
- •LIBRARY OF CONGRESS CATALOGING-IN-PUBLICATION DATA
- •CONTENTS
- •FOREWORD
- •PREFACE
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. A Nice Equation for an Heuristic Power
- •3. SWOT Method, Non Integer Diff-Integral and Co-Dimension
- •4. The Generalization of the Exponential Concept
- •5. Diffusion Under Field
- •6. Riemann Zeta Function and Non-Integer Differentiation
- •7. Auto Organization and Emergence
- •Conclusion
- •Acknowledgment
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Preliminaries
- •3. The Model
- •4. Numerical Simulations
- •5. Synchronization
- •6. Conclusion
- •Acknowledgments
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction: A Short Literature Review
- •2. The Injection System
- •3. The Control Strategy: Switching of Fractional Order Controllers by Gain Scheduling
- •4. Fractional Order Control Design
- •5. Simulation Results
- •6. Conclusion
- •Acknowledgment
- •References
- •Abstract
- •Introduction
- •1. Basic Definitions and Preliminaries
- •Conclusion
- •Acknowledgments
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Context and Problematic
- •2. Parameters and Definitions
- •3. Semi-Infinite Plane
- •4. Responses in the Semi-Infinite Plane
- •5. Finite Plane
- •6. Responses in Finite Plane
- •7. Simulink Responses
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Modelling
- •3. Temperature Control
- •4. Conclusion
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Preliminaries
- •3. Second Order Sliding Mode Control Strategy
- •4. Adaptation Law Synthesis
- •5. Numerical Studies
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Rabotnov’s Fractional Operators and Main Formulas of Algebra of Fractional Operators
- •4. Calculation of the Main Viscoelastic Operators
- •5. Relationship of Rabotnov Fractional Operators with Other Fractional Operators
- •8. Application of Rabotnov’s Operators in Problems of Impact Response of Thin Structures
- •9. Conclusion
- •Acknowledgments
- •References
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •3. Theory of Diffusive Stresses
- •4. Diffusive Stresses
- •5. Conclusion
- •References
- •Abstract
- •Introduction
- •Methods
- •Conclusion
- •Acknowledgment
- •Abstract
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Basics of Fractional PID Controllers
- •3. Tuning Methodology for Fuzzy Fractional PID Controllers
- •4. Optimal Fuzzy Fractional PID Controllers
- •5. Conclusion
- •References
- •INDEX

156 |
Danial Senejohnny, Mohammadreza Faieghi and Hadi Delavari |
|
|
The stability is guaranteed if the derivative of the Lyapunov function is negative definite, also known as the reaching condition. Taking the first time derivative from (18) one gets:
|
|
|
V S |
S |
k |
(1 |
sb k D ) |
k D S |
f |
k |
(x) k Db k s |
S |
k |
|
|
|
(19) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k k k |
k k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k k k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f |
|
(x) |
|
|
|||||||||||||
Assuming that |
f |
k |
(x) |
are bounded, namely |
k |
|
sup |
x |
k |
, and s 1 k Db , then |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k |
k |
k |
||||
one gets 1 s k Db |
0 . As a result, the expression (19) can be rewritten as |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
k |
k k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sk |
|
|
|
1 ksbk kkD kkD k |
|
Sk |
|
|
kkDbk kks |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Vk |
Sk |
|
|
|
|
|
Sk |
|
|
(20) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sk |
|
|
|
Sk |
|
|
1 ksbk kkD kkDbk kks kkD k |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
Sk |
|
ks kkDbk 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Therefore, |
provided |
k s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to |
dominate the model |
|
matched |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
bk |
|
|
|
|
|
kkD |
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
uncertainties [33], then Vk will be negative which implies asymptotic stability of the system and Sk (t) and Sk (t) tend to zero as t .
4. Adaptation Law Synthesis
In this section an adaptive scheme based on Lyapunov function for switching feedback control gains is derived. The adaptation law guarantees the system stability regardless of model uncertainty bound. Take the following Lyapunov function
|
|
|
|
|
Vk |
|
1 |
Sk |
Sk |
2k 1 |
(k |
) |
2 |
2k |
(kk ) |
2 |
|
(21) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
1 |
s |
|
1 |
s |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
ˆs |
s |
|
s |
ˆs |
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where k |
k |
k |
, |
kk |
kk |
kk |
denote the estimation error. Taking time derivative from |
|||||||||||
(21) with respect to time and with the sense of (20), one has:
Vk |
|
Sk |
|
|
Sk |
|
s |
D |
D |
|
s |
D |
|
Sk |
|
1 |
|
s |
s |
1 s s |
(22) |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 k bk kk |
kk |
bk kk |
kk k |
2k 1 k |
k |
2k kk kk |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
adding and subtracting some terms, Eq. (22) can be rewritten as follows |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vk |
|
Sk |
|
|
|
Sk |
|
|
ˆs D |
|
ˆs |
D |
|
D |
|
s |
D |
|
Sk |
|
|
s |
D |
|
Sk |
|
Sk |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 k kk bk |
kk bk kk |
kk k |
kk bk kk |
|
|
k bk kk |
|
|
|
(23) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
s s |
1k s k s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
2k 1 |
|
|
k k |
|
|
|
2k k |
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ˆs |
|
|
|
|
ˆs |
can be chosen such that |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
It is clear that kk |
and k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Complimentary Contributor Copy
Adaptive Second-Order Fractional Sliding Mode Control … |
157 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sk |
Sk 1 |
k bk kk |
kk bk kk |
kk k 0 , |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
ˆs D |
ˆs D |
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
so the adaptation law can be derived directly from (23) as follow
sb k D |
|
S |
k |
|
S |
k |
1 |
s s 0 s |
2k 1 |
k Db |
|
S |
k |
|
S |
k |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
k k k |
|
|
|
|
2k 1 |
k k |
k |
|
|
k k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(24) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
1k s k s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
k sb k D |
|
S |
k |
0 |
k s |
|
2k |
k Db |
S |
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
k k k |
|
|
|
|
|
2k k k |
|
k |
|
k k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The switching controller parameters ks and kks in switching control (13) are evaluated
through the adaptive algorithm derived in (24).
As the bound of uncertainty is not available, choosing switching controller gains manually can make chattering effect worst. Therefore, by virtue of adaptation law (24) switching controller parameters assume their gains by making a compromise between chattering suppression and reaching condition.
5. Numerical Studies
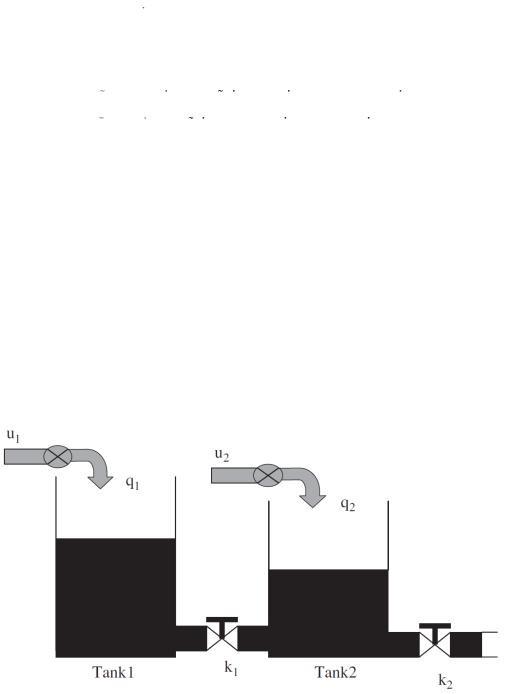
The twin-tanks system comprised of two small tanks mounted above a reservoir which provides storage for the water, Figure 2. Water is pumped into the bottom of each tank by two independent pumps. The pump only increases the liquid level and is not responsible for pumping the water out of the tank [8].
Figure 2. The plant of a liquid-level control system.
The twin-connected tanks system is a nonlinear dynamical system and the governing dynamical equations can be written as [8, 34]
Complimentary Contributor Copy
158 |
Danial Senejohnny, Mohammadreza Faieghi and Hadi Delavari |
|
|
|
k1 |
|
|
|
|
|
sign(h h ) |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
h |
|
|
h h |
q |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
A1 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
|
A1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(25) |
||||
|
|
k1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k2 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
h2 |
|
|
h1 h2 |
sign(h1 |
h2 ) |
h2 |
q2 |
||||||||||||||
A2 |
|
A2 |
A2 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
where h1 and h2 are the total water heads in Tank 1 and Tank 2 respectively, which are the two outputs of interest, and q1 , q2 are the two inflows into the tanks. It is assumed that A1 and A2 are the capacities of Tank-1 and Tank-2 respectively. Both tanks assumed to have the same cross sectional area i.e. A1 A2 A .
It has been seen in [35] that in chemical plants, selecting the flow rate as an input is more effective than using flow as the input. Thus, if the flow rates are considered as the inputs, i.e., q1 u1 and q2 u2 , the system dynamics can be written as
h1 |
k1 |
|
|
h1 h2 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
u1 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
2A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
h1 h2 |
|
|
|
|
|
(26) |
|||||||||||||
|
k1 |
|
|
|
h1 h2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
k2 |
|
|
||||||||
h2 |
|
|
|
|
|
h2 |
1 |
u2 |
||||||||||||||
2A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
||||||||||||
|
|
h1 h2 |
|
|
|
2A h2 |
||||||||||||||||
It seems from (25) and (26) that there is a discontinuity at h1 h2 , so desired water level is selected as hd1 hd 2 .
A mathematical model of Twin Tank can be expressed as follows:
x1 (t) x2 (t) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
k1 |
|
x2 x4 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
x2 (t) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
u1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
x1 x3 |
|
|
|
|
(27) |
||||||||||||
x3 (t) x4 (t) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
k1 |
x2 x4 |
|
k2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|||||||||||
x4 (t) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x4 |
|
|
u2 |
||||||
2A |
|
|
x1 x3 |
|
|
2A x3 |
A |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
System constraints: The flowed fluid into |
the tanks |
( q1 and q2 ) cannot be negative |
|||||||||||||||||
because the pumps can only pump water into the tanks. Therefore constraints on the inflow
are given by |
q1 , q2 0 . In the steady state, for constant water level set points, the respective |
|||||
derivatives |
must be zero separately i.e. h1 0, |
h2 0 . Therefore, the inequality |
||||
|
|
k 2 |
|
h |
1 must hold [8]. |
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
||
|
k 2 |
k 2 |
h |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
Complimentary Contributor Copy
|
Adaptive Second-Order Fractional Sliding Mode Control … |
|
|
|
159 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Both tanks have the same area of 70 cm2 , |
k |
14 and |
k |
2 |
10 , the set point water level is |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
selected as |
hd ,1 xd ,1 |
8 cm and |
hd ,3 xd ,3 |
6 cm , with |
initial |
water |
level |
h1 (0) 4 , |
||||||||
h2 (0) 2 . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Eq. |
(9) sliding |
surface |
parameters |
are |
selected |
to |
be as |
k P 3 , |
k D |
7 |
, k FD 1, |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
k I 0.5 , |
1, |
0.8 , |
k P |
3 , k D |
7 , k FD 1, |
|
2 |
1, k I 0.5 |
, |
2 |
0.8 . The |
|||||
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|||
initial conditions are chosen as |
S1 (0) 0.5 |
and |
S2 (0) 0.5 |
as well. In order to smooth the |
||||||||||||
control action, instead of sgn(.) function tanh(.) is used. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
The simulation |
results with |
20% variations in |
system’s |
nominal |
parameters (i.e |
|||||||||||
A 84 cm2 , k1 16.8 and k2 12 ) shows good stabilization of the water levels in both tanks
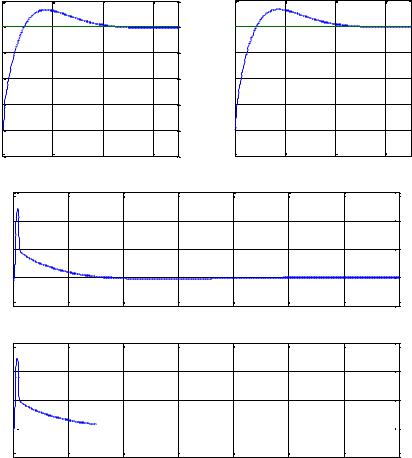
Figs. 3, dashed-line and solid-line represents system’s response and desired trajectory, respectively. The value of inflow in both tanks settles to the steady state values shown in Figure 3, the pumps only increases the liquid level, so their value is always positive.
h1(m)
inlet flow, q1
inlet flow, q2
9 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
(m) |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
h |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
30 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
|
10 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
|
time (sec) |
|
|
|
|
time (sec) |
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1000 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
|
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
time (sec) |
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200
100
0 
























-1000 |
2 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
time (sec) |
|
|
|
Figure 3. 2-SMC with PIDDα surface and +20% variation in parameters of Twin Tank system.
Complimentary Contributor Copy
160 |
Danial Senejohnny, Mohammadreza Faieghi and Hadi Delavari |
|
|
8 |
1 |
8 |
1 |
k |
λ |
||
8 |
2 |
8 |
2 |
k |
λ |
||
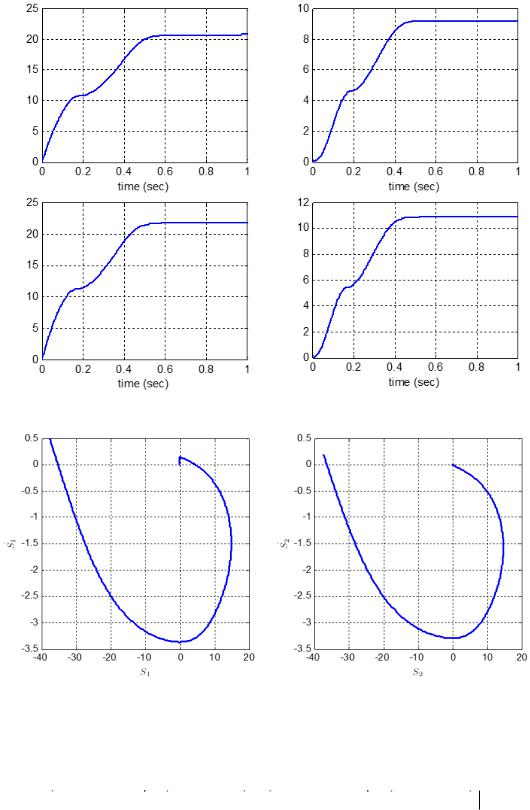
Figure 4. Adaptive parameters versus time.
1 |
|
2 |
Ṡ |
|
Ṡ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
S1 |
S2 |
Figure 5. Phase plot.
Adaptive parameters 1s , k 1s , 2s , k 2s in (24) are estimated as follow with zero initial conditions shown in Figure 4.
s k Db |
|
S |
|
|
S |
, k s k Db |
S |
, s |
k Db |
|
S |
2 |
|
S |
2 |
k s |
k Db |
S |
2 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Complimentary Contributor Copy
