
- •Understanding Why Communication Matters
- •Communicating as a Professional
- •Exploring the Communication Process
- •Committing to Ethical Communication
- •Communicating in a World of Diversity
- •Using Technology to Improve Business Communication
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Understanding the Three-Step Writing Process
- •Analyzing the Situation
- •Gathering Information
- •Selecting the Right Medium
- •Organizing Your Message
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Adapting to Your Audience: Building Strong Relationships
- •Adapting to Your Audience: Controlling Your Style and Tone
- •Composing Your Message: Choosing Powerful Words
- •Composing Your Message: Creating Effective Sentences
- •Composing Your Message: Crafting Coherent Paragraphs
- •Using Technology to Compose and Shape Your Messages
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Revising Your Message: Evaluating the First Draft
- •Revising to Improve Readability
- •Editing for Clarity and Conciseness
- •Using Technology to Revise Your Message
- •Producing Your Message
- •Proofreading Your Message
- •Distributing Your Message
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Electronic Media for Business Communication
- •Social Networks
- •Information and Media Sharing Sites
- •Instant Messaging and Text Messaging
- •Blogging
- •Podcasting
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Strategy for Routine Requests
- •Common Examples of Routine Requests
- •Strategy for Routine Replies and Positive Messages
- •Common Examples of Routine Replies and Positive Messages
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Using the Three-Step Writing Process for Negative Messages
- •Using the Direct Approach for Negative Messages
- •Using the Indirect Approach for Negative Messages
- •Sending Negative Messages on Routine Business Matters
- •Sending Negative Employment Messages
- •Sending Negative Organizational News
- •Responding to Negative Information in a Social Media Environment
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Using the Three-Step Writing Process for Persuasive Messages
- •Developing Persuasive Business Messages
- •Common Examples of Persuasive Business Messages
- •Developing Marketing and Sales Messages
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Applying the Three-Step Writing Process to Reports and Proposals
- •Supporting Your Messages with Reliable Information
- •Conducting Secondary Research
- •Conducting Primary Research
- •Planning Informational Reports
- •Planning Analytical Reports
- •Planning Proposals
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Writing Reports and Proposals
- •Writing for Websites and Wikis
- •Illustrating Your Reports with Effective Visuals
- •Completing Reports and Proposals
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Finding the Ideal Opportunity in Today’s Job Market
- •Planning Your Résumé
- •Writing Your Résumé
- •Completing Your Résumé
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Submitting Your Résumé
- •Understanding the Interviewing Process
- •Preparing for a Job Interview
- •Interviewing for Success
- •Following Up After an Interview
- •Chapter Review and Activities
- •Test Your Knowledge
- •Apply Your Knowledge
- •Practice Your Skills
- •Expand Your Skills
- •References
- •Index

Chapter 7: Writing Routine and Positive Messages |
167 |
Strategy for Routine Requests
Much of your daily business communication will involve routine and positive messages, including routine requests for information or action, replies on routine business matters, and positive messages such as good-news announcements and goodwill messages, from product operation hints and technical support to refunds and ordering glitches. These messages are the focus of this chapter. Chapter 8 covers messages in which you convey negative information, and Chapter 9 addresses persuasive messages.
Making requests is a routine part of business. In most cases, your audience will be prepared to comply, as long as you’re not being unreasonable or asking people to do something they would expect you to do yourself. By applying a clear strategy and tailoring your approach to each situation, you’ll be able to generate effective requests quickly.
Like all other business messages, routine requests have three parts: an opening, a body, and a close. Using the direct approach, open with your main idea, which is a clear statement of your request. Use the body to give details and justify your request, then close by requesting specific action.
1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Outline an effective strategy for writing routine business requests.
For routine requests and positive messages
■State the request or main idea
■Give necessary details
■Close with a cordial request for specific action
Stating Your Request Up Front
With routine requests, you can make your request at the beginning of the message. Of course, getting right to the point should not be interpreted as license to be abrupt or tactless:
■Pay attention to tone. Instead of demanding action (“Send me the latest version of the budget spreadsheet”), show respect by using words such as please and I would appreciate.
■Assume that your audience will comply. Because the request is routine, you can generally assume that your readers will comply when they clearly understand the reason for your request.
■Be specific. State precisely what you want. For example, if you request the latest market data from your research department, be sure to say whether you want a 1-page summary or 100 pages of raw data.
Explaining and Justifying Your Request
Use the body of your message to explain your request, as needed. Make the explanation a smooth and logical outgrowth of your opening remarks. If complying with the request could benefit the reader, be sure to mention that. If you have multiple requests or questions, consider these tips:
■Ask the most important questions first. If cost is your main concern, for example, you might begin with a question such as “How much will it cost to have our new website created by an outside firm?” Then you may want to ask more specific but related questions, such as whether discounts are available for paying early.
■Deal with only one topic per question. If you have an unusual or complex request, break it down into specific, individual questions so that the reader can address each one separately. This consideration not only shows respect for your audience’s time but also gets you a more accurate answer in less time.
Take care that your direct approach doesn’t come across as abrupt or tactless.
If you have multiple requests or questions, start with the most important one.
Requesting Specific Action in a Courteous Close
Close your message with three important elements: (1) a specific request that includes any relevant deadlines, (2) information about how you can be reached (if it isn’t obvious), and (3) an expression of appreciation or goodwill. For example: “Please send the figures by April 5 so that I can return first-quarter results to you before the April 15 board meeting. I appreciate your help.” Conclude your message by sincerely expressing your goodwill and appreciation. However, don’t thank the reader “in advance” for cooperating; many people find that presumptuous.
Close request messages with
■A request for some specific action
■Information about how you can be reached
■An expression of appreciation
168 Unit 3: Brief Business Messages
Common Examples of Routine Requests
The most common types of routine messages are asking for information or action, asking 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVE for recommendations, and making claims and requesting adjustments.
Describe three common types of
routine requests.
Routine requests can be handled with simple, straightforward messages, but more complicated requests can require additional justification and explanation.
Asking for Information or Action
Routine requests can have up to three basic elements:
■What you want to know or what you want your readers to do
■Why you’re making the request (not required in all cases)
■Why it may be in your readers’ interest to help you (not applicable in all cases)
For simple requests, using the direct approach gets the job done with a minimum of fuss. In more complex situations, you may need to provide more extensive reasons and justification for your request. If applicable, point out any benefits to the reader of complying with your request. Naturally, be sure to adapt your request to your audience and the situation (see Figure 7.1).
Always ask for permission before using someone as a reference.
Refresh the memory of any potential reference you haven’t been in touch with for a while.
Asking for Recommendations
The need to inquire about people arises often in business. For example, before extending credit or awarding contracts, jobs, promotions, or scholarships, companies often ask applicants to supply references. Companies ask applicants to list references who can vouch for their ability, skills, integrity, character, and fitness for the job. Before you volunteer someone’s name as a reference, ask permission to do so. Some people don’t want you to use their names, perhaps because they don’t know enough about you to feel comfortable writing a letter or because they or their employers have a policy of not providing recommendations.
Requests for recommendations and references are routine, so you can organize your inquiry using the direct approach. Open your message by clearly stating why the recommendation is required (if it’s not for a job, be sure to explain its purpose) and that you would like your reader to write the letter. If you haven’t had contact with the person for some time, use the opening to trigger the reader’s memory of the relationship you had, the dates of asso-
ciation, and any special events or accomplishments that might bring a clear and favorable picture of you to mind.
Use the body of the request to list all the information the recipient would need to write the recommendation, including the full name and address or email address of the person to whom the recommendation should be sent. Consider including an updated résumé if you’ve had significant career advancement since your last contact.
Close your message with an expression of appreciation. When asking for an immediate recommendation, you should also mention the deadline. If you are requesting a printed letter, always be sure to enclose a stamped, preaddressed envelope as a convenience to the other party. Figure 7.2 on page 170 provides an example of a request that follows these guidelines.
When writing a claim or requesting an adjustment
■Explain the problem and give details
■Provide backup information
■Request specific action
Be prepared to document any claims you make with a company. Send copies and keep the original documents.
Making Claims and Requesting Adjustments
If you’re dissatisfied with a company’s product or service, you can opt to make a claim (a formal complaint) or request an adjustment (a settlement of a claim). In either case, it’s important to maintain a professional tone in all your communication, no matter how angry or frustrated you are. Keeping your cool will help you get the situation resolved sooner.
Open with a clear and calm statement of the problem along with your request. In the body, give a complete, specific explanation of the details. Provide any information the recipient needs to verify your complaint. In your close, politely request specific action or convey a sincere desire to find a solution. And, if appropriate, suggest that the business relationship will continue if the problem is solved satisfactorily. Be prepared to back up your claim with invoices, sales receipts, canceled checks, dated correspondence, and any other relevant documents. Send copies and keep the originals for your files.
|
|
Chapter 7: Writing Routine and Positive Messages 169 |
|
|
|
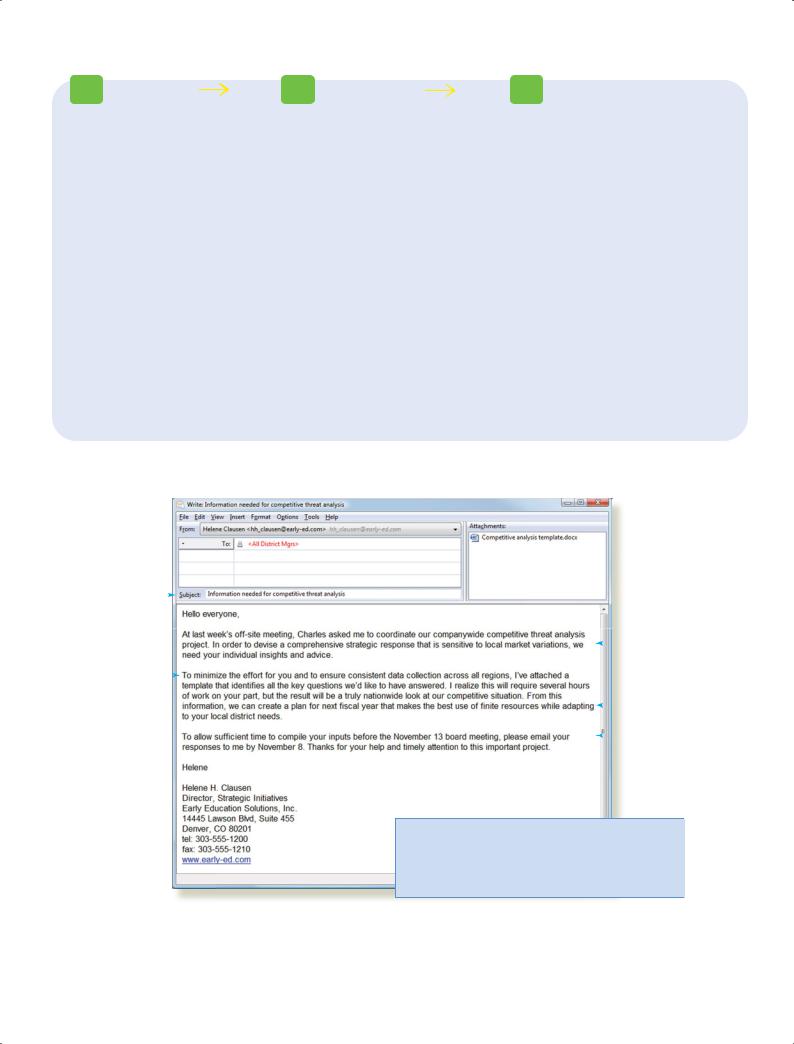
1 Plan |
2 Write |
3 Complete |
Analyze the Situation
Verify that the purpose is to request information from company managers.
Gather Information
Gather accurate, complete information about local competitive threats.
Select the Right Medium
Choose email for this internal message, which also allows the attachment of a Word document to collect the information.
Organize the Information
Clarify that the main idea is collecting information that will lead to a better competitive strategy, which will in turn help the various district managers.
Adapt to Your Audience
Show sensitivity to audience needs with a “you” attitude, politeness, positive emphasis, and bias-free language. The writer already has credibility, as manager of the department.
Compose the Message
Maintain a style that is conversational but still businesslike, using plain English and appropriate voice.
Revise the Message
Evaluate content and review readability; avoid unnecessary details.
Produce the Message
Simple email format is all the design this message needs.
Proofread the Message
Review for errors in layout, spelling, and mechanics.
Distribute the Message
Deliver the message via the company’s email system.
The informative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
subject line alerts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
the audience to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
an important request. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The opening explains the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
context of the message, |
She acknowledges |
|
|
|
|
then gets to the point |
|
|
|
|
|
of the request. |
||
|
|
|||||
that responding to |
|
|
|
|
The body explains the |
|
the request will |
|
|
|
|
||
require some work |
|
|
|
|
benefit of responding |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
but emphasizes that |
|
|
|
|
to the request. |
|
the result will benefit |
|
|
|
|
The close provides a |
|
everyone. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
clear deadline, then |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
concludes in a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
courteous manner. |
Pointers for Making a Routine Request ss Use the direct approach.
ss Maintain a polite, personal tone and don’t demand a response. ss If necessary, justify the request or explain its importance.
ss If applicable, explain the benefits to the reader of responding. ss Close courteously, with a request for specific action.
Figure 7.1 Routine Message Requesting Action
In this email request to district managers across the country, Helene Clausen asks them to fill out an attached information collection form. Although the request is not unusual and responding to it is part of the managers’ responsibility, Clausen asks for their help in a courteous manner and points out the benefits of responding.

170 Unit 3: Brief Business Messages |
|
|
1 Plan |
2 Write |
3 Complete |
Analyze the Situation
Verify that the purpose is to request a recommendation letter from a college professor.
Gather Information
Gather information on classes and dates to help the reader recall you and to clarify the position you seek.
Select the Right Medium
The letter format gives this message an appropriate level of
formality, although many professors prefer to be contacted by email.
Organize the Information
Messages like this are common and expected, so a direct approach is fine.
Adapt to Your Audience
Show sensitivity to audience needs with a “you” attitude, politeness, positive emphasis, and bias-free language.
Compose the Message
Style is respectful and businesslike, while still using plain English and appropriate voice.
Revise the Message
Evaluate content and review readability; avoid unnecessary details.
Produce the Message
Simple letter format is all the design this message needs.
Proofread the Message
Review for errors in layout, spelling, and mechanics.
Distribute the Message
Deliver the message via postal mail or email if you have the professor’s email address.
|
|
|
1181 Ashport Drive |
|
|
|
Tate Springs, TN 38101 |
|
|
|
March 14, 2013 |
|
|
|
Professor Lyndon Kenton |
|
|
|
School of Business |
|
|
|
University of Tennessee, Knoxville |
|
|
|
Knoxville, TN 37916 |
|
|
|
Dear Professor Kenton: |
|
|
|
I recently interviewed with Strategic Investments and have been called for a |
|
|
|
second interview for their Analyst Training Program (ATP). They have |
|
|
|
requested at least one recommendation from a professor, and I immediately |
|
|
|
thought of you. May I have a letter of recommendation from you? |
Tucker includes |
|
As you may recall, I took BUS 485, Financial Analysis, from you in the fall of |
|
|
|||
information near |
2011. I enjoyed the class and finished the term with an “A.” Professor Kenton, |
||
the opening to |
your comments on assertiveness and cold-calling impressed me beyond the |
||
refresh her |
scope of the actual course material. In fact, taking your course helped me |
||
professor’s memory. |
decide on a future as a financial analyst. |
||
|
|
|
My enclosed résumé includes all my relevant work experience and volunteer |
|
|
|
activities. I would also like to add that I’ve handled the financial planning for |
|
|
|
our family since my father passed away several years ago. Although I initially |
|
|
|
learned by trial and error, I have increasingly applied my business training in |
|
|
|
deciding what stocks or bonds to trade. This, I believe, has given me a practical |
|
|
|
edge over others who may be applying for the same job. |
She provides a |
|
|
If possible, Ms. Blackmon in Human Resources needs to receive your letter by |
|
|
March 30. For your convenience, I’ve enclosed a preaddressed, stamped |
|
|
|
||
deadline for |
envelope. |
||
response and |
|
||
includes information |
I appreciate your time and effort in writing this letter of recommendation for |
||
about the person |
me. It will be great to put my education to work, and I’ll keep you informed of |
||
who is expecting |
my progress. Thank you for your consideration in this matter. |
||
the recommendation. |
Sincerely, |
||
|
|
|
|
The opening states the purpose of the letter and makes the request, assuming the reader will want to
comply with the request.
The body refers to the enclosed résumé and mentions experience that could set the applicant
apart from other candidates— information the professor could use in writing
the recommendation.
The close mentions the preaddressed, stamped envelope to encourage a timely response.
Joanne Tucker
Enclosure
Figure 7.2 Effective Request for a Recommendation
This writer uses a direct approach when asking for a recommendation from a former professor. Note how she takes care to refresh the professor’s memory because she took the class a year and a half ago. She also indicates the date by which the letter is needed and points to the enclosure of a stamped, preaddressed envelope.

Chapter 7: Writing Routine and Positive Messages |
171 |
If the remedy is obvious, tell your reader exactly what you expect from the company, such as exchanging incorrectly shipped merchandise for the right item or issuing a refund if the item is out of stock. In some cases, you might ask the recipient to resolve a problem. However, if you’re uncertain about the precise nature of the trouble, you could ask the company to make an assessment and then advise you on how the situation could be fixed. Supply your contact information so that the company can discuss the situation with you, if necessary. Compare the poor and improved versions in Figure 7.3.
Poor
The opening is too emotional and has too many details.
The body has a defensive tone and blames the meter reader.
The close has irrelevant information and a weak defense.
ed Improv
Covington provides details in the body so that the reader can understand why she thinks
a problem exists
She requests specific action in the close and provides contact information to make responding easy.
MyBCommLab Apply
Figure 7.3’s key concepts. Go to mybcommlab.com and follow this path: Course Content Chapter 7
DOCUMENT MAKEOVERS
Dear Customer Service Representative:
A comparison of our electricity bills with those of our neighboring businesses suggests that the utility meter in our store may not be accurate. Please send a technician to check it.
a technician to check it.
The European Connection opened at our current location on December 1, and we
have received two monthly bills since then. In both instances the amount of our bill 
 was nearly twice what neighboring businesses in this building were charged, even
was nearly twice what neighboring businesses in this building were charged, even
though we all have similar storefronts and equipment. We paid $815.00 in December and $817.50 in January. In contrast, the highest bills that neighboring businesses paid were $543.50 and $545.67 for those two months.
If your representative would visit our store, he or she could do an analysis of how much  energy we are using. I understand that you regularly provide this helpful service to
energy we are using. I understand that you regularly provide this helpful service to
customers, and I would appreciate hearing from you this week. You can reach me by calling (805) 979-7727 during business hours. I look forward to hearing from you.
The opening clearly and calmly states the problem.
Details are presented clearly, concisely, and completely.
Sincerely,
Laura Covington
Proprietor
Pointers for Making a Claim
ss Establish rapport by praising some aspect of the product or explaining why you purchased it. ss Present facts clearly, politely, and honestly.
ssShow confidence in the reader’s sense of fairness; avoid threats, sarcasm, hostility, or exaggeration.
ssAvoid any accusations that you cannot support with facts.
ss Close with a request for specific action.
Figure 7.3 Poor and Improved Versions of a Claim
Note the difference in both tone and information content in these two versions. The poor version is emotional and unprofessional, whereas the improved version communicates calmly and clearly.
Source: Used with permission from Microsoft.
