydro-technical construction.
Revolving shovels are also subdivided into universal, semi-universal and special types.
Universal shovels are designed for operating with various alternative attachments: face shovel (Fig.6a), drag shovel (Fig.6b), dragline (Fig.6c), crane (Fig.6e), clamshell (Fig.6d), tower crane, pile driver (Fig.6f) and a frozen soil ripper.
Face shovels, drag shovels and draglines are the principal and most widespread kinds of replaceable attachments.
In addition to the principal attachments, semi-universal shovels have one or two auxiliary rigs. Most commonly such shovels carry a face shovel, a dragline or a crane. Special heavy type shovels are designed with only one type of attachment – a dragline or a face bucket.
The power plant of a shovel may be a diesel engine, an electric drive powered from an external supply or a diesel-electric drive. Most building shovels are powered by a diesel engine which can sometimes be replaced by an electric motor powered from the mains.
VIII. Define the functions of the shovels.
1. Building shovels a) are intended for digging deep cuts in soft soil
in hydro-technical construction.
2. Quarry shovels b) are used in construction and in small quarries
for excavating building materials.
3. Stripping shovels c) are employed for removing the capping and
dumping it in piles in open-cast mining.
4. Walking draglines d) are intended for extracting raw materials in
quarries and for digging very heavy soil.
