
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •Pattern Approach for Lung Imaging
- •1: Nodule
- •Solitary Pulmonary Nodule (SPN), Solid
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lung Cancer (Solid Adenocarcinoma)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Carcinoid or Atypical Carcinoid
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •BALT Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Tuberculoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Hamartoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Sclerosing Hemangioma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity Nodule
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia (AAH)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •2: Mass
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Sarcoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Progressive Massive Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Actinomycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •3: Consolidation
- •Lobar Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Infarction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Patchy and Nodular Consolidation
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Cryptococcosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •IgG4-Related Lung Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •4: Beaded Septum Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •References
- •5: Comet Tail Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rounded Atelectasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •6: CT Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Angioinvasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Metastatic Hemorrhagic Tumors
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Endometriosis with Catamenial Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •7: Galaxy Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Galaxy Sign in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •8: Reversed Halo Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Mucormycosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •9: Tree-in-Bud Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspiration Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body-Induced Pulmonary Vasculitis (Cellulose and Talc Granulomatosis)
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Bronchial Atresia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Bronchial Tuberculosis and Mucoid Impaction
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Foreign-Body Aspiration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •11: Lobar Atelectasis Sign
- •Disease Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Right Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Left Upper Lobar Atelectasis
- •Right Middle Lobar Atelectasis
- •Lower Lobar Atelectasis
- •References
- •Cavity
- •Diseases Causing the Cavity
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Septic Pulmonary Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paragonimiasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cyst
- •Diseases Causing the Cyst
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Blebs and Bullae
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sequestration
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Intrapulmonary Bronchogenic Cyst
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Traumatic Lung Cysts
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Mosaic Attenuation
- •Diseases Causing the Mosaic Attenuation Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Constrictive Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Pulmonary Thromboembolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Airway Disease (Bronchiectasis and Bronchiolectasis)
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Swyer-James-MacLeod Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Dyskinetic Cilia Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •14: Air-Crescent Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Aspergilloma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Rasmussen’s Aneurysm
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •15: Signet Ring Sign
- •Diseases Causing the Sign
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •16: Interlobular Septal Thickening
- •Smooth Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Edema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Niemann–Pick Disease
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Nodular Septal Thickening
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT-Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •17: Honeycombing
- •Honeycombing with Subpleural or Basal Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Asbestosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Honeycombing with Upper Lung Zone Predominance
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern and Distribution
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Idiopathic Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •End-stage Fibrotic Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •18: Small Nodules
- •Small Nodules with Centrilobular Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Follicular Bronchiolitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Tumor Embolism
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumoconiosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveoloseptal Amyloidosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Small Nodules with Random (Miliary) Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Miliary Tuberculosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Miliary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •19: Multiple Nodular or Mass(-like) Pattern
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pulmonary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Lymphoma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Amyloidomas
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •ANCA-Associated Granulomatous Vasculitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation and Fibrosis
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Ground-Glass Opacity with Reticulation, but without Fibrosis (Crazy-Paving Appearance)
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lipoid Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Mucinous Adenocarcinoma or Adenocarcinoma in Situ, Diffuse Form
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, with Small Nodules
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Ground-Glass Opacity without Reticulation, Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Acute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •22: Consolidation
- •Consolidation with Subpleural or Patchy Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Churg–Strauss Syndrome
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Radiation Pneumonitis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Consolidation with Diffuse Distribution
- •Diseases Causing the Pattern
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Viral Pneumonias
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Acute Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •23: Decreased Opacity with Cystic Walls
- •Cavities
- •Diseases Causing Cavities
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Rheumatoid Lung Nodules
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cavitary Metastasis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Cysts
- •Diseases Causing Multiple Cysts
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Emphysema
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Centrilobular Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Paraseptal Emphysema
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •24: Decreased Opacity without Cystic Walls
- •Mosaic Attenuation, Vascular
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Airway Diseases Causing Mosaic Attenuation
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Asthma
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •Distribution
- •Clinical Considerations
- •Cystic Fibrosis
- •Pathology and Pathogenesis
- •Symptoms and Signs
- •CT Findings
- •CT–Pathology Comparisons
- •Patient Prognosis
- •References
- •26: Pneumonia
- •Lobar Pneumonia
- •Bronchopneumonia
- •Interstitial Pneumonia
- •27: Drug-Induced Lung Disease
- •Interstitial Pneumonitis and Fibrosis
- •Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- •Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
- •Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- •Hypersensitivity Pneumonia
- •References
- •Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- •Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- •Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (PSS)
- •Sjögren’s Syndrome
- •Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
- •Ankylosing Spondylitis
- •References
Galaxy Sign |
7 |
|
Definition
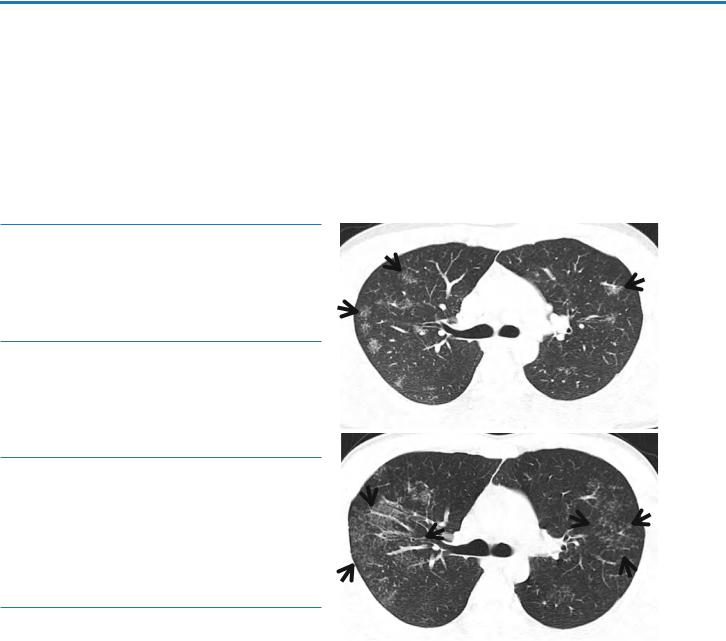
A large pulmonary nodule composed of multiple small nodules and surrounded by many very smaller satellite nodules is called a galaxy sign [1] (Fig. 7.1).
Diseases Causing the Sign
The nodule(s) with CT galaxy sign is (are) observed in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis and active pulmonary tuberculosis [2] (Table 7.1) (Figs. 7.2 and 7.3).
Distribution
The CT galaxy sign in pulmonary sarcoidosis, as in the cases of other pulmonary sarcoidosis, is usually located in the upper and middle lung zones but can also be seen in the lower lung zones. In tuberculosis, the galaxy sign is noticed speciÞcally in the upper lobes or the superior segments of the lower lobes.
Clinical Considerations
Tuberculous galaxy sign indicates active disease, thus reversible to antituberculous chemotherapy [2]. Also the galaxy sign in sarcoidosis is reversible. According to a report of Heo and his colleagues, a single galaxy sign is far more frequent in patients with tuberculosis than in those with sarcoidosis [2].
a
b
Fig. 7.1 CT galaxy sign in a 23-year-old man with pulmonary sarcoidosis. (a, b) Consecutive thin-section (2.5-mm section thickness) CT scans obtained at levels of the right upper lobar bronchi show multifocal areas of CT galaxy sign (arrows) that are comprised of multiple small nodules and surrounded by many very small satellite nodules, particularly in the right upper lobe. Mediastinal window images (not shown here) demonstrated enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum and hilum, bilaterally
K.S. Lee et al., Radiology Illustrated: Chest Radiology, Radiology Illustrated, |
63 |
DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-37096-0_7, © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2014 |
|
64 |
7 Galaxy Sign |
|
|
Table 7.1 Common diseases manifesting as galaxy sign
Disease |
Key points for differential diagnosis |
Sarcoidosis |
Associated with lymphadenopathy |
Pulmonary |
Associated with tree-in-bud pattern, upper lung |
tuberculosis |
predominance |
a
c
b
d
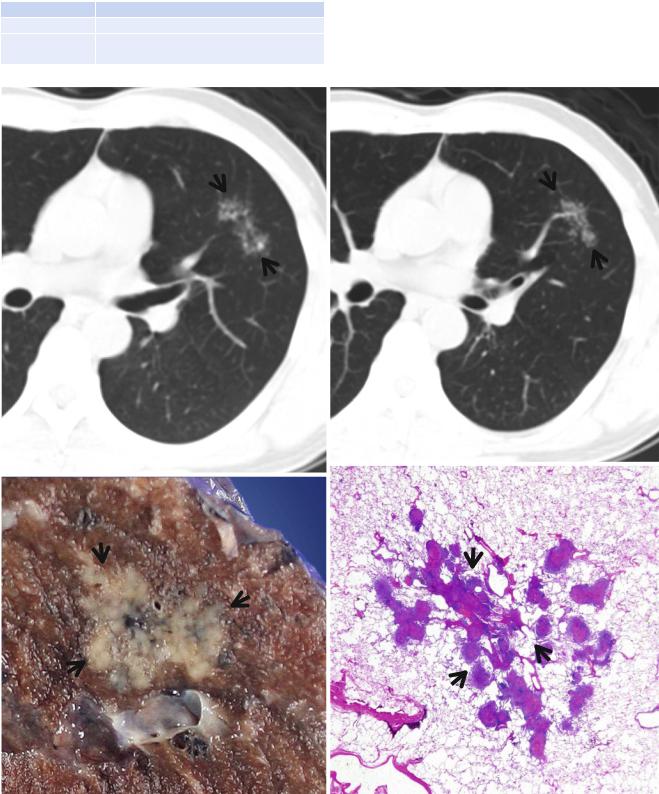
Br
Fig. 7.2 CT galaxy sign in a 44-year-old man with active pulmonary tuberculosis. (a, b) Consecutive (5.0-mm section thickness, low-dose technique) CT scans obtained at level of the right bronchus intermedius show CT galaxy sign (arrows) in superior lingular segment of the left upper lobe. On these relatively thick-section CT images, caution should be given not to interpret this galaxy sign as ground-glass opacity lesion, thus invasive lung adenocarcinoma. (c) Gross pathology specimen
obtained from the left upper lobe with surgical lung biopsy demonstrates nodular aggregation (arrows) of small granulomas. (d) LowmagniÞcation (×4) photomicrograph discloses nodular aggregation of granulomas having central necrosis in the peribronchiolar interstitium. Granulomas are concentrated toward the center of nodular cluster (arrows) than in its periphery. Br bronchiole
