
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf-Acute hypertension (hypertension of sudden onset)
-Non-pharmacological
-• Admit patient to paediatric high dependence care unit
-• Monitor BP every 10 minutes until stable – thereafter every 30 minutes for 24 hours
-• Insert two peripheral intravenous drips
-• Rest on cardiac bed
-• Control fluid intake and output (restriction)
-• Restrict dietary sodium
-Pharmacological
-• do not combine drugs of the same class
-• Furosemide, IV, 1–2 mg/kg as a bolus slowly over 5 minutes, Increase up to 8 mg/kg/day
-• nifedipine 0.25-0.5mg/kg (max: 10mg) sublingual OR
-Amlodipine, oral, 0.2 mg/kg/dose. May be repeated 6 hours later, thereafter every 12 hours
-• Refer the patient to a specialist when the patient is stable
-Recommendations
-- For acute or chronic hypertension Blood Pressure needs to be lowered cautiously
-- Aim to reduce the SBP slowly over the next 24 - 48 hours,do not decrease BP to < 95th percentile in first 24 hours
-- Advise a change in lifestyle
-- Institute and monitor a weight reduction program for obese individuals
-- Regular aerobic exercise is recommended in essential hypertension
-- dietary advice
-- Limit salt and saturated fat intake
-- Increase dietary fiber intake
-Chronic Hypertension
-Non-pharmacological management
-• Introduce physical activity, diet management and weight reduction, if obese
-• Advise against smoking in teenagers
-• Follow up to monitor Blood Pressure and educate patient on hypertension
-• If Blood Pressure decreases, continue with non-drug management and follow up
-• If BP is increasing progressively, reinvestigate to exclude secondary causes or refer to the specialist
-•If BP is stable but persistently > 95th percentile and secondary causes have been excluded, start drug treatment after failed nondrug management for 6 months
-• Consider earlier initiation of drug treatment if positive family history for cardiovascular disease, essential hypertension or diabetes mellitus
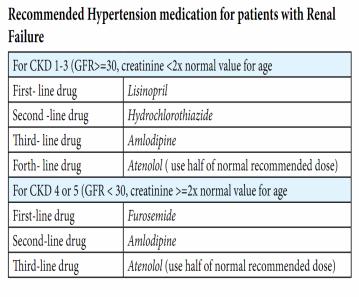
-Pharmacological management
-Recommended medication and dosage for patients with chronic Hypertension
-
-Recommendations
-- All patients with hypertension and persistent proteinuria should be treated with an ACE inhibitor
-- Always exclude bilateral renal artery stenosis before treating with an ACE inhibitor
-- Renal function must be monitored when an ACE inhibitor is prescribed because it may cause a decline in GFR resulting in deterioration of renal function and hyperkalaemia
-- Patients with hypertension due to a neurosecretory tumour
-(phaeochromocytoma or neuroblastoma) should receive an a-blocker either as single drug or in combination with ß-adrenergic blocker
-For patients with persistent hypertension despite the use of first line drugs, a second/third drug should be added
-Specific classes of antihypertensive drugs should be used according to the underlying pathogenesis or illness
-- For patients with a predominant fluid overload: use diuretics with/without ß-blocker
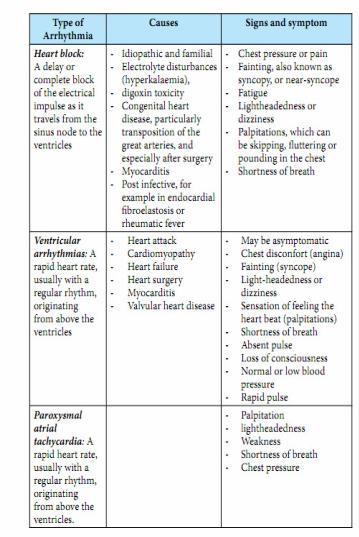
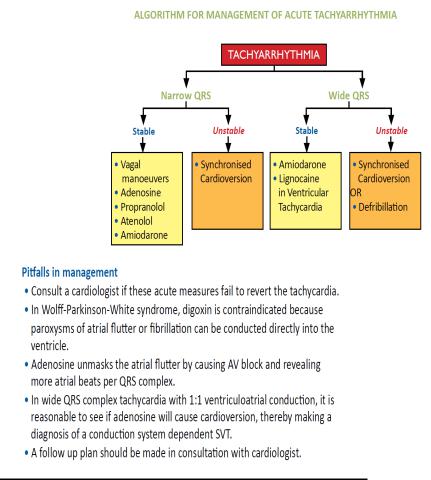
-3.9. Cardiac Arrhythmias in children
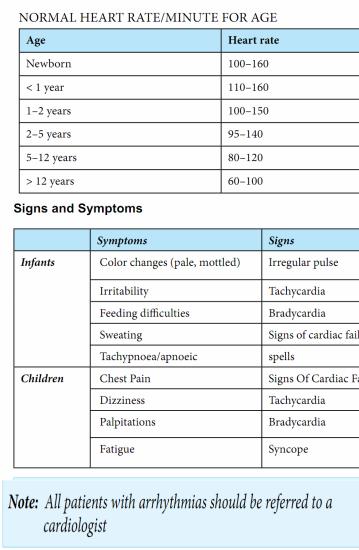
-Definition: Heart rate that is abnormally slow or fast for age or irregular.
-There are three types of arrhythmias in children
-- Heart block
-- Ventricular arrhythmias
-- Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
-
-
-
-
-
-
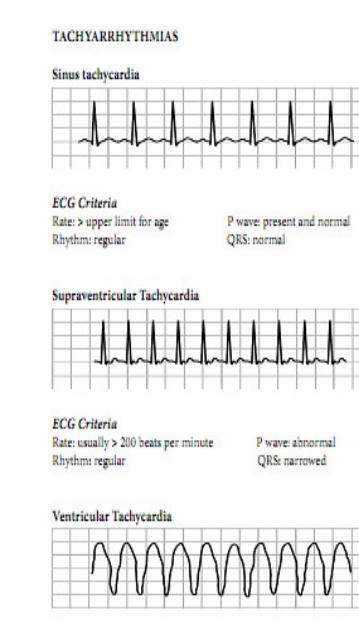
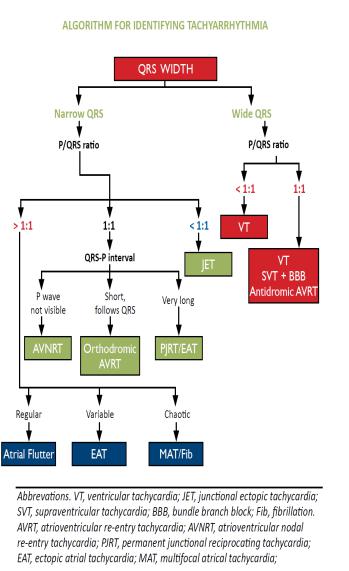
- Investigations
-- ECG is essential for diagnosis, preferably a 12 lead ECG
-- Echocardiogram
-- Other according to the suspected etiology
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 3.10. Bradyarrhythmias
-
-
