
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •Pattern Approach for Lung Imaging
- •1: Nodule
- •Solitary Pulmonary Nodule (SPN), Solid
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lung Cancer (Solid Adenocarcinoma)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Carcinoid or Atypical Carcinoid
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •BALT Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Tuberculoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Hamartoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Sclerosing Hemangioma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity Nodule
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia (AAH)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •2: Mass
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Sarcoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Progressive Massive Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Actinomycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •3: Consolidation
- •Lobar Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Infarction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Patchy and Nodular Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Cryptococcosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •IgG4-Related Lung Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •4: Beaded Septum Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •References
- •5: Comet Tail Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rounded Atelectasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •6: CT Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Angioinvasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Metastatic Hemorrhagic Tumors
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Endometriosis with Catamenial Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •7: Galaxy Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Galaxy Sign in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •8: Reversed Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Mucormycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •9: Tree-in-Bud Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspiration Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body-Induced Pulmonary Vasculitis (Cellulose and Talc Granulomatosis)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Bronchial Atresia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Bronchial Tuberculosis and Mucoid Impaction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body Aspiration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •11: Lobar Atelectasis Sign
- •Disease Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Right Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Left Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Right Middle Lobar Atelectasis
- •Lower Lobar Atelectasis
- •References
- •Cavity
- •Diseases Causing the Cavity
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Septic Pulmonary Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paragonimiasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cyst
- •Diseases Causing the Cyst
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Blebs and Bullae
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sequestration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Intrapulmonary Bronchogenic Cyst
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Traumatic Lung Cysts
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Mosaic Attenuation
- •Diseases Causing the Mosaic Attenuation Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Constrictive Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Pulmonary Thromboembolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Airway Disease (Bronchiectasis and Bronchiolectasis)
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Swyer-James-MacLeod Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Dyskinetic Cilia Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •14: Air-Crescent Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspergilloma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Rasmussen’s Aneurysm
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •15: Signet Ring Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •16: Interlobular Septal Thickening
- •Smooth Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Edema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Niemann–Pick Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Nodular Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •17: Honeycombing
- •Honeycombing with Subpleural or Basal Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Asbestosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Honeycombing with Upper Lung Zone Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern and Distribution
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Idiopathic Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •End-stage Fibrotic Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •18: Small Nodules
- •Small Nodules with Centrilobular Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Follicular Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Tumor Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumoconiosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveoloseptal Amyloidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Small Nodules with Random (Miliary) Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Miliary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Miliary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •19: Multiple Nodular or Mass(-like) Pattern
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Amyloidomas
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •ANCA-Associated Granulomatous Vasculitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation and Fibrosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation, but without Fibrosis (Crazy-Paving Appearance)
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lipoid Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Mucinous Adenocarcinoma or Adenocarcinoma in Situ, Diffuse Form
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, with Small Nodules
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Acute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •22: Consolidation
- •Consolidation with Subpleural or Patchy Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Churg–Strauss Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Radiation Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Consolidation with Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Viral Pneumonias
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •23: Decreased Opacity with Cystic Walls
- •Cavities
- •Diseases Causing Cavities
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rheumatoid Lung Nodules
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cysts
- •Diseases Causing Multiple Cysts
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Emphysema
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Centrilobular Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paraseptal Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •24: Decreased Opacity without Cystic Walls
- •Mosaic Attenuation, Vascular
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway Diseases Causing Mosaic Attenuation
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Asthma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •26: Pneumonia
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Bronchopneumonia
- •Interstitial Pneumonia
- •27: Drug-Induced Lung Disease
- •Interstitial Pneumonitis and Fibrosis
- •Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- •Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •References
- •Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- •Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- •Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (PSS)
- •Sjögren’s Syndrome
- •Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
- •Ankylosing Spondylitis
- •References
Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis |
213 |
|
|
a |
b |
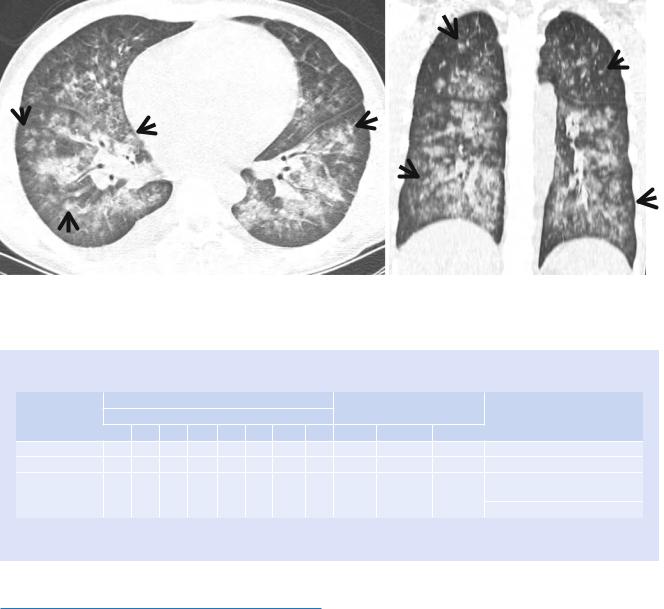
Fig. 21.5 Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in a 15-year-old boy with IgA nephropathy and pulmonary capillaritis. (a, b) Lung window image of CT (2.5-mm section thickness) scan obtained at level of inferior pulmo-
nary veins shows patchy and extensive parenchymal opacity in both lungs. Please also note small poorly formed centrilobular nodules (arrows) in both lungs
Key Points for Differential Diagnosis
|
|
Distribution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zones |
|
|
|
|
|
Clinical presentations |
|
|
Diseases |
|
U |
M |
L |
SP C |
R |
BV R |
Acute Subacute Chronic |
|
Others |
|
|
|||||||||
Subacute HP |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Bird fanciers, farmers |
|
CMV pneumonia |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Immunocompromised patients |
|
DAH |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Hemoptysis, anemia, pulmonary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vasculitis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interlobular septal thickening |
Note: HP hypersensitivity pneumonitis, CMV cytomegalovirus, DAH diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, U upper, M middle, L lower, SP subpleural, C central, R random, BV bronchovascular
Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Pathology and Pathogenesis
The histopathologic features of subacute HP are a subacute or chronic inßammatory interstitial pneumonia associated with bronchiolitis and small, indistinct, non-necrotizing interstitial granulomas. The histopathology of HP raises a differential diagnosis that includes other cellular interstitial pneumonias, such as NSIP. At low magniÞcation, the surgical lung biopsy shows a moderately dense interstitial inÞltrate, composed of plasma cells and small lymphocytes, causing slight widening of the alveolar walls. A bronchiolocentric distribution may be evident (Fig. 21.3) and thus is called a granulomatous interstitial bronchiolocentric pneumonitis. Typically, the granulomas are small, non-necrotizing, poorly formed, and loosely arranged [23].
Symptoms and Signs
Subacute form of HP is characterized by gradual development of cough and dyspnea over several days and weeks [24]. Some patients present with fever, fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss. Physical examination reveals tachypnea and bibasilar inspiratory crackles.
CT Findings
The most characteristic features of subacute HP on thinsection CT are bilateral patchy areas of GGO, poorly deÞned small centrilobular nodules, and lobular areas of mosaic attenuation on inspiratory images and of air trapping on expiratory CT images [17, 25] (Fig. 21.3). Sometimes, thin-walled cysts can be seen in a small percentage of patients [26].
