
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf
Treatment
Aim to suppress inflammatory response so as to minimize cardiac damage,
provide symptomatic relief and eradicate pharyngeal streptococcal infection
•Bed rest. Restrict activity until acute phase reactants return to normal.
•Anti-streptococcal therapy:
•IV C. Penicillin 5C CCCU/kg/dose 6H
or Oral Penicillin V 25C mg 6H (<3Ckg), 5CC mg 6H (>3Ckg) for +C days
•Oral Erythromycin for +C days if allergic to penicillin.
•Anti-inflammatory therapy
•mild / no carditis:
Oral Aspirin 8C-+CC mg/kg/day in 4 doses for 2-4 weeks, tapering over 4 weeks.
• pericarditis, or moderate to severe carditis:
Oral Prednisolone 2 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 2 - 4 weeks,taper with addition of aspirin as above.
•anti-failure medications
•Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, digoxin (to be used with caution).

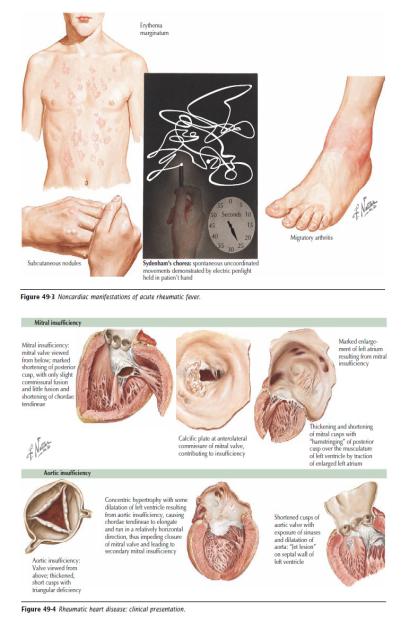
•Chorea
→Most mild-moderate cases do not need medication
→Provide calm and supportive environment (prevent accidental self-harm)
→For severe cases: carbamazepine per os
<6 years: 10-20mg/kg/day divided in 3 doses
6-12 years: 400-800mg/day divided in 3 doses
>12 years: 200mg x 2/day
OR
→ Valproic acid 20-30mg/kg/day divided in 2 doses; duration: 2 weeks
•Carditis
→Bed rest if in cardiac failure
→Anti-failure medication as above
→Anti-coagulation medication if atrial fibrillation is present
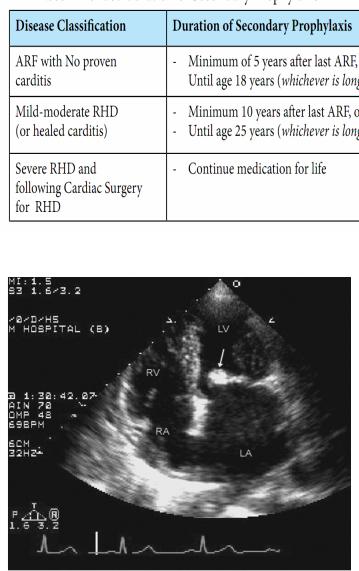
-Recommended duration of Secondary Prophylaxis
-
-
- 3.5.2. Rheumatic Heart Diseases
-
- Apical four-chamber view recorded in a patient with rheumatic mitral stenosis. Note the
marked dilation of the left atrium (LA). In this example, there is substantial but focal calcification of the anterior mitral valve leaflet (arrow). Note also the relatively restricted motion of both leaflets along their full length. LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
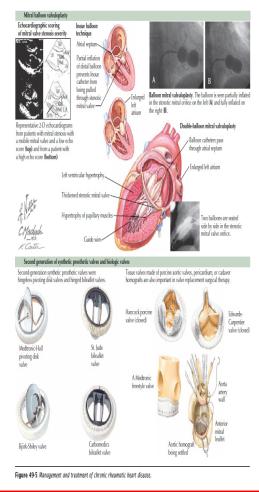
-Definition: It is an inflammatory damage of the heart valves, as a complication of acute rheumatic fever. The mitral valve is the most commonly involved valve, although any valve may be affected.
-Types of valvular lesions
-- Mitral regurgitation/stenosis
-- Aortic regurgitation/stenosis
-- Tricuspid regurgitation
-- Mixed regurgitation and stenosis
-- Multivalvular heart diseases
-Signs and Symptoms
-- May be asymptomatic when minor lesions
-- Heart murmurs over affected valve
-Complications
-- Congestive cardiac failure with pulmonary oedema
-- Bacterial endocarditis
-Investigations
-- Chest x-ray
-- ECG
-- Echocardiography
-Management
-- Treat underlying complication, e.g., heart failure, pulmonary oedema
-- Continue prophylaxis against recurrent rheumatic fever
-- Ensure oral hygiene
-- Endocarditis prophylaxis if dental procedures, urinary tract instrumentation, and GIT manipulations
-• Procedure done above the diaphragm
-→ Amoxicillin 50mg/kg (Max 2gr) 1 hour before the procedur
-Or→ Erythromycin 50mg/kg (max 1.5gr) – if allergic to Penicillins
-• Below the diaphragm
-→ Ampicillin 50mg/kg IV or IM (max 2gr) with
-Gentamycine, 2mg/kg (max 120mg) 30minutes before the procedure
-Then
-→ Amoxycillin per os 25mg/kg (max1gr) 6 hours after the procedure
-- Ensure good follow up by cardiologist
-3.5.3. Infective Endocarditis (IE)
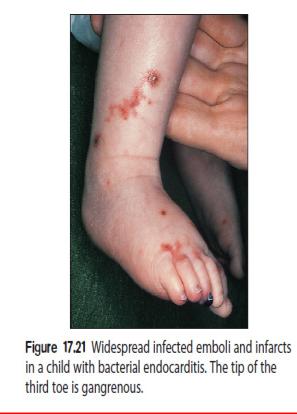
-
