
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf-o 5 kg to <10 kg: 5 mg once daily
-o 10 kg to ≤20 kg: 10 mg once daily
-o >20 kg: 20 mg once daily
-Alternate dosing: 1 mg/kg/dose once or twice daily; higher doses may be necessary in children between 1-6 years
-→ Add
-■ Pro-Kinetics: Domperidone (Motilium) 0.3
–0.6 mg/kg/24hrs PO divided in 3 doses (TdS).
-Maximum 30mg/24 hours
-→ ANd
-■ Metoclopromide IV/IM/PO 0.1- 0.2mg/kg/dose
-TdS. Maximum dose 0.5mg/kg/24 hours
-Recommendations
-- Refer to tertiary level gastro-oesophageal reflux not responding to treatment
-- Educate parents/guardians on patient diet
-- Eat small, frequent meals
-2.9. Tropical Splenomegaly (Hyperreactive
-malarious splenomegaly) (HMS)
-Definition: It is a massive enlargement of the spleen resulting from
-abnormal immune response to repeated attacks of malaria
-Signs and Symptoms
-- Chronic abdominal swelling and pain.
-- Weight loss
-- Intermittent fever
-- Some patients present with anaemia, generalized weakness,
-cough, dyspnea, epistaxis, headache, increased skin and respiratory infections
-Clinical diagnosis
-- Splenomegaly of at least 10cms
-- Regression of the spleen by at least 40% by 6 months on antimalarial therapy.
-Complications
-Hypersplenism leading to anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia, bleeding
-Splenic lymphoma
-- death
-Investigations
-- Blood smear
-- Complete blood count (for Hb, Platelets)
-- Serum levels of IgM (at least 2Sd above normal limit)
-Management
-Pharmacological treatment
-• Doxycycline tabs /day for 6 months
-→ Children >8 years (<45 kg): 5 mg/kg/day Od
-→ Children >8 years (>45 kg): treat as adults
-Or
-• Mefloquine 5mg/kg weekly without exceeding 250mg/week of adult dose for 6 months
Dr: Essam Abdullah 01123232188
-
-3. Cardiovascular Diseases
-Most cardiac diseases in young children are congenital, while those in
-older children may be acquired or congenital.
-3.1. Heart Failure (Congestive Cardiac
Failure)
-
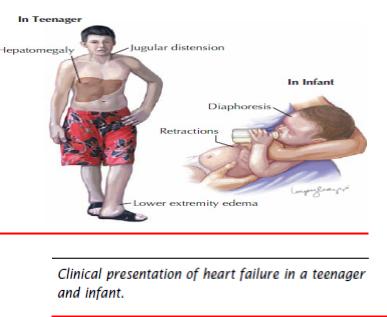
-Definition: It is a clinical syndrome reflecting the inability of the myocardium to meet the oxygen and nutritional metabolic requirements of the body.
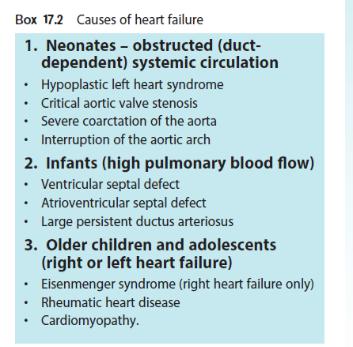
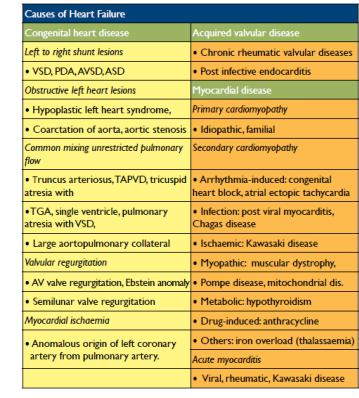
-Causes
-
-
Clinical presentation
•Varies with age of presentation.
•Symptoms of heart failure in infancy:
-• Feeding difficulty: poor suck, prolonged time to feed, sweating during feed.
•Signs of heart failure in infancy:
•Resting tachypnoea, subcostal recession.
•Tachycardia, Poor peripheral pulses, poor peripheral perfusion.
•Hyperactive praecordium, praecordial bulge.
•Hepatomegaly.
•Wheezing.
•Common signs of heart failure in adults, i.e. increased jugular venous
pressure, leg oedema and basal lung crackles are not usually found in children.
•Recurrent chest infections.
-• Failure to thrive.
-Investigations
-- FBC, Electrolytes, Urea and Creatinine, Blood Gas if available
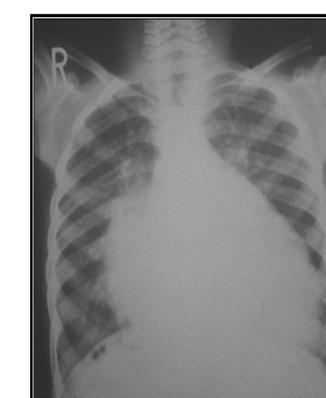
-- Chest X-ray
-
- |
- |
-ECG
-- Echocardiogram
-
-Management
-Non pharmacological
-• Oxygen therapy
-• SemiSitting position (cardiac bed)
-• Restrict fluids to 2/3 of maintenance ( aim at urine output of 2ml/kg/h)
-• Low sodium diet
-• Strict bed rest
-• Ensure adequate nutrition
-• Recognize and treat the underlying conditions e.g. fluid overload, hypertension infection
-• Monitoring of vital signs: RR, HR, BP, O2 saturation, urine output
-Pharmacological
Antifailure medications
•Frusemide (loop diuretic) Dose: 1 mg/kg/dose OD to QID, oral or IV
•o 3 uous IV i usio at C 1 – C 5 mg/kg/hour i severe luid overload
•Use with potassium suppleme ts (1 - 2 mmol/kg/day) or add potassium spari g diuretics
•Spiro olacto e (potassium spari g diuretic, modest diure3c eDect) Dose: 1 mg/kg/dose .D
•aptopril A giote si co verti g e zyme i hibitor, a terload reductio age t
•Dose: C 1 mg/kg/dose TDS, gradual i crease up to 1 mg/kg/dose TDS
•Mo itor potassium level (risk o hyperkalaemia)
•Digoxi
•Role co troversial
•Use ul i heart ailure with excessive tachycardia, suprave tricular tachyarrhythmias
•IV i otropic age ts - i e Dopami e, Dobutami e, Adre ali e, Milri o e
•Use i acute heart ailure, cardioge ic shock, post-op low output sy drome
Specific management
•Establishme t o de i itive aetiology is o crucial importa ce
•Speci ic treatme t targeted to u derlyi g aetiology Examples:
•Surgical/tra scatheter treatme t o co ge ital heart lesio
•Pacemaker impla tatio or heart block
•o trol o blood pressure i post-i ectious glomerulo ephritis
-• High dose aspiri ± steroid i acute rheumatic carditis
-3.2. Cardiogenic Shock
-Definition: It is a dramatic syndrome characterized by inadequate
-circulatory provision of oxygen due to cardiac pump failure secondary to poor myocardial function, so that the metabolic demands of vital organs and tissues are not met.
-The patient often has a known case of heart disease with signs of heart failure but may also be a new case with heart failure.
-Signs and Symptoms
-- Hypotension
-- Tachycardia
