
- •International Trade
- •International Trade
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Insurance
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Money Transfer. Western Union
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •International Business
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Business
- •Infrastructure, industries, the global regime, host-countries, investments, environment
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial institutions
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial Institutions
- •Investment opportunities, unit of account, should focus, to settle, contributed
- •International Trade 2
Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
currency n – валюта, гроші; hard currency – вільно конвертована валюта; soft currency – неконвертована валюта
e.g. Today each country has its own currency with names such as hryvnia, dollar, euro, pound, etc.
exchange n – 1) обмін; 2) іноземна валюта; 3) операції з іноземною валютою; 4) переказний вексель; 5) біржа
e.g. The term “foreign exchange” means foreign currency, short term credit instruments in foreign currencies and the system of dealing in foreign currencies.
convert v – 1)перетворювати; 2) обмінювати; 3) конвертувати; convertible currency – (вільно) конвертована валюта
e.g. Foreign exchange also means the system of converting the currency of one country into that of another.
exchange rate/rate of exchange – курс обміну валют; floating exchange rate – плаваючий курс обміну валют; fixed exchange rate – фіксований курс обміну валют
supply n – 1) постачання, поставка; 2) пропозиція
supplier n – постачальник; supply and demand - пропозиція і попит
e.g. The price of the US dollar is determined by the supply and the demand for this currency on the foreign exchange market.
fluctuate v – коливатись
fluctuation n – коливання
e.g. As demand fluctuates, the rates of exchange also fluctuate.
accumulate v – накопичувати
accumulation n – накопичення
e.g. The National Bank accumulates foreign currency in its foreign exchange reserves.
deplete v – 1) вичерпувати; 2) виснажувати (запаси, резерви)
depletion n – виснаження, вичерпання
e.g. If the demand increases, the bank depletes its foreign exchange reserves.
II. Read and translate the text:
Foreign Exchange
Centuries ago gold or silver coins were used as money. The value of each nation’s money was determined by the gold (or silver) content of each coin. Today, each country has its own currency with names such as euro, dollar, pound, hryvnia, etc. A distinction is made between domestic currency and foreign currency. A distinction can also be made between foreign currency and foreign exchange.
Foreign exchange is a broader term than foreign currency, as it also includes short term credit instruments (bills of exchange, etc.) in foreign currencies. (Foreign exchange also means the system of dealing in and converting the currency of one country into that of another).
Currencies can be (a) free or convertible (hard) currencies (b) transferable currencies, which can be transferred from one bank to a foreign bank on the basis of agreements, and (c) closed currencies (soft currencies), which can only be used by special arrangement in international payments.
The price at which one currency can be exchanged for another (i.e. the price of a currency on the foreign exchange market) is called the exchange rate or rate of exchange.
Under a floating exchange rate the rates of exchange are determined by market trading based on the supply of and demand for specific currencies. As demand fluctuates, the rates fluctuate also – rising when demand is greater than supply and declining when supply exceeds demand. Under a fixed exchange rate the government keeps the price fixed, in the short run by accumulating or depleting its foreign exchange reserves or else by borrowing abroad or introducing foreign exchange restrictions.
III. Answer the following questions:
How was the value of money determined in the past?
Which of the terms “foreign currency” or “foreign exchange” is broader and why?
What kinds of currency do you know?
What do we call “hard currency”? “transferable currency”? “soft currency”?
What does the rate of exchange show?
How is the floating rate of exchange determined?
Who determines the fixed exchange rate and how is this done?
IV. Give Ukrainian equivalents of the following:
a distinction is made between; a broader term; a bill of exchange; the system of dealing in foreign currencies; by special arrangement; based on the supply and demand; in the short run; to keep the price fixed.
V. Give English equivalents of the following:
вміст золота (або срібла) в монеті; короткострокові кредитні інструменти; на основі угод; валютний ринок/біржа; торги на ринку; шляхом накопичення або спустошення; вводити обмеження обміну валют; позичати закордон.
VI. Match the definition on the right with the word on the left. Translate and learn the definitions:
currency |
|
credit |
|
exchange |
|
to borrow |
|
to lend |
|
to fluctuate |
|
In what situations do you exchange currency? borrow currency? lend currency?
VII. Fill in the gaps with the words from the list below:
supply, demand, currency, fluctuations, exchange office, lending
… is usually backed by gold and silver.
Exchange rate … are a problem both for buyers and sellers.
Yesterday the … of the US dollar was greater than the … so its exchange rate against the hryvnia slightly declined.
You can convert your money into the currency you need at the ….
There is always some risk in … money.
VIII. Look at the exchange rates and convert the following sums according to the model:
As the exchange rate of the US dollar against the pound sterling is 0.70 we get 70 pounds for 100 US dollars.
1000 yen into Swiss francs; 200 pounds into euros; 500 euros into yen; 100 Swedish kronen into pounds sterling; 50 Canadian dollars into US dollars. (All data given as of March, 2002)
Country |
Name of the currency unit |
Currency units |
|||
per $ |
per £ |
per € |
per¥100
|
||
Britain Canada Japan Sweden Switzerland United States Euro area |
pound sterling dollar yen krona frank dollar euro |
0.70 1.59 132 10.41 1.70 - 1.15 |
- 2.26 188 14.8 2.41 1.42 1.64 |
0.61 1.38 115 9.04 1.48 0.87 - |
0.53 1.20 - 7.87 1.28 0.76 0.87 |
Write down your sentences.
IX. Match the synonyms. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X. Match the words with opposite meaning. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XI. Translate into English:
Ми можемо обміняти внутрішню валюту на іноземну в обмінних пунктах
Банки мають справу з операціями в іноземній валюті.
Неконвертовані валюти можуть використовуватись лише за окремими узгодженнями в міжнародних платежах.
Коливання курсу обміну валют впливають на економіку країни.
Коли попит на окрему валюту перевищує пропозицію, її курс зростає.
Існує декілька способів, якими уряд може підтримувати ціну валюти фіксованою.
XII. Topics for discussion:
Explain the difference between the terms “domestic currency”, “foreign currency”, “foreign exchange”.
Speak about the kinds of currency and their distinction.
Speak about exchange rate, its determination and types.
Skills practice:
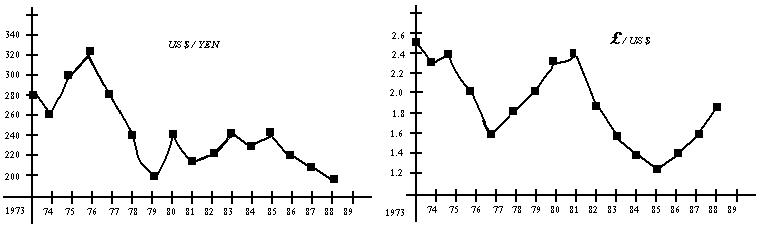
Assignment. Look at the fluctuations of the currencies above.
Between 1973 and 1980 how big/small was the drop/rise in the exchange rate of the Yen and the pound sterling?
And between 1981 and 1984?
When was the greatest drop of the £? Of the ¥?
How much has your currency fluctuated against the US $ in the past year/6 months?
Draw the graph of UAH fluctuations in the past 3 years and explain it.
Unit Five
Payments agreements
