
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •Pattern Approach for Lung Imaging
- •1: Nodule
- •Solitary Pulmonary Nodule (SPN), Solid
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lung Cancer (Solid Adenocarcinoma)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Carcinoid or Atypical Carcinoid
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •BALT Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Tuberculoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Hamartoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Sclerosing Hemangioma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity Nodule
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia (AAH)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •2: Mass
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Sarcoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Progressive Massive Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Actinomycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •3: Consolidation
- •Lobar Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Infarction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Patchy and Nodular Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Cryptococcosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •IgG4-Related Lung Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •4: Beaded Septum Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •References
- •5: Comet Tail Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rounded Atelectasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •6: CT Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Angioinvasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Metastatic Hemorrhagic Tumors
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Endometriosis with Catamenial Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •7: Galaxy Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Galaxy Sign in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •8: Reversed Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Mucormycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •9: Tree-in-Bud Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspiration Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body-Induced Pulmonary Vasculitis (Cellulose and Talc Granulomatosis)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Bronchial Atresia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Bronchial Tuberculosis and Mucoid Impaction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body Aspiration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •11: Lobar Atelectasis Sign
- •Disease Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Right Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Left Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Right Middle Lobar Atelectasis
- •Lower Lobar Atelectasis
- •References
- •Cavity
- •Diseases Causing the Cavity
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Septic Pulmonary Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paragonimiasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cyst
- •Diseases Causing the Cyst
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Blebs and Bullae
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sequestration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Intrapulmonary Bronchogenic Cyst
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Traumatic Lung Cysts
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Mosaic Attenuation
- •Diseases Causing the Mosaic Attenuation Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Constrictive Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Pulmonary Thromboembolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Airway Disease (Bronchiectasis and Bronchiolectasis)
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Swyer-James-MacLeod Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Dyskinetic Cilia Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •14: Air-Crescent Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspergilloma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Rasmussen’s Aneurysm
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •15: Signet Ring Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •16: Interlobular Septal Thickening
- •Smooth Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Edema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Niemann–Pick Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Nodular Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •17: Honeycombing
- •Honeycombing with Subpleural or Basal Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Asbestosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Honeycombing with Upper Lung Zone Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern and Distribution
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Idiopathic Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •End-stage Fibrotic Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •18: Small Nodules
- •Small Nodules with Centrilobular Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Follicular Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Tumor Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumoconiosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveoloseptal Amyloidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Small Nodules with Random (Miliary) Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Miliary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Miliary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •19: Multiple Nodular or Mass(-like) Pattern
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Amyloidomas
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •ANCA-Associated Granulomatous Vasculitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation and Fibrosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation, but without Fibrosis (Crazy-Paving Appearance)
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lipoid Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Mucinous Adenocarcinoma or Adenocarcinoma in Situ, Diffuse Form
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, with Small Nodules
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Acute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •22: Consolidation
- •Consolidation with Subpleural or Patchy Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Churg–Strauss Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Radiation Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Consolidation with Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Viral Pneumonias
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •23: Decreased Opacity with Cystic Walls
- •Cavities
- •Diseases Causing Cavities
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rheumatoid Lung Nodules
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cysts
- •Diseases Causing Multiple Cysts
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Emphysema
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Centrilobular Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paraseptal Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •24: Decreased Opacity without Cystic Walls
- •Mosaic Attenuation, Vascular
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway Diseases Causing Mosaic Attenuation
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Asthma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •26: Pneumonia
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Bronchopneumonia
- •Interstitial Pneumonia
- •27: Drug-Induced Lung Disease
- •Interstitial Pneumonitis and Fibrosis
- •Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- •Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •References
- •Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- •Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- •Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (PSS)
- •Sjögren’s Syndrome
- •Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
- •Ankylosing Spondylitis
- •References
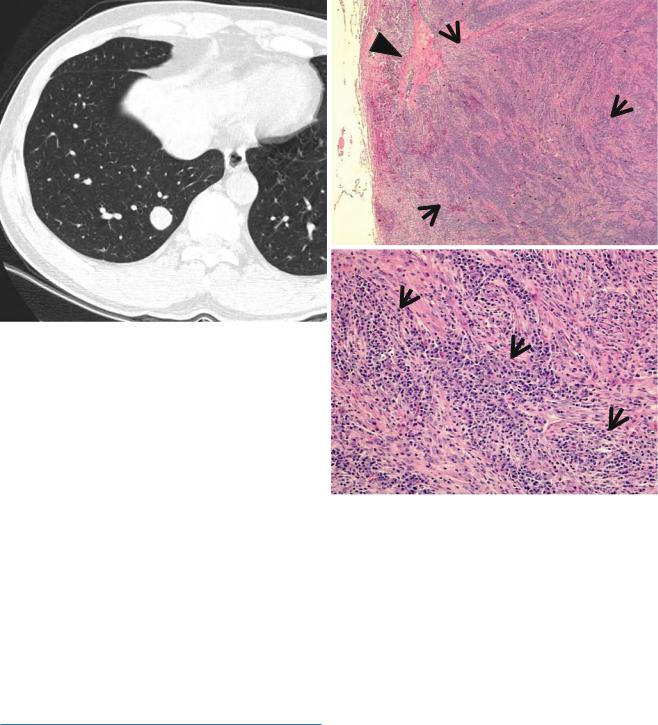
BALT Lymphoma |
11 |
|
|
a |
b |
c
Fig. 1.9 Inßammatory myoÞbroblastic tumor in a 29-year-old man. (a) Thin-section (2.5-mm section thickness) CT scan obtained at level of suprahepatic inferior vena cava (IVC) shows a 19-mm-sized welldeÞned nodule in the right lower lobe. (b) Low-magniÞcation (×2) photomicrograph of wedge resection of tumor from the right lower lobe
demonstrates areas of inßammatory cell inÞltration (arrows; mainly composed of plasma cells) and Þbrosis (arrowhead). (c) HighmagniÞcation (×100) photomicrograph discloses fascicular spindle cell proliferation and admixed areas of lymphocytes and plasma cells (arrows)
However, all carcinoids are malignant although indolent. Nodal involvement clearly affects survival [19]. The 5-year survival of patients with atypical carcinoids is only 57 %.
secondary to inßammatory or autoimmune processes. The neoplastic cells inÞltrate the bronchiolar epithelium, forming lymphoepithelial lesion [20] (Fig. 1.5).
BALT Lymphoma
Pathology and Pathogenesis
Pulmonary marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of bronchusassociated lymphoid tissue (BALT) is an extranodal lymphoma, which is thought to arise in acquired MALT
Symptoms and Signs
BALT lymphoma of SPN rarely causes pulmonary symptoms. Weightlossandnightsweatingmaybefound.Extrapulmonary symptoms and signs of connective tissue diseases such as SjšgrenÕs syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis may occur.
12 |
|
1 Nodule |
|
|
|
a |
Table 1.1 Common diseases manifesting as solitary pulmonary |
|
nodule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disease |
Key points for differential diagnosis |
|
||
|
Malignant nodule |
|
|
Lung cancer |
Wash-in values of >25 HU, lobulated |
|
|
or spiculated margin, and absence of a |
|
|
satellite nodule |
|
Carcinoid |
Lobulated nodule with dense |
|
|
enhancement |
|
BALT lymphoma |
Consolidation or nodules with air |
|
|
bronchograms |
|
Solitary metastasis |
|
|
Benign nodule |
|
|
Granuloma |
No or little enhancement, satellite |
|
|
nodules |
|
Hamartoma |
Focal areas of fat or calciÞcation, |
|
|
septal or cleft-like enhancement |
|
Sclerosing hemangioma |
Subpleural homogeneous mass, rapid |
|
|
and strong enhancement |
|
Inßammatory |
|
|
myoÞbroblastic tumor |
|
|
Rheumatoid nodule |
|
|
Parasitic infection (PW) |
Cavitary nodules or masses in the |
|
|
subpleural or subÞssural areas |
b |
ANCA-associated |
Multiple, bilateral, subpleural nodules |
|
granulomatous vasculitis |
or masses |
Note: HU HounsÞeld unit, BALT bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue, PW
Paragonimus westermani, ANCA antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
common Þndings include ground-glass opacity (GGO) lesion, interlobular septal thickening, centrilobular nodules, and bronchial wall thickening and pleural effusion.
CT–Pathology Comparisons
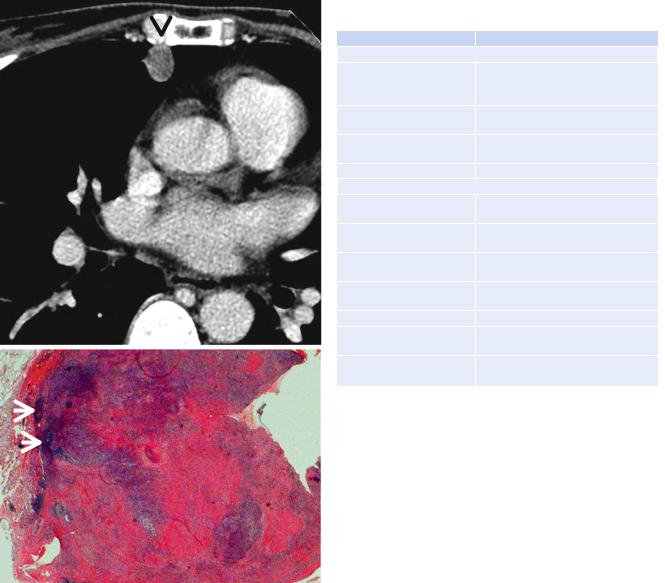
Fig. 1.10 ANCA (antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody)-associated granulomatous vasculitis (former WegenerÕs granulomatosis) manifesting as a solitary pulmonary nodule in a 51-year-old woman. (a) Mediastinal window image of CT scan (5.0-mm section thickness) obtained at level of the right middle lobar bronchus shows a 13-mm- sized nodule (arrow) in the right middle lobe. (b) Low-magniÞcation (×40) photomicrograph of wedge resection of tumor from the right middle lobe demonstrates basophilic inßammatory nodule containing geographic necrotic areas (arrows)
CT Þndings of BALT lymphoma showing solitary or multifocal nodules or masses and areas of airspace consolidation are related to proliferation of tumor cells within the interstitium such that the alveolar airspaces and transitional airways are obliterated [22] (Fig. 1.5). Because the bronchi and membranous bronchioles tend to be unaffected, an air bronchogram is common. Interlobular septal thickening, centrilobular nodules, and bronchial wall thickening on CT images are related to perilymphatic interstitial inÞltration of tumor cells.
CT Findings
Typical CT Þndings of BALT lymphoma include solitary (Fig. 1.5) or multifocal nodules or masses and areas of airspace consolidation with an air bronchogram [20, 21]. Less
Patient Prognosis
BALT lymphoma shows the indolent clinical course. The estimated 5- and 10-year overall survival rates have been reported to be 90 and 72 %, respectively [23]. Age and performance status are the prognostic factors.
