
Pediatrics(2)
.pdf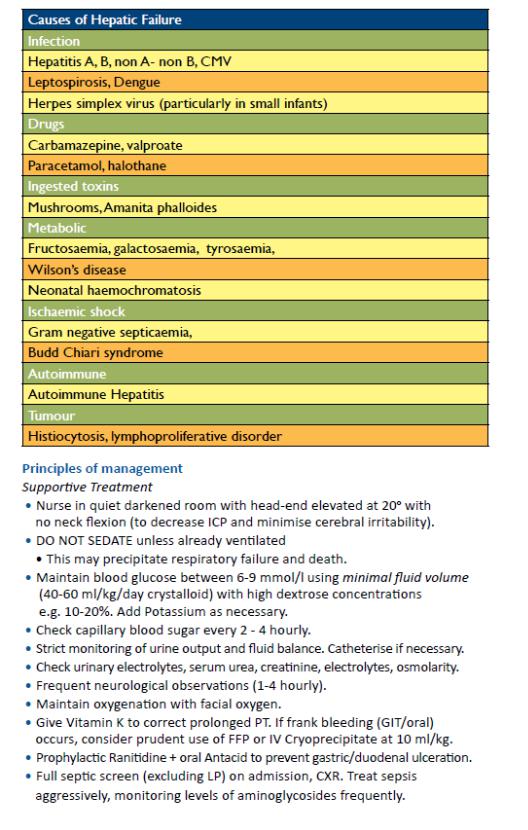
-
-
-
-
-9.6. Septicaemia
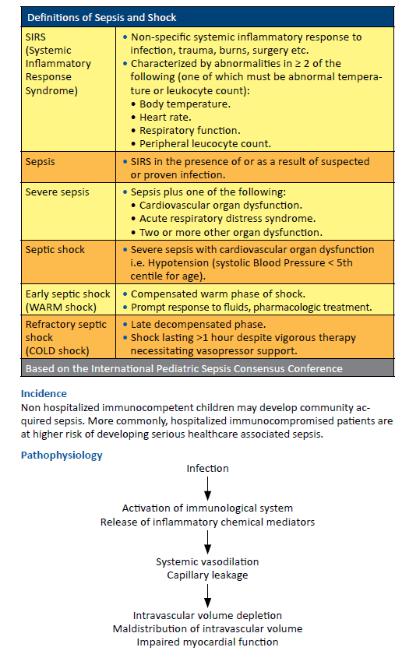
-Definition: Is a suspected or proven infection plus a systemic
-inflammatory response syndrome (e.g., fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, and leukocytosis).
-Causes
-- Bacteremia: (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Neisseria meningitidis, group A streptococcus,
-S. aureus, Salmonella)
-- Viral infection: (influenza, enteroviruses, hemorrhagic fever group, HSV, RSV, CMV, EBV)
-- Encephalitis: (arboviruses, enteroviruses, HSV)
-- Vaccine reaction (pertussis, influenza, measles)
-- Toxin-mediated reaction (toxic shock, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome)
-Clinical evaluation
-- Assess Air way, Breathing (RR, signs of respiratory distress and pulse oximetry), Circulation (HR, BP, skin for signs of dehydration, JVP)
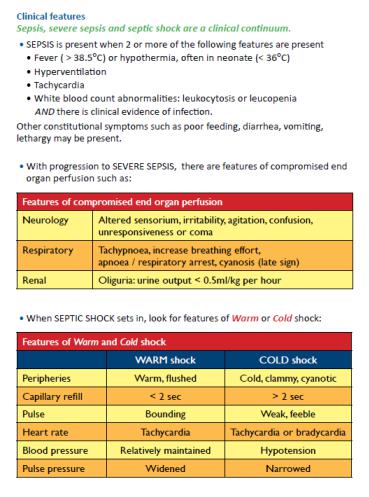
-- Identify SIRS (on the basis of ≥2 of the following):
-• Increased heart rate (>90/min)
- • Increased respiratory rate (>20/min) or PaCO2 <32 mm Hg
-• Increased temperature (>38°C) or decreased temperature(<36°C)
-• Increased WBC (>12,000/mm3) or decreased (<4000/mm3)
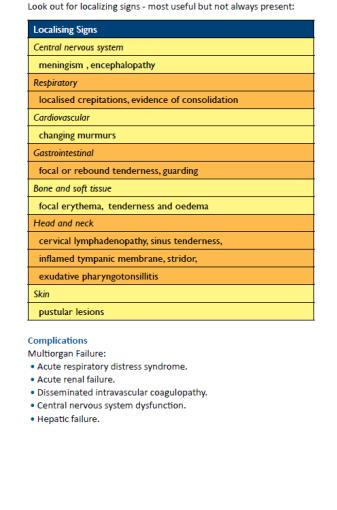
-- Identify source of infection e.g pneumonia, abdominal abscess, meningitis etc.
-- Assess organ function e.g. CNS (LOC, focal signs), renal function for urinary output
-Complications
-- Convulsions
-- Confusion or coma
-- dehydration
-- Shock
-- Cardiac failure
-- disseminated intravascular coagulation (with bleeding episodes)
-- Pneumonia
- - Septicaemic shock is an important cause of death
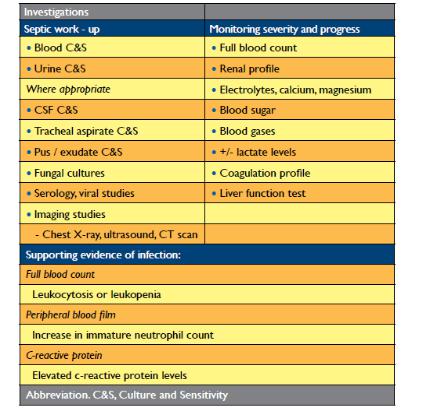
-Investigations
-- Identify SIRS; CBC and White-cell differential
-- Identify source of infection; blood and urine culture and
-sensitivity, sputum, CSF analysis, chest radiography and ultrasonography
-- Assess organ function;
-• Renal function: electrolytes, BUN, creatinine
-• Hepatic function: Bilirubin, AST, alkaline phosphatase
-• Coagulation: INR, PTT, platelets
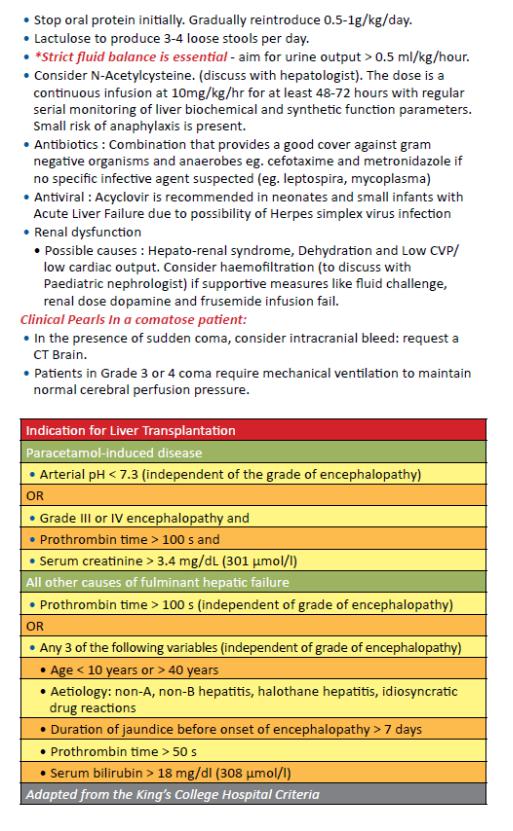
-Management
-- Assess for Air way, Breathing, Circulation, dehydration and manage accordingly
-- Control the source of sepsis e.g abscess, peritonitis
-- First choice treatment:
-• I.V cefotaxime 80mg/kg/dose every 8 hours for 7 days
-Alternative
-• I.V infusion ceftriaxone 75-100mg/kg/day once over 30-60 minutes for 7 days
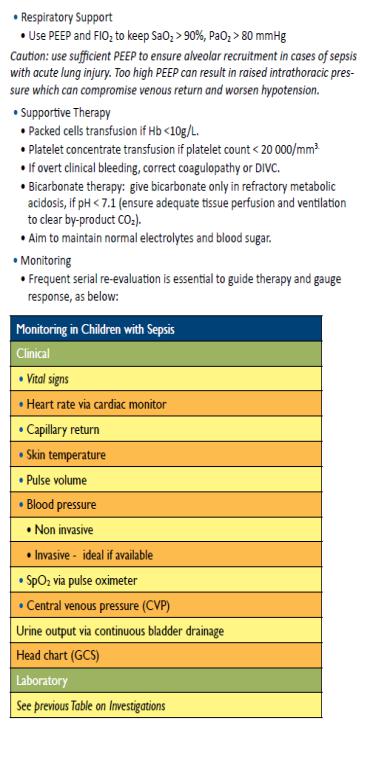
-Monitoring
-The child should be checked by nurses at least every 3 hours and by a doctor at least twice a day. Check for the presence of complications such as shock, reduced urine output, signs of bleeding (petechiae, purpura, bleeding from venepuncture sites), or skin ulceration.
-Recommendation
-- Immunization with the conjugate H. influenzae type b and S. pneumoniae vaccines is for all infants
-Note: Use of corticosteroids in patients with sepsis has adverse effects like hyperglycemia and immunosuppression thus leading to nosocomial infection and impaired wound healing. Studies reveal that early use of short-course, high-dose corticosteroids does not improve survival in severe sepsis.
-
-
-
-

-
-
-9.7. Salmonella Infections (Typhoid Fever)
-Definition: is a systemic infection with the bacterium Salmonella
-enterica serotype typhi.
