- •Методический комментарий
- •Introduction
- •1. Write or say the word you think of first to go with each of the words below. Possible answers are given on the right.
- •2. Now, play the game the other way round. Write or say the nationality you associate with the things listed below.
- •Exercise 3. Where are they?
- •In which cities are the following landmarks?
- •He/she comes from… He/she is… He/she speaks…
- •1.1 National characters
- •Text 1*
- •III. Comprehension check
- •V. Writing
- •Text 2 notes on the british*
- •In the following extract Bill Bryson, an American writer, makes observations of the British people.
- •IV. Language focus
- •1. Match the word with its definition.
- •2. Pick out the words from the text describing the American and the British ways of life.
- •Italian neighbours*
- •II. Skim Extract 1 with Tim’s interview about his living in Italy and find answers to the questions:
- •Extract 2
- •Baby? I'd rather have a mobile phone
- •VIII. Writing
- •Text 4 westerners and the japanese
- •II. Read the first part of the text about Leadership and decide which of the following statements accurately reflect John Mole’s comments.
- •Leadership
- •Attitudes and Behaviour
- •IV. Language focus
- •1. Find English equivalents to:
- •2. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •V. Speaking
- •Text 5 the amish
- •II. Read the article carefully and do the tasks that follow.
- •III. Comprehension check
- •V. Writing
- •Vocabulary box
- •Achievement test 1 national characters
- •Information check (orally)
- •Vocabulary check (in writing)
- •1. Match the two columns.
- •2. Match the definitions below with the words from the box.
- •3. Translate the sentences into English.
- •1.2 Communicating interculturally
- •Importance of intercultural communication*
- •II. Read the text and find information on the following points.
- •IV. Speaking
- •V. Writing
- •Text 2 main concepts of intercultural communication*
- •Culture
- •Subculture
- •Culture Shock
- •Ethnocentric reactions
- •IV. Writing
- •Text 3 understanding culture*
- •II. Read the following text and check if your predictions were right.
- •Text 4 activity orientation
- •Text 5 time orientation
- •Text 6 predictions of communication problems*
- •In what way can we predict communication problems with people from foreign countries?
- •II. Read the text and check whether your predictions were right.
- •1. Control Issues
- •2. Intrapersonal Factors
- •3. Biological Factors
- •4. Interpersonal Factors
- •5. Space and Time Factors
- •6. Geopolitical Factors
- •IV. Language focus
- •V. Speaking
- •VI. Writing
- •Text 7 recognizing cultural differences
- •II. Read the following text and write down the main cultural factors to fill in the table below the text.
- •IV. Writing
- •Text 8 dealing with language barriers
- •Barriers to written communication
- •Barriers to oral communication
- •IV. Language focus
- •1. Fill in the gaps with the prepositions where necessary.
- •2. Find synonyms to the following words in the chart below and learn them.
- •V. Speaking
- •Text 9 suggestions for the cross-cultural sojourner*
- •1. Learn the Rules of the New Culture.
- •2. Assume Responsibility
- •3. Observe Carefully
- •4. Tolerate Differences
- •5. Develop Flexibility
- •IV. Speaking
- •V. Writing
- •Acting out
- •1. Role-play the conversation.
- •2. Role-play the conversation in a travel-bureau.
- •Project writing
- •Social Customs
- •Vocabulary box
- •Achievement test 2 communicating interculturally
- •Information check (orally)
- •Vocabulary check (in writing)
- •1. Define the meaning of the following words in English.
- •2. Match the two columns.
- •3. Translate the sentences into English.
- •1.3 English as a global language
- •Text 1 ways of learning*
- •Starter activities
- •How do you like to learn languages? Look at these extracts from advertisements for methods of learning languages. Choose the methods you would like. Explain and discuss your answers.
- •People learn languages in different ways. Here are some descriptions and explanations of different kinds of language learners. Match the descriptions (1-6) to the explanations (a-f).
- •The table below lists the ways of learning. Complete the column about “you” and discuss your answers.
- •Discussion
- •Text 2 why don’t we all speak the same language?
- •How Did the English Language Begin?
- •III. Comprehension check
- •Text 3 the english language*
- •The english language
- •The english language in north america
- •1. Say whether each of the following sentences is true or false. Correct the false sentences to make them true.
- •2. Give examples of different borrowings in the English language.
- •V. Speaking
- •Text 4 british and american english*
- •The main differences of American English in pronunciation are:
- •1) The pronunciation of r in all positions, e.G. Part, first, corner;
- •VI. Writing
- •Text 5 english as a world language*
- •In the countries listed in the table, English is used either as a first language or as a second. Identify the 7 countries in which it is used as a first language.
- •II. Read the text carefully the spread of english
- •Basic characteristics
- •III. Comprehension check
- •IV. Speaking
- •Text 6 a global language*
- •II. Read the text and check your guesses.
- •V. Writing
- •Imperial english*
- •In this article below Professor Anne Eisenberg writes about the importance of English in the scientific world. For which jobs or subjects is it important to know English in your country?
- •II. Reading
- •1. The statements below express the main idea of each of paragraph. Read the article and match the statements to the paragraphs.
- •2. Decide which sentences in each paragraph express the main ideas.
- •97 % Населения мира предпочитают английский язык для международного общения
- •Text 8 the language of business
- •II. Read the text and write questions for these answers.
- •Look at the expressions in the box using rule. Use your dictionary to check the meanings of any of the expressions that you don’t know.
- •Complete these sentences using the expressions from the box in Exercise 1. Change the verb tense if necessary.
- •Do You Speak Japanese?
- •Project writing
- •Essay writing
- •Vocabulary box
- •Acievement test 3 english as a global language
- •Information check (orally)
- •Vocabulary check (in writing)
- •1. Define the meaning of the following words in English.
- •2. Give synonyms to:
- •3. Match the professional areas with language needs.
- •3. Complete each sentence with the words from the box.
- •For reading, discussing and reporting
- •Text 2 the japanese sense of beauty
- •Text 3 you have to catch them young…
- •Text 4 when the locals are friendly Free accommodation with plenty of surprises ... Servas is a cheap - and enlightening - way to see the world, says Patricia Cleveland-Peck
- •Text 5 must one be so polite that it hurt?
- •Text 6 should americans be required to learn another language?
- •Discussion
- •Text 7 tips for communicating with people from other cultures
- •Text 8 developing intercultural competence
- •1. Privacy and its implications
- •2. "So much for complaining"
- •3. "When in Rome, do as the Romans do"
- •4. Meals
- •5. Attitude to time
- •6. Academic life
- •7. Facial expressions
- •8. Gestures
- •9. Clothes
- •10. Topics for small talk
- •11. Politeness Strategies
- •Text 9 the image of russia in western travel guides
How Did the English Language Begin?
Practically all languages spoken on earth today can be traced by scholars back to some common source, that is, an ancestor language that has many descendants. The ancestor language - together with all the languages, which have developed from it - is called a «family» of languages.
English is considered a member of the Indo-European family of languages. Other languages belonging to the same family are French, Italian, German, Norwegian, and Greek.
In this Indo-European family of languages there are various branches and English is a member of the «West Teutonic» branch. Actually, English dates from about the middle of the fifth century, when invaders from across the North Sea conquered the native Celts and settled on the island now known as England.
For the sake of convenience, the history of the English language is divided into three great periods: the old English (or Anglo-Saxon), from about 400 to 1100; Middle English, from 1100 to 1500; and Modern English, from 1500 to the present day.
So the original language spoken in English was Celtic. But the Anglo-Saxons (the Angles, the Jutes, and the Saxons) conquered the island so thoroughly that very few Celtic words were kept in the new language.
The Anglo-Saxons themselves spoke several dialects. Later on, the Norsemen invaded England and they introduced a Scandinavian element into the language. This influence, which was a Germanic language, became a part of the language.
In 1066, William the Conqueror brought over still another influence to the language. He made Norman French the language of his Court. At first, this «Norman» language was spoken only by the upper classes. But gradually its influence spread and a language quite different from the Anglo-Saxon developed. This language became the chief source of modern English.
III. Comprehension check
Answer the questions.
-
Why don’t we all speak the same language?
-
How can a dialect become a language?
-
How did the English language begin?
-
What language family English can be subscribed to?
-
What are the 3 periods in the history of English?
-
What was the original language spoken in England?
-
What happened in 1066?
IV. Report writing
Find out the information about the origin of the Belarusian language. Make a report on it, and then present your findings in class.
Text 3 the english language*
(Intermediate – upper-intermediate)
I. Pre-reading task
The English language is one of the 5,000 languages in the world now. It is used in many countries and it is by no means entirely uniform. Read Extract 1 speaking about the subdivision of Standard English into different kinds of the English language. Say how many people in all speak English.
Extract 1
The english language
Where did English come from? The obvious answer is England. However, in the past two thousand years very many people came to England and changed the language. Perhaps most of the language comes from the Anglo-Saxons who came to England in the fifth to the seventh centuries. But there are also Roman words from the time when England was a part of the Roman Empire: the ending — 'Chester' in the name of an English town such as Colchester comes from the Latin word 'castra' and shows that there was a Roman town there. The Vikings brought many words with them, such as 'they' and 'their'; the Normans governed England for many years and brought French words with them. Then the English brought many words from different countries — 'kangaroo' from Australia, 'pyjamas' from India, and 'anorak' from Canada.
But what is English now? It is no longer spoken just in England and there are many different kinds of English in different parts of the world. In his book, Peter Strevens gives the following diagram:
|
S |
|||
|
American English Family |
British English Family
|
|
|
|
United States |
Canada |
West Indies Britain Australia Africa |
|
He says that there are two main families of Standard English, the American and the British. American English is spoken in the USA and in Canada. British English is spoken in the West Indies, Britain, Australasia, and Africa. However, many other parts of the world also use English. In India English is an official language still and there is a special kind of Indian English. In several African countries, such as Nigeria and Ghana, English is spoken in schools and colleges. In many sciences English is the language of communication. There are about 350 million people who speak English as a first language, and there are another 450 million who use it as a second language. So English is now an international language and is useful to people who never go to England.
II. Comprehension check
-
What are two main families of Standard English?
-
What countries is American English spoken in?
-
Why is English considered to be an international language?
-
What languages have lent words to English?
III. The term "melting pot” applied to the United States refers to the idea that the country is a place where people from many lands have come together and formed a unified culture. American English absorbed much of the vocabulary of different nations inhabiting the country. Read Extract 2 and state briefly in 3 or 4 sentences what cultures the American variety of English reflects.
Extract 2

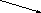
 tandard
English
tandard
English