
- •International Trade
- •International Trade
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Incoterms
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Insurance
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Money Transfer. Western Union
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Trade Organisations
- •International Business
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Business
- •Infrastructure, industries, the global regime, host-countries, investments, environment
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •I. Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial institutions
- •Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
- •International Financial Institutions
- •Investment opportunities, unit of account, should focus, to settle, contributed
- •International Trade 2
Вступ
Навчальний посібник “English for Students of International Economics” призначено для студентів, які вивчають міжнародну економіку, а також для всіх тих, хто бажає вдосконалити володіння англійською мовою фахового спрямування в галузі бізнесу та економіки.
Мета посібника ознайомити студентів з основними поняттями та термінами сфери міжнародної економіки, сприяти активному засвоєнню професійної лексики, розвивати навички усного мовлення в фаховій галузі та роботи з фаховою літературою.
Посібник складається з 20 уроків (Units) з уніфікованою структурою завдань: тематичний термінологічний англо-український словник для активного засвоєння, фаховий текст, вправи та творчі завдання для формування різних аспектів мовленнєвої діяльності, практичні завдання, спрямовані на розвиток та вдосконалення навичок професійного спілкування, читання та інтерпретації англомовної економічної літератури.
Матеріал посібника складають адаптовані тексти з сучасних англомовних учбових та періодичних видань, розташовані за принципом «від простого до складного» в логічній послідовності, яка забезпечить формування об’ємного тематичного словника та активне засвоєння професійної лексики.
Умовні скорочення
adj – adjective – прикметник
adv – adverb - прислівник
n – noun – іменник
v – verb – дієслово
pl. – plural – множина
opp. – opposite – антонім
syn. – synonym – синонім
etc. – etcetera (латина) – і т.д., і т.п.
i.e. – id est (латина), that is – тобто
e.g. – exempli gratia (латина), for example – наприклад
A.E. – American English – американський варіант англійської мови
B.E. – British English – британський варіант англійської мови
Unit One
International Trade
Read and learn the following words and word combinations. Translate the examples:
trade n – 1) торгівля; 2) галузь торгівлі; 3) професія, ремесло, заняття; home trade – внутрішня торгівля; foreign trade – зовнішня торгівля; countertrade – зустрічна торгівля.
trade v – торгувати
e.g. International trade is very important for developing international relations.
barter n – бартер
e.g. Barter is a simple exchange of goods (property, etc.) for other goods, etc.
transaction n – 1) угода, операція, справа; 2) ведення справ
e.g. Both sides confirmed the mechanism of this transaction.
export n – 1) вивіз, експорт, експортування; 2) pl. статті експорту, предмети вивозу; visible exports – експорт товарів; invisible export – невидимий експорт
export v– експортувати, вивозити
exporter n – експортер
e.g. Today trade is not confined to visible exports and imports.
import n – 1) ввіз, імпорт; 2) pl. статті імпорту; товари, що ввозяться
import v – імпортувати, ввозити
importer n – імпортер
e.g. Last year the company imported a new production line.
item n – 1) кожний окремий предмет в переліку, позиція; 2) стаття (імпорту, експорту); 3) виріб; 4) пункт, параграф, стаття.
e.g. Insurance constitute an invisible item of both exports and imports.
avantage n – перевага; comparative advantage – відносна перевага
e.g. Comparative advantage allows countries to specialize in certain goods and services.
balance of trade – торгівельний баланс
e.g. Balance of trade is an important indicator of economic activity.
value n – 1) вартість; 2) цінність; 3) ціна; added value – додана вартість
e.g. They calculated the total value of the goods.
balance of payments – платіжний баланс;
capital transfer – переказ капіталу, трансфер(т) капіталу
e.g. Balance of payments includes invisible items and capital transfers.
deficit n – дефіцит; нестача
e.g. Negative balance of trade shows a deficit.
surplus n – 1) надлишок; 2) активне сальдо (бюджету, платіжного балансу); 3) профіцит
e.g. When exports exceed imports the balance of trade shows surplus.
terms of trade – 1) умови торгівлі; 2) співвідношення імпортних та експортних цін
e.g. Terms of trade show the rate at which exports are exchanged for imports.
demand n – 1) попит; 2) вимога
e.g. The demand for these goods is constantly increasing.
goods n – pl. товари, вироби, товар; a good (AE)
e.g. Goods are things that people either want or need.
service n –1) послуга, сфера послуг; 2) обслуговування, сервіс; to render services – надавати послуги
e.g. This region must develop service industries.
II. Read and translate the text:
International Trade
The history of trade is largely the history of civilization. First it was what we call barter, a simple exchange of goods. Goods like cloth and glass beads were taken to distant places and exchanged for things like oriental spices. Sometimes this was a dangerous and risky business.
International trade has now developed into an intricate mechanism of transactions. Today trade is not confined to visible exports and imports of goods but also includes invisible items like services, transportation, insurance, expenditure by tourists, etc.
Countries usually specialize in certain products and commercial activities. This specialization depends on such factors as differences in climate, natural resources, labour force skills and technology. These special conditions give one country an advantage over others in producing certain goods or services.
A country has a comparative advantage in a certain product if it is produced more efficiently and at lower cost. Nations usually specialize in those goods and services in which they have the greatest comparative advantage and exchange their surplus for things they need and want but do not produce themselves.
When countries engage in international trade they express their agreement to specialize in order to produce more of certain goods or services. Countries that trade can together produce more goods and services than they could in the absence of trade.
The balance of trade indicates the difference between the total value of a country’s imports and exports of visible items (goods). The balance of trade is an important part of the balance payments, which also includes invisible items and capital transfers from one country to another. If the total value of the goods imported (visibles) is higher than that of the goods exported, the balance of trade is bad (adverse or unfavourable), that is to say it shows a deficit. If the reverse case is true, the balance of trade is good or favourable and it shows a surplus. Invisible items can cover the deficit of the balance of trade and as a result the country will have a favourable balance of payments.
What a country can achieve in international trade is shown by the terms of trade. The terms of trade are the rate at which a country’s exports are exchanged for its imports. Terms are said to be good or favourable to a country when the prices of its exports are high in relation to the prices of its imports, and bad or unfavourable when the reverse is the case. The terms of trade become even more favourable if the demand for a country’s exports increases, or if the demand for its imports decreases, for then its import prices will fall and its export prices will rise, and it will be able to receive a greater volume of imports for a given volume of exports. On a global scale imports must equal exports, since every good exported by one country must be imported by another.
Answer the following questions:
What was the first form of trade and does it still exist?
How does the concept of comparative advantage influence international trade?
What is the difference between visible and invisible exports and imports?
What does the balance of trade indicate?
How does the balance of payments differ from the balance of trade?
In what case is the balance of trade negative? positive?
How can a country with the deficit of the balance of trade achieve a favourable balance of payments?
What do the terms of trade indicate?
In what case are the terms of trade good? bad?
How can an increase in the demand for a country’s exports influence its terms of trade?
How do export prices change if the demand for a country’s exports increases?
How are the terms of trade changed when import prices fall?
Give Ukrainian equivalents of the following:
dangerous and risky business; intricate mechanism of transactions; expenditure by tourists; the total value of a country’s exports and imports; visibles; if the reverse case is true; that is to say; to cover the deficit; in relation to; labour force skills.
Give English equivalents of the following:
простий обмін товарами; не обмежуватись чимось; невидимі статті експорту/імпорту; переказ капіталу з однієї країни в іншу; несприятливий торгівельний баланс; дефіцитний баланс; профіцитний баланс; співвідношення; кажуть, що умови торгівлі сприятливі/несприятливі для країни; попит зростає/ спадає; експортні/імпортні ціни; даний об’єм експорту; в протилежному випадку; відносна перевага.
Match the definition on the right with the word on the left. Learn the definitions:
business
a) desire by people ready to buy, employ, etc; need
capital
b) buying and selling; commerce; trade
demand
c) single article or unit in a list
Item
d) a piece of business
Transaction
e) wealth/money/ property that may be used for the production of more wealth
Decide which word from ex.VI. goes in which gap in the sentences below:
Money with which a business is started is called…
We do not do much … with them.
They carried out a profitable … last year.
When … increases prices rise.
What … have you chosen from the catalogue?
Match the synonyms. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own.
1) trade
a) opposite
2) demand
b) price
3) value
c) commerce
4) reverse
d) need
Match the words with the opposite meaning. Use any 5 words in the sentences of your own.
Good
a) unfavourable
Increase
b) fall
Rise
deficit
surplus
favourable
invisible
false
6) visible
f) decrease
7) true
g) bad
Translate into English:
Сучасна міжнародна торгівля перетворилась у складний механізм угод.
Платіжний баланс країни включає як видимі, так і невидимі статті експорту та імпорту.
Попит на українську експортну продукцію постійно зростає.
Оскільки українська харчова промисловість розвивається, попит на імпорт в цій галузі знижується.
Якщо країна імпортує більше, ніж експортує, вона має дефіцит в торгівельному балансі.
В минулому році умови торгівлі для України були сприятливі.
Topics for discussion:
Speak about the development of international trade and its present-day structure.
Speak about such indicators of international trade as a) the balance of trade; b) the balance of payments; c) the terms of trade.
How does Ukraine use the concept of comparative advantage in its trade policy?
Skills practice:
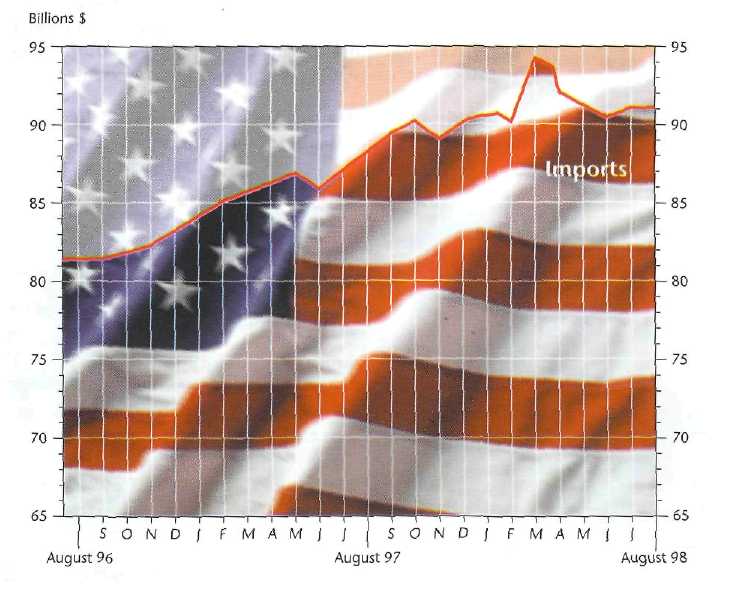
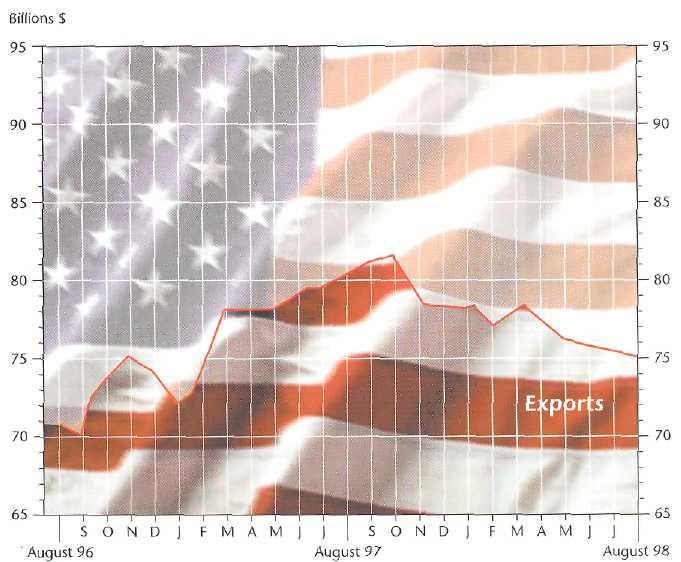
Work in pairs. You will each study a graph showing US trade from August 1996 to August 1998.
Graph A
Graph B
Student A: Look at the graph A. It shows US imports of goods and services from August 1996 to August 1998. Describe the information to student B using the language you have learnt. Then listen to student B’s description of US exports for the same period and complete the graph using a different colour.
Student B. Look at the graph B. It shows US exports of goods services from August 1996 to August 1998. Listen to Student’s A’s description of US Imports for the same period and complete the graph using a different colour. Then describe the information in your graph to Student A. Compare your results.
Did the US have a trade deficit or surplus?
In pairs, calculate the balance of payments for the following periods.
a) May 1997 deficit of $9 bn
b) October 1997
c) March 1998
3. a) When did the US have the lowest deficit in the period from August 1996 to August 1997?
b) When did the US import the most?
c) When did the US export the most?
Unit Two
The means of controlling foreign trade
