
- •Англійська мова для професійного спілкування
- •Передмова
- •Brief contents
- •Unit 1 structure and bonding
- •1. You are going to read three texts which are all connected with chemistry. Read the texts and be able to make intelligent guesses about:
- •2. Decide what books the texts come from. What helped you to make up your mind? Choose from the following:
- •3. Which sentence could be the opening sentence of the text?
- •4. Think about the first sentences above and decide which you think are likely to introduce a paragraph with:
- •6. Give the definitions of the following terms:
- •2. Look at Appendix 3 and Render the following text.
- •3. Read the following text. Discuss the point with your colleagues. What do you know about the methods of scientific investigation? The Scientific Method
- •The Scientific Method
- •1. Culture clips: London life
- •2.What museums are there in your city/town? Have you ever visited any?
- •3.Have you ever visited science museum of the “kpi”? Are there any in your university? Imagine that you are a guide at such museum, tell about the most interesting museum piece.
- •2. What was said in the text about:
- •3. Render the following text.
- •1. Imagine that you are starting a presentation. What phrases might you use?
- •2. Listen totwowaysofopeningpresentationsandseeifyoucanhearsomeofthephrasesabove.
- •3. Read some advices on delivering effective presentations in the Appendix 7 and write your own opening for the topic “Stereochemistry”.
- •Imagine that you are a major distributor of the following product. Look at Business English section and write a letter asking more information about the product presented below.
- •Unit 3 molecular symetry
- •2. Find five things in the texts to finish the sentence: “It reminds me of…”
- •2. Read the flowcharts given in the figure 1 and 2.
- •3. Read some information about creation of the flow charts in the Appendix 4-6 and create your own describing any experiment you made in the laboratory.
- •4. Create a list of rules related to the theme of the text given in the exercise 1. Share and compare the rules with your partners and think how they might be improved, choose the best ones.
- •5. Render the text given in the exercise 1.
- •2. Listen to two ways of giving presentations and see if you can hear some of the phrases above.
- •3. Read some advices on delivering effective presentations in the Appendix 7 and write your own presentation for the topic “Molecular symmetry”.
- •You ordered: Beckman du64 uv/VisSpectrophotometer
- •Unit 4 stereochemistry of reactions
- •Chiral Drug
- •1.Presentation: questions.
- •Unit 5 resolution of enantiomers
- •Resolution of enantiomers
- •1. Method of resolution is the title of the text in this section. What is the likely content of the article? Predict the methods which might be described.
- •3. Mark and talk about five things from the text you are glad to find out about. Talk in pairs about these things and why you chose them.
- •5.Render the text.
- •4. Think of three reasons you liked the text and three reasons you didn’t like it. Share and compare your reasons with other students. Find out how many other students share your opinion.
- •1.Presentation: useful tips.
- •3.Complete the sentence with the correct phrase.
- •Principles of Stereochemistry
- •Enantiomeric Relationships
- •Diastereomeric Relationships
- •Methods of determining configuration
- •The Cause of Optical Activity
- •Molecules With More Than One Chiral (Stereogenic) Center
- •Asymmetric Synthesis
- •Business english
- •Formal letter
- •1.Titles and addresses
- •2Covering the issues
- •3 Beginning your letter
- •4 Ordering ideas
- •5 Range
- •6 Ending the letter
- •Sample formal letter
- •Informal letter or email
- •1 Titles and addresses
- •2 Openings
- •3 Covering all the issues
- •4 Using informal language
- •5 Range
- •6 Connectors
- •7 Closing statements
- •Writing a tactful advice letter
- •How to write a request letter
- •Complaint letter
- •If necessary, add any further information:
- •Writing claim letter
- •Inquiry letter
- •Establish Your Objective
- •Determine Your Scope
- •Organize Your Letter
- •Draft Your Letter
- •Close Your Letter
- •Review and Revise Your Inquiry Letter
- •Sample Inquiry Letter __________Better Widget Makers, Inc.__________
- •5555 Widget Avenue
- •Appendices appendix 1 exclamations
- •Appendix 2 general conversation gambits
- •Appendix 3 the scheme of rendering the text
- •Appendix 4 flow charts
- •Appendix 5 graph
- •Appendix 6 reading and interpreting graphs
- •Types of Graphs
- •Appendix 7 presentations
- •Typescripts
- •Bbc Learning English. Talking Business
- •(Bbclearningenglish. Com)
- •Bibliography 1
- •Bibliography 2
3. Read the following text. Discuss the point with your colleagues. What do you know about the methods of scientific investigation? The Scientific Method
The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming is an example of the scientific method at work. Fleming was studying the growth of bacteria. One day, his experiment was ruined because colonies of mold were growing on his plates. From this failed experiment, Fleming made an observation that would change the practice of medicine: Bacterial colonies could not grow in the area around the mold colonies. Fleming hypothesized that the mold was making a chemical compound that inhibited the growth of the bacteria. He performed a series of experiments designed to test this hypothesis.
The key to the scientific method is the design of carefully controlled experiments that will either support or disprove the hypothesis. This is exactly what Fleming did.
In one experiment he used two sets of tubes containing sterile nutrient broth. To one set he added mold cells. The second set (the control tubes) remained sterile. The mold was allowed to grow for several days. Then the broth from each of the tubes (experimental and control) was passed through a filter to remove any mold cells. Next, bacteria were placed in each tube. If Fleming’s hypothesis was correct, the tubes in which the mold had grown would contain the chemical that inhibits growth, and the bacteria would not grow. On the other hand, the control tubes (which were never used to grow mold) would allow bacterial growth. This is exactly what Fleming observed.
Within a few years this antibiotic, penicillin, was being used to treat bacterial infections in patients.
Study the steps of a scientific investigation and put the paragraphs of the following text into correct order. Be ready to summarize the information.
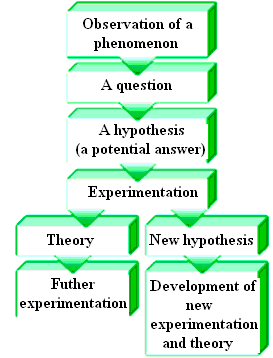
The Scientific Method
Experimentation. Demonstrating the correctness of hypotheses and theories is at the heart of the scientific method. This is done by carrying out carefully designed experiments that will either support or disprove the theory or hypothesis.
Characteristics of the scientific process include the following:
1) The scientific method is a systematic approach to the discovery of new information.
2) Formulation of a question. Humankind’s fundamental curiosity motivates questions of why and how things work.
3) Summarizing information. A scientific law is nothing more than the summary of a large quantity of information. For example, the law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. This statement represents a massive body of chemical information gathered from experiments.
4) How do we learn about the properties of matter, the way it behaves in nature, and how it can be modified to make useful products? Chemists do this by using the scientific method to study the way in which matter changes under carefully controlled conditions. The scientific method is not a “cookbook recipe” that, if followed faithfully, will yield new discoveries; rather, it is an organized approach to solving scientific problems. Every scientist brings his or her own curiosity, creativity, and imagination to scientific study. But scientific inquiry still involves some of the “cookbook approach.”
5) Pattern recognition. If a scientist finds a cause-and-effect relationship, it may be the basis of a generalized explanation of substances and their behavior.
Developing theories. When scientists observe a phenomenon, they want to explain it. The process of explaining observed behavior begins with a hypothesis. A hypothesis is simply an attempt to explain an observation, or series of observations, in a commonsense way. If many experiments support a hypothesis, it may attain the status of a theory. A theory is a hypothesis supported by extensive testing (experimentation) that explains scientific facts and can predict new facts.
6) Observation. The description of, for example, the color, taste, or odor of a substance is a result of observation. The measurement of the temperature of a liquid or the size or mass of a solid results from observation.
Tell about your scientific research.
Listening
