
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf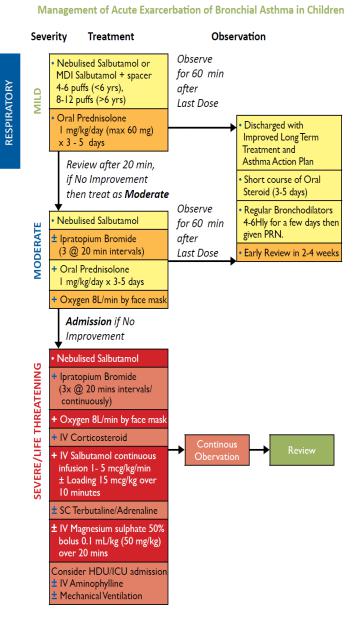
•
Footnotes on Management of Acute Exacerbation of Asthma:
+. ,onitor pulse, colour, P-FR, A./ and 01 2atura3on. Close monitoring for at least 4 hours.
1. Hydra3on - give maintenance fluids.
3.Role of Aminophylline debated due to its potential toxicity. To be used with caution, in a controlled environment like ICU.
4.IV ,agnesium 2ulphate : Consider as an adjunct treatment in severe
exacerbations unresponsive to the initial treatment. It is safe and beneficial in severe acute asthma.
5.Avoid Chest physiotherapy as it may increase pa3ent discomfort.
:. An3bio3cs indicated only if bacterial infec3on suspected.
;. Avoid seda3ves and mucoly3cs.
8.- cacy of prednisolone in the first year of life is poor. >. 0n discharge, pa3ents must be provided with an Action Plan to assist parents or patients to prevent/terminate asthma attacks.
The plan must include:
a. How to recognize worsening asthma. b. How to treat worsening asthma.
c. How and when to seek medical attention.
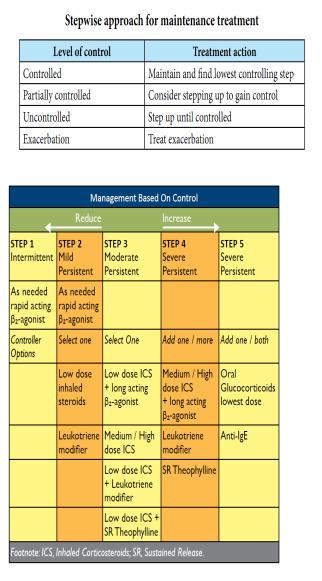
• 2albutamol ,DI vs nebulizer
< : year old: : x +00 mcg pu = 1.5 mg 2albutamol nebules.
: year old: +1 x +00 mcg pu = 5.0 mg 2albutamol nebules.
1.4. Ear Nose and Throat Conditions
1.4.1. Acute Otitis Media
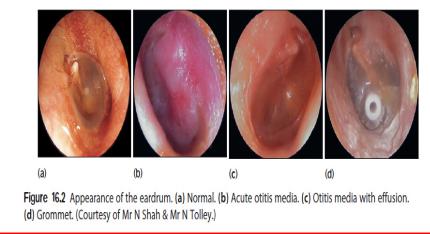
Definition: It is the inflammation of the middle ear cavities.
Causes
-Viral
-Bacterial (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis etc.)
-Predisposing factors include poor living conditions, adenoids, sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, tonsillitis, asthma etc.
Signs and Symptoms
-Fever
-Retroauricular pain
-Crying with ear scrubbing
-Gastro intestinal signs
-Otalgia
-Cervical lymphadenopathy
-Otorrhea (if tympanic membrane perforated)
-Impaired hearing
-Redness of eardrum
-Sometimes bulging of the eardrum Complications
-Secretory otitis media (ear glue)
-Chronic otitis media with perforation
-Acute mastoiditis sometimes with periosteal abscess
-Intracranial (meningitis, brain abscess, subdural abscess, etc)
-Facial paralysis
-Labyrinthitis
Investigations
-Clinical including otoscopy
-FBC and CRP if signs of sepsis Management
-General measures: elimination of risk factors Pharmacological
-Treatment of first choice
•Amoxicillin, Po 30mg/kg/dose P.O. Q8h for 7-10 days
•When associated with rhinitis add Xylometazoline (Otrivine) 0.5% nose drops or simple argyrol drops 1% , 0.05%
•Paracetamol 10-15mg/kg/dose Q6hr if high fever or pain
- Alternative treatment
•Amoxi-clav (Augmentin) 50mg/kg/day P.O, Q8h for 7 -10 days;
Or cefadroxyl : 25mg/kg/dose Q12h for 7 days
•cefuroxime (Zinat): 15mg/kg /dose Q12h for 7 days
•Azithromycine 10mg/kg/dose Q24h for 3 days
•Erythromycine 20 mg/kg/dose Q8h for 10 days
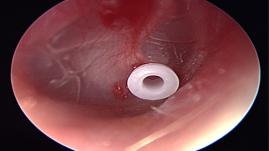
-Surgical: Myringotomy (if necessary)
Note tube sitting in antero-inferior quadrant of tympanic membrane to avoid damage to the structures of the middle ear.
mendation
- Avoid getting in the inside of the wet ear
1.4.2. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
Definition: It is a chronic inflammation of the middle ear with
recurrent ear discharges or otorrhoea through a tympanic perforation for more than 2 weeks.
Predisposing risk factors
-Inadequate management of otitis media
-Frequent upper respiratory tract infections
-Anatomic factor: short eustachian tube
-Poor living conditions, poor housing, hygiene and nutrition analphabetism
-Immunosupression (e.g.: HIV infection)
Causes
-Tuberculosis
-P. aeruginosa
-S.pneumoniae
-Staphyllococcus aureus
-H. Influenza Signs and Symptoms
-Recurrent pus ear discharge
-Large perforation of the eardrum on examination
-Progressive hypoacousia with impaired hearing
-Buzzing (acouphene)
-History of recurrent otitis media
-Loss of transparency of tympanic membrane Complications
-Subperiosteal abscesses
-Facial nerve paralysis
-Lateral sinus thrombophlebitis
-Suppurative labyrinthitis
-Brain abscess
-Meningitis
-Mastoiditis
-Extradural and subdural Empyema
-Otitic hydrocephalus
-Hearing impairment
-deafness
Investigations
-Bacterial Cultures
-Search for predisposing factors
-Audiogram
-CT-scan Management
Non pharmacological management
• dry mopping
• Aural toilet by medicines’ droppers (with Hydrogen peroxide or polyvidone iodine saline solutions)
• Avoid getting the inside of the ear wet. e.g.: bathing and swimming
Pharmacological management
• Topical quinolones (ciprofloxacin ear drops Q12h for 7 days)
• Systemic treatment: ceftazidime IV or IM 50mg/kg/dose Q8h (max:6gr/day) for 7 days Surgical
• In case of mastoiditis: Mastoidectomy Recommendations
-Proper management of acute otitis media
-Avoid getting the inside of the ear wet. e.g: bathing and swimming
-Refer to the tertiary health facility for further management
1.4.3. tonsillitis
