
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf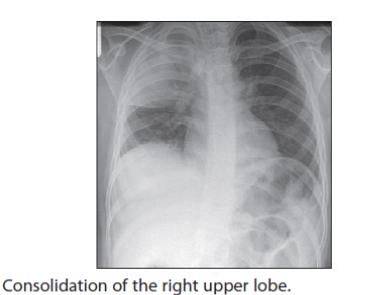
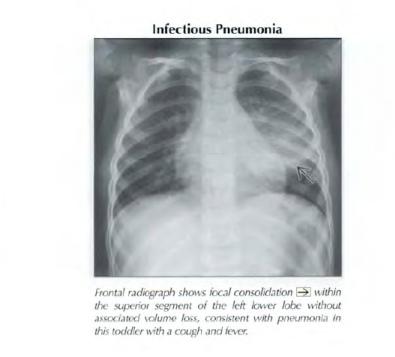
-Blood culture
-HIV test Management
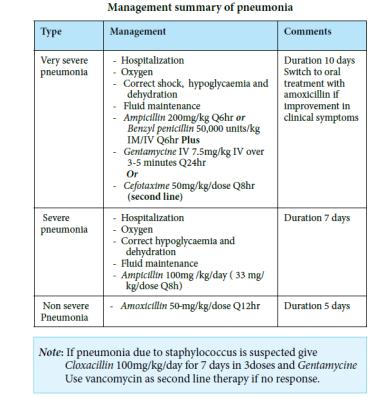
Criteria for hospitalization
• Community acquired pneumonia can be treated at home
• Identify indicators of severity in children who need admission, as pneumonia can be fatal. The following indicators can be used as a guide for admission:
• Children aged 3 months and below, whatever the severity of pneumonia.
•Fever ( more than 38.5 C ), refusal to feed and vomiting
•Fast breathing with or without cyanosis
•Associated systemic manifestation
•Failure of previous antibiotic therapy
•Recurrent pneumonia
•Severe underlying disorder, e.g. Immunodeficiency - Severe respiratory distress
•Supplemental oxygen
•dehydration
•Vomiting
•No response to appropriate oral antibiotic therapy
Recommendations
- Recurrent/persistent pneumonia
In case of persistent pneumonia (abnormal X-ray more than30 days after treatment) the patient should be referred for
investigations (CT Scan, bronchoscopy) to exclude:
•Foreign body
•Congenital malformation (adenomatosis)
•Immotile cilia syndrome
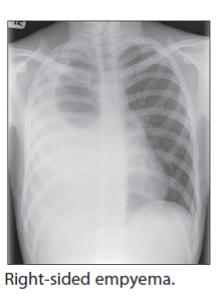
- Likewise, in case of recurrent pneumonia, an underlying cause should be suspected and the child referred for further investigations.
• Pleural effusion
- In case of pleural effusion, think of Staphylococcus aureus,
streptococcus pneumonia, mycoplasma pneumonia, tuberculosis
•Exclude Tuberculosis
•Ultrasound to measure the volume of liquid and aspiration for culture
•drainage of fluid if important and respiratory distress
1.3. Wheezing child/Asthma and Bronchiolitis
Wheezing child
Definition: A wheeze is a musical and continuous sound that originates from oscillations in narrowed airways. Wheezing is heard mostly in expiration as a result of critical airway obstruction.
Causes/ Risk factors
-Bronchiolitis
-Asthma
-Esophageal foreign bodies
-Aspiration syndrome (gastro-esophageal reflux diseases)
1.3.1. Acute Bronchiolitis
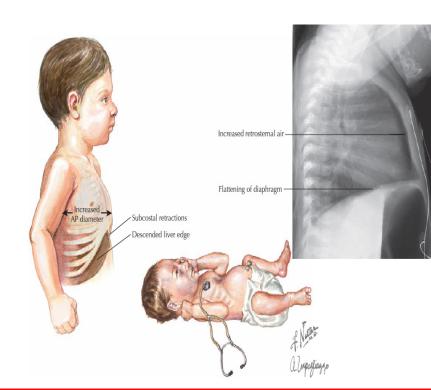
Definition: Bronchiolitis is an inflammation of the bronchiole tubes
due to viral organism resulting in wheezing. In children under 2 years old, it may lead to fatal respiratory distress. Occurs with seasonal
variations and has epidemic potential. Causes
-Acute bronchiolitis is predominantly a viral disease
-Respiratory Syncytial Virus is the most common (>50% cases)
-Other agents: parainfluenza, adenovirus, Mycoplasma, and occasionally other viruses especially Human metapneuo virus
Clinical signs
-dyspnea with cough (both day and night)
-distension of the thorax
-Low-grade fever
-Prolonged expiration with diffuse wheeze on pulmonary auscultation
-Occasionally fine, diffuse, bilateral late inspiratory crepitations
-Signs of serious illness include tachypnea, central cyanosis (tongue and gingiva), Nasal flaring, Chest indrawing, periods of apnoea, altered level of consciousness, difficulty drinking or breastfeeding, and silence on auscultation (corresponding to an intense bronchospasm)
Complications
-Bacterial secondary infection
-Atelectasis
-Apnoea especially in neonatal and infant period Investigations
-FBC
-CRP (Less contributory as viral infection)
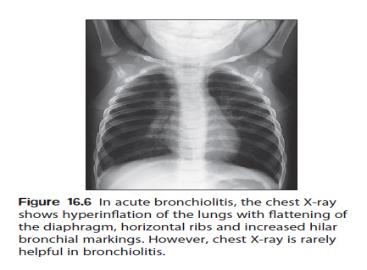
-Chest X-ray: show hyperinflated lungs with patchy atelectasis
- Viral testing (usually rapid immunofluorescence, polymerase chain reaction, or viral culture) is helpful if the diagnosis is uncertain or for epidemiologic purposes Management
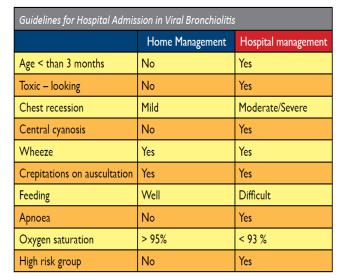
- Treatment is symptomatic
•Hospitalize children if signs of serious illness
•Administer high humidified oxygen at 8L/min in 30 to 40 % oxygen
•Attention to pulmonary toilet including suctioning,
percussion and postural drainage
•IV fluid > maintenance
•Tube feeding when the child is in improved respiratory distress state
•In case of respiratory failure, use non-invasive nasal CPAP or mechanical ventilation
Recommendations
•Antibiotics are recommended for all infants with
- Recurrent apnoea and circulatory impairment.
