- •International Trade
- •International Trade
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Insurance
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Money Transfer. Western Union
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •International Business
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Business
- •Infrastructure, industries, the global regime, host-countries, investments, environment
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial institutions
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial Institutions
- •Investment opportunities, unit of account, should focus, to settle, contributed
- •International Trade 2
I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
portfolio n – портфель; efficient portfolio –портфель цінних паперів з максимальним прибутком при будь-якому ризику або з мінімальним ризиком прибудь-якому прибутку, ефективний портфель; investment portfolio – інвестиційний портфель
e.g. Efficient portfolio should contain 15 to 20 randomly selected securities.
return n – 1) повернення; 2) прибуток, надходження, виручка; in return for – в обмін на; after-tax return – прибуток після відрахування податків; average returns – середній розмір прибутку/надходжень; annual return – річний прибуток; gross return – валовий прибуток; rate of return – ставка/норма прибутку; annual rate of return – річна ставка прибутку; total return – сукупний прибуток; expected return – очікуваний прибуток
e.g. Portfolio investments are based on higher rates of return abroad.
risk n – ризик; risky – ризикований; total risk – сукупний ризик; risk diversification – диверсифікація/розподіл ризику; expected risk – очікуваний ризик
e.g. Risk diversification helps to create an efficient portfolio of assets.
loss n – 1) втрата; 2) шкóда; 3) збитки
e.g. Risk can be defined as a chance of financial loss, associated with a given asset.
minimum n – мінімум, мінімальне значення
minimize v – скорочувати, зводити до мінімуму; minimal – мінімальний
maximum n – максимум, максимальне значення
maximize v – доводити до максимуму; maximal – максимальний
e.g. To minimize risk and to maximize return it is advisable to create a portfolio of assets.
average n – 1) середнє значення/число; 2) середнє арифметичне; 3) страх. аварія
average v – 1) складати в середньому; 2) виводити середньоарифметичну величину/значення
e.g. What is the average return on these assets?
correlation n – кореляція, узгодження, відповідність, співвідношення
correlate v – узгоджувати, приводити у відповідність до; співвідноситись
e.g. The total risk of the portfolio declines if the assets have negative or low positive correlation.
limit n – ліміт, межа; to approach limit – прямувати до межі
limit v – обмежувати, встановлювати межу; limited – 1) обмежений; 2) з обмеженою відповідальністю (Ltd); limitation - обмеження
e.g. Due to the effect of risk diversification the total portfolio risk approaches the limit.
abundance n – достаток; abundant – той, що є в достатку; надмірний
e.g. This country has abundant financial wealth and unattractive investment opportunities.
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) – внутрішній валовий продукт
Read and translate the text:
Foreign Portfolio Investments
Investment flows are cash flows associated with purchase and sale of both fixed assets and business interest. In return for cash investors acquire shares or bonds that guarantee their property rights and interest. The price of a share is determined by two key characteristics: risk and return. Each financial decision must be viewed in terms of expected risk, expected return and their combined impact on share price.
In the most basic sense risk can be defined as the chance of financial loss, associated with a given asset. Assets that have greater chances of loss are viewed as more risky than those with lesser chances of loss. In other words, the more certain return from an asset, the less the risk. The return on an investment is measured as the total gain or loss experienced on behalf of the owner over a given period of time.
To minimize risk or to maximize return it is advisable to create a portfolio of assets. A portfolio is a collection or group of assets. The return on a portfolio is calculated as an average of returns on the individual assets from which it is formed. To develop an efficient portfolio of assets that is to minimize the total risk and maximize the total return one must apply the concept of risk diversification. Diversification means combining or adding to the portfolio assets that have a negative (or low positive) correlation. When we expand the portfolio by acquiring new assets (securities) the total portfolio risk declines due to the effects of diversification and approaches the limit. Research has shown that most of the benefits of diversification (in terms of risk reduction) can be gained by forming portfolios containing 15 to 20 randomly selected securities.
Portfolio investments are very common in international finance. They include short-term credit bills (to be redeemed within a year or less), crediting or buying assets in foreign business.
What makes investors lend money abroad? Let us assume that there exist a country A that has abundant financial wealth and unattractive investment opportunities, and a country B with limited financial wealth and abundant opportunities to capital investments. If all investments are made within the national borders, creditors in the country A should agree to the low annual rate of return, say 2%, due to the competition in the financial sector, while deficit of capital in the country B pushed the level of annual rate of return up to say 8% due to the competition for credits. If all barriers to financial flows are eliminated the creditors in the country A and those who demand credits in the country B will have strong incentives to cooperate. So credits will flow to the country B, where annual rate of return is considerably higher. Both countries will mutually benefit: the GDP in the country A will increase due to the possibility to invest its financial resources abroad at higher annual rate, while the availability of more production capital will allow the country B to increase its output. Thus portfolio investments based on higher rates of return abroad are advantageous for the world economy as a whole.
Answer the following questions:
What do investors require in return for cash?
What do securities guarantee?
How is a share price determined?
What factors must a person consider before buying stocks?
What is the aim of creating a portfolio of assets?
How is the return on a portfolio calculated?
What is “risk diversification” in financial matters?
How must assets correlate to reduce the risk?
What portfolio is considered to be the most efficient (least risky)?
What kinds of investments are treated as portfolio investments?
How can you explain the incentives to lend money abroad?
In what way do portfolio investments benefit both the lenders and the borrowers?
Give Ukrainian equivalents of the following:
investment flow; key characteristics; combined impact; the more certain return, the less the risk; it is advisable; to apply a concept; randomly selected securities; to be redeemed within a year; let us assume; to eliminate; strong incentives; to be advantageous for the economy as a whole.
Give English equivalents of the following:
основний капітал; процент/прибуток з капіталовкладень; розглядатись з точки зору/відносно чогось; можливість фінансових збитків; вдосконалювати ефективний портфель; завдяки впливу; короткостроковий кредитний вексель; отримувати взаємну користь.
Based on the text define the following terms:
risk, portfolio, return, diversification
Match the synonyms. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own:
guarantee
motivation, drive
chance
correspond
associated
secure
incentive
connected, related
correlate
possibility
Match the words with the opposite meaning. Use any 5 in the sentences of your own:
abundant
subtraction
availability
monopoly
competition
whole
addition
absence
individual
limited, scarce
Some verbs are always followed by the same preposition, for example, to depend on, to consist of. Match the prepositions with the verbs below. Consult your dictionary if necessary. Translate the combinations:
from in (3) to (4) for of on (2) |
apply ___ somebody ___ something;
benefit ___
approve ___
result ___
believe ___
refer ___
succeed ___
belong ___
depend ___
report ___ somebody ___ something
Complete the sentences using verbs and prepositions from ex. IX in the proper form. The first is done for you:
1. In the purchasing department there is a manager and five employees who report to her.
In this company, we firmly _____ ___ the value of creativity and innovation.
The development of computer technology has _____ ___ enormous changes in the way that people work.
Whether or not we succeed in creating and selling new products _____ ___ a number of factors.
Most of our staff _____ ___ at least one of the company’s sports or leisure clubs.
The Personnel Manager thinks that we would all _____ ___ further training in how to use office software.
XI. Translate into English:
Очікуваний середній прибуток залежить від рівня активів.
Низька ставка річного прибутку примушує власних кредиторів позичати гроші закордон.
Місцеве керівництво проінформувало громадськість про привабливі інвестиційні можливості регіону.
Для успіху цій компанії слід розширити свій інвестиційний портфель.
Портфельні інвестиції спричинені (зумовлені) вищою нормою прибутку закордоном.
Плануючи купити цінні папери, корисно порахувати очікуваний ризик та очікуваний прибуток та їх сукупний вплив на ціну акцій.
XII. Topics for discussion:
Risk, return and their impact on share price.
The necessity to create a portfolio of assets.
The concept of risk diversification and its impact on the efficiency of a portfolio.
Causes of foreign portfolio investments and their effect on the world economy.
XIII. Skills practice:
Solve the following problem:
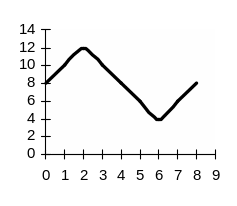
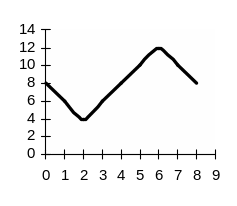
Assume that you have already invested in the machine-tool manufacturing business in one of the LDCs. This business is very cyclical, having high sales when the economy is expanding and low sales during recession (see chart, asset A). Having high return on your asset you plan to create a portfolio of assets and have to consider two options.
Option 1. To acquire shares is another machine-tool manufacturing company with sales that positively correlate with those of the firm you already have (see chart, asset B).
Option 2. To acquire shares in a sewing-machine manufacturing company which is countercyclical, having low sales during economic expansion and high sales during recession, since consumers are more likely to make their own clothes at such a time (see chart, asset C).
Assignment 1. What would your expected return be in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd … 8th year if you combined:
asset A + asset B (50% + 50% in your portfolio);
asset A + asset C (50% + 50% in your portfolio)?
Explain your calculations.
Assignment 2. Explain the risk in the first and the second case. Which portfolio would be more risky and why?
Chart
Return (%) asset A
Time, years |
Return (%) asset B
Time, years |
Return (%) asset C
Time, years |
Unit Nineteen
Foreign direct investment
Read and learn the following words and word combinations, translate the examples:
participate v – брати участь; syn. to take part
participant/participator n – учасник
participation n – участь
e.g. Equity participation that exceeds 10% of shares in foreign business constitutes foreign direct investment according to the classification adopted in the USA.
shift v – переміщувати; shift – 1) переміщення, перестановка; 2) зміна
e.g. By the early 1970s the flow of international investment began to shift.
estimate v – 1) оцінювати ; 2) підраховувати приблизно; 3) складати кошторис; estimation n – оцінка, розрахунок, калькуляція, кошторис
e.g. By the end of 1989 US.FDI abroad was estimated at 368 billion USD.
replica n – точна копія, модель, репліка
replicate v – копіювати, повторювати; replication – копіювання
e.g. Horizontal foreign direct investment means that investing firm replicates abroad some aspects of its domestic operation.
disperse v – розповсюджувати, розсіювати, розпорошувати; syn. to disseminate; to disperse/disseminate information – розповсюджувати інформацію
e.g. Various stages of component production and final assembly of components are dispersed throughout the world.
mobility n – рухливість, мобільність; mobile – рухливий, мобільний
e.g. Modern capital flows are characterized by increasing mobility.
intensify v – підсилювати
intensity n – інтенсивність, сила, напруга; work intensity – інтенсивність праці; intensive adj – інтенсивний, напружений
e.g. Competition to attract foreign investments has greatly intensified.
II. Read and translate the text:
Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign portfolio investments are sometimes called indirect investments as opposed to foreign direct investments. According to the classification adopted in the USA any investment be it acquisition of new assets or simple crediting is considered to be a foreign direct investment as long as the investor owns or receives more than 10% of shares in a foreign firm. Here are several examples illustrating both types of foreign investment.
US foreign direct investment 1. Acquisition by ALKOA corporation of 50% shares in a newly founded Jamaican firm producing bauxites. 2. Loan given by Ford corporation to a Canadian subsidiary producing spare parts, in which Ford owns 55% of shares. |
|
US foreign portfolio investment 1.Acquisition by ALKOA corporation of 5% shares in a newly founded Jamaican firm producing bauxites. 2. Loan given by Ford corporation to a Canadian company, in which Ford owns 8% of shares.
|
Thus the main difference between foreign direct and foreign portfolio investments lies in the sphere of control over a foreign firm.
By definition foreign direct investment (FDI) is the transfer by a transnational corporation (TNC) of capital, managerial and technical assets from its home country to a host country. FDI involves equity participation (property rights) which can be 100% (a wholly owned foreign subsidiary) or less (a joint venture with foreign participants), managerial control and day-to-day operational activity on the part of TNCs.
The primary motivation of FDI is to take advantage of lower costs of production, local tax benefits and, especially in the case of American firms, U.S. tariff schedules that encourage foreign production of component parts. FDI tends to be sector-specific and is usually based on the existence of some competitive advantage over local firms. Until the last quarter of the XX century the two most important types of FDI were manufacturing investments in developed OECD economies (countries-members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) and extractive industry investments, especially petroleum, in the less developed countries (LDCs). In later decades more and more FDIs are directed into services.
For a number of decades, U.S.-based TNCs dominated in terms of both the flow and stock of FDI. The total FDI stock of the U.S.-based TNCs, for instance, increased from 7.7billion US dollars in 1929 to over 232.5 billion US dollars at the end of 1985. In 1981, American FDI was more than two-fifths of the world's total FDI.
By the early I970s the flow of international investment began to shift. European and later Japanese TNCs also began to invest heavily and to produce abroad; the TNCs of several NICs were investing abroad. TNCs started crisscrossing investments in one another's home economies. For instance, the FDI into the United States by the end of 1989 was valued at 390 billion USD, while U.S.FDI abroad was estimated at 368 billion USD.
The pattern of FDI has been considerably changed in recent decades. Previously FDI was "horizontal", that is the investing firm replicated abroad some aspects of its domestic operation. Nowadays firms increase "vertical" investments, i.e. they invest in activities that 1) provide inputs for the home production process, 2) use the output of home plants. Thus, vertical FDI entails the fragmentation of the production process and dispersing throughout the world of various stages of component production and final assembly of components
Through increasing mobility of capital international competition for FDI has intensified. Using tax policies, the erection of trade barriers and even the creation of a skilled and disciplined labour force (e.g. Taiwan), governments try to attract investments and influence the international location of economic activities.
III. Answer the following questions:
1. What investments, according to US classification, are considered to be foreign direct investments?
2. What is the main difference between foreign direct and foreign portfolio investment?
3. How is foreign direct investment (FDI) defined?
4. How big is the equity participation in a subsidiary as compared to joint venture?
5. What control do TNCs achieve through FDI?
6. What is the primary motivation of FDI?
7. Into what sectors of economy are FDIs usually directed?
8. How big is the share of American FDI in the world’s total FDI?
9. In what way has the flow of international investment changed since the early 1970s?
10. What are crisscrossing investments?
11. What is meant by “horizontal” FDI?
12. Where do firms invest using the “vertical” pattern?
13. What does “vertical” FDI entail?
14. How do governments attract FDI?
IV. Give Ukrainian equivalents of the following:
by definition; a newly founded firm; to involve; a wholly owned foreign subsidiary; on the part of TNCs; local tax benefits; tends to be sector-specific; OECD economies; in terms of; to invest heavily; in recent decades; to replicate domestic operation; thus; final assembly of components; international location of economic activities.
V. Give English equivalents of the following:
згідно класифікації, прийнятої у США; при умові, що (поки); повсякденна оперативна діяльність; більш низькі виробничі затрати; тарифний режим; конкурентна перевага над; впродовж декількох десятиріч; перехресні інвестиції; раніше; забезпечувати затрати; спричиняти/тягти за собою; кваліфікована робоча сила.
VI. Read the definition of the term “investment”. Based on the definition make written translation of the proposed sentence:
Investment. New capital additions to a firm’s capital stock. Although capital is measured at a given point of time (a stock), investment is measured over a period of time (a flow). The flow of investment increases the stock of capital.
For a number of decades, US-based TNCs dominated in both the flow and stock of FDI.
VII. Match the definition on the right with the words on the left. Learn the definitions:
interest |
|
input |
|
output |
|
labour force |
|
GDP (gross domestic product) |
|
VIII. Verbs are sometimes formed with the suffix –ize/ise, for example, to make a summary – to summarize. Write down verbs that have the following meanings:
to put something in a category –
to introduce computers –
to make a state industry private –
to make a private industry national –
to make something legal –
to make a general statement –
to give a subsidy –
to have a special knowledge –
to make something more rational –
to make something more modern –
IX. Suffix –en helps to form verbs from adjectives, like soften – to make something soft. Form the verbs from these adjectives; translate them:
tight, weak, loose, hard, bright, flat, wide, sharp, sweet
X. Find in the list of words to the text one more verb-forming suffix. Supply several examples of its application.
XI. Match the synonyms. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own:
|
|
2) entail |
|
3) disperses |
|
4) value |
|
5) skilled |
|
Form opposites to the following words, using the prefixes of opposite meaning. Consult the dictionary if necessary:
direct, skilled, advantage, specific, developed, encourage, employment, increase, mobility, disciplined, logical, rational
Translate into English:
Відмінність між прямими зарубіжними інвестиціями та портфельними зарубіжними інвестиціями лежить у сфері контролю.
За американською класифікацією, зарубіжною прямою інвестицією вважається будь-яка інвестиція при умові, що інвестор отримує більше 10% акцій зарубіжної компанії.
Зарубіжні прямі інвестиції спрямовуються у промислове виробництво, послуги та видобувну промисловість.
Стимулом для інвестування закордон є нижчі виробничі затрати, місцеві податкові пільги, наявність корисних копалин.
Схема «вертикального» інвестування сприяє роздрібненню процесу виробництва та росту торгівлі компонентами в межах однієї компанії.
Через зарубіжні прямі інвестиції ТНК мають вплив на економічне, соціальне та політичне середовище приймаючих країн.
Topics for discussion.
FDI as a means of business control.
Sector-specificity of FDI.
USA as the biggest source of FDI.
Change in the pattern of FDI and its consequences.
Skills practice:
Each of the following statements refers to one of the companies mentioned in texts A-C. Write the letter of the text referred to (A, B or C) and the name of the company in the spaces provided.
A company that is combining several acquisitions into a new business unit.
text: company:
A company that has reached an agreement with another one that will help it to perform better.
text: company:____
A company whose shareholders have rejected an offer. text: company:
A company that is working with one of its direct competitors. text: company: or
A company that has been trying to take control of a foreign operation but that has faced unexpected opposition.
text: company:
A company that was hoping to own almost two thirds of the share capital of another.
text: company:
A company that will soon lose one of its top executives. text: company:
A company that has a guaranteed source of revenue for the next few years. text: company:
A company that has started negotiations to purchase one part of another business.
text: company:
10. A company that will now have to review its expansion strategy. text: company:
MADRID - Endesa SA's shares fell Thursday after Spain's largest power company lost a bid to control Enersis SA, Chile's biggest utility* holding** company. Enersis shareholders blocked a $ 1.5 billion offer late Wednesday that would have let Endesa double its 32 percent stake. The shareholders refused to increase the maximum amount an investor can own in Enersis, dashing Endesa's hopes of taking over Enersis to make it the vehicle for its Latin American expansion plans. "We were very surprised by the outcome of the vote," said Ramon Olleros, a fund manager at AB Asesores, a brokerage in Madrid. "It's very bad news for Endesa."
International Herald Tribune
* utility company = a company which supplies the public with gas, water, electricity etc.
** holding company = a company that holds a controlling number of shares in one or more companies
B. NEW YORK - Dell Computer Corp said Thursday that it would buy $16 billion of equipment from International Business Machines Corp under a seven-year deal that also calls for the companies to jointly develop new computer technology. Both companies' stock rose on the announcement. The deal initially calls for Dell to buy such IBM equipment as disk drives, flat-panel displays and memory chips to use in its computers. The companies eventually expect broader sharing of technology, including co-developing new products.
Dell said the deal would help the company increase its competitiveness in notebook personal computers, storage products and servers, which are powerful corporate machines that run networks of PCs. IBM, in turn, will get a guaranteed source of sales.
"These companies are about the biggest competitors that I've ever seen get together on a technology agreement," said George Logemann of the Boston consulting firm Yankee Group.
International Herald Tribune
C. NEW YORK - Siemens AG of Germany is about to expand into the fast-growing data networking business by forming a new American subsidiary, acquiring two private companies in the United States, investing in a third and hiring a senior executive from IBM, executives close to the company's planning said. Siemens, one of Europe's biggest manufacturing companies, also is in preliminary discussions with 3Com Corp about paying $1.2 billion for the 3Com unit that sells networking equipment to telephone companies, the executives said. Siemens plans to announce Monday that it has agreed to acquire Castle Networks Inc, a private data-networking company based n Westford Massachusetts, for about $300 million in cash, and Argon Networks Inc, a private data-networking company in Littleton, Massachusetts, for about $240 million in cash, executives said. Siemens also will announce an agreement to acquire a $30 million stake in Accelerated Networks Inc, a private company based in Moorpark, California. The acquisitions will be folded into a new Siemens venture to be based in Boston, the executives said.
International Herald Tribune
Unit Twenty