
- •Главная
- •1.1 Напряжений и концентраторы
- •1.1.3 Концентраторы напряжения
- •1.3 Stress concentration factor
- •1.7 Elastic-plastic stress concentration
- •1.8 Joints: bolts and welds
- •3. Механические свойства конструкционных материалов
- •3.1 Напряженности испытания
- •3.2 Stress - strain diagram
- •3.3 Testing schemes
- •3.4 Strength
- •4 Прочность материалов
- •4.1 Tension and compression
- •4.2 Shear and torsion
- •4.3 Stress-strain state
- •4.4 Bending: force and moment diagrams
- •4.5 Geometrical characteristics of sections
- •4.6 Bending: stress and deformation
- •4.7 Mixed mode loading
- •4.8 Buckling
- •4.9 Statically indeterminate systems
- •4.10 Three-dimensional structures
- •References
- •5. Theory of elasticity
- •5.1 Deformation
- •5.2 Stress
- •5.3 Hooke's law
- •5.4 Plane problems
- •5.5 Torsion
- •5.6 Bending
- •5.7 Polar coordinates
- •5.8 Plates
- •5.9 Shells
- •5.10 Contact stresses
- •6.2 Distribution functions
- •6.3 Structural models of reliability
- •6.4 Limiting state
- •6.5 Dispersion
- •6.6 Durabilty
- •6.7 Design by reliability criterion
- •6.8 Risk
- •6.9 Safety classes
- •6.10 Risk : structural and social
- •References
- •7 Materials science
- •7.1 Crystalline solids
- •7.2 Mechanical properties
- •7.3 Failure
- •7.4 Phase diagrams
- •7.5 Heat treatment of metals and alloys
- •7.6 Corrosion of metals and alloys
- •7.7 Casting
- •7.8 Polymers
- •7.9 Composites
- •7.10 Forming of metals
- •8.2 Mechanical properties
- •8.3 Stress concentration
- •8.4 Defects
- •8.5 Residual Stress
- •8.6 Strength
- •8.7 Fatigue strength
- •8.8 Fracture
- •8.9 Weldability
- •References
- •9 Composites
- •9.1 Structure of composites
- •9.2 Fibers
- •9.3 Rigidity
- •9.4 Strength
- •9.5 Crack resistance
- •9.6 Optimization
- •9.7 Fatigue and temperature effect
- •9.8 Reliability
- •9.9 Joints
- •9.10 Material selection
- •References
- •10 Finite element analysis
- •10.1 Finite element method
- •10.2 Finite elements
- •10.3 Meshing
- •10.4 Boundary conditions
- •10.5 Deformation
- •10.6 Accuracy
- •10.7 Heat transfer analysis
- •10.8 Dynamics
- •10.9 Computational fluid dynamics
- •10.10 Design analysis
- •References
9.9 Joints
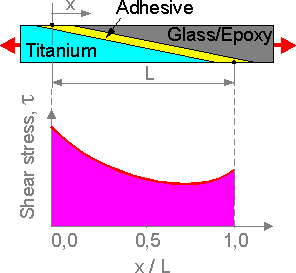
 There
is high stress concentration in the lap joint. It can be decreased if
the Young's modulus of the adhesive decreases at the edges.
There
is high stress concentration in the lap joint. It can be decreased if
the Young's modulus of the adhesive decreases at the edges.
 Stress
concentration is smaller for a В«smoothВ»
transition from one structural element (adherent) to
another.
Stress
concentration is smaller for a В«smoothВ»
transition from one structural element (adherent) to
another.
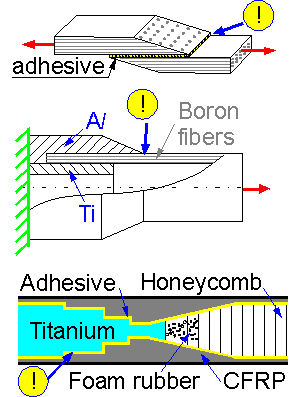
 Stress
concentration is higher at a more rigid material. Proper laminar
orientation can decrease the stress concentration.
Stress
concentration is higher at a more rigid material. Proper laminar
orientation can decrease the stress concentration.
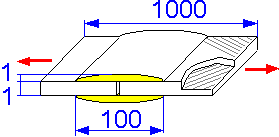 The
joint's bond surface must be sufficiently larger than it's
cross-sectional area. The joint can be reinforced by fabric
fibers.
The
joint's bond surface must be sufficiently larger than it's
cross-sectional area. The joint can be reinforced by fabric
fibers.
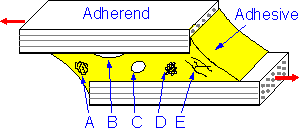 Manufacturing
defects in the adhesive can decrease strength of joints and can be
detected by nondestructive testing. The following are examples of
some defects:
A. Matrix cure is caused by incorrect
mixing or thermal exposure.
B. Disbond or zero-volume unbond is
caused by incorrect surface preparation.
C. Voids can be caused
by air entrapment.
D. Porosity is associated with volatiles and
entrained gases.
E. Adhesive cracks can be caused by thermal
shrinkage during manufacturing.
Manufacturing
defects in the adhesive can decrease strength of joints and can be
detected by nondestructive testing. The following are examples of
some defects:
A. Matrix cure is caused by incorrect
mixing or thermal exposure.
B. Disbond or zero-volume unbond is
caused by incorrect surface preparation.
C. Voids can be caused
by air entrapment.
D. Porosity is associated with volatiles and
entrained gases.
E. Adhesive cracks can be caused by thermal
shrinkage during manufacturing.
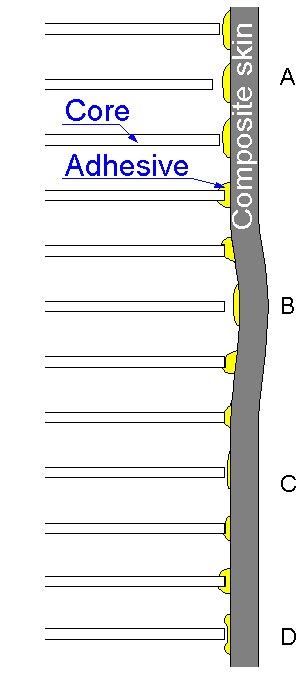 Composite
honeycomb structures have high flexural stiffness and strength.
Defects decrease flexural and compressive strength of honeycomb
structures:
A. Core damage.
B. Skin imperfection.
C.
Lack of adhesive.
D. Improperly formed adhesive
fillet.
Composite
honeycomb structures have high flexural stiffness and strength.
Defects decrease flexural and compressive strength of honeycomb
structures:
A. Core damage.
B. Skin imperfection.
C.
Lack of adhesive.
D. Improperly formed adhesive
fillet.
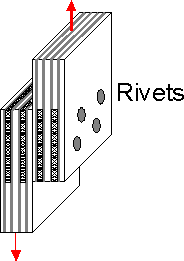 Rivets
are widely used in composite skin connection. Strength of rivet
joints can be increased by increasing the number of smaller rivets
and/or by metal foil reinforcement.
Rivets
are widely used in composite skin connection. Strength of rivet
joints can be increased by increasing the number of smaller rivets
and/or by metal foil reinforcement.
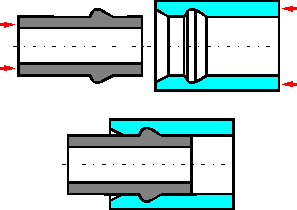 Connection
of the composite tubes can be made by elastic deformation in the
composites. Filament winding increases the carrying ability of the
joint.
Connection
of the composite tubes can be made by elastic deformation in the
composites. Filament winding increases the carrying ability of the
joint.
9.10 Material selection
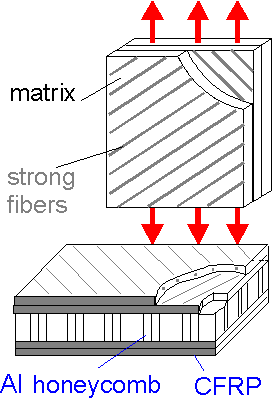 Advanced
composite materials have unique mechanical properties in comparison
with steel or aluminum alloys: fatigue strength, specific strength
(ratio of strength to weight), specific rigidity (ratio of modulus of
elasticity to weight), strength redundancy and high resistance of
damaged structures to external loads. Contrary to metals, crack
resistance of modern composite materials increase as strength
increases. Crack resistance of composite materials depends on fiber
tensile strength, its scatter, matrix tensile strength, and bond
shear strength. Splitting of the bond between matrix and fiber helps
material to stop macrocracks.
Advanced
composite materials have unique mechanical properties in comparison
with steel or aluminum alloys: fatigue strength, specific strength
(ratio of strength to weight), specific rigidity (ratio of modulus of
elasticity to weight), strength redundancy and high resistance of
damaged structures to external loads. Contrary to metals, crack
resistance of modern composite materials increase as strength
increases. Crack resistance of composite materials depends on fiber
tensile strength, its scatter, matrix tensile strength, and bond
shear strength. Splitting of the bond between matrix and fiber helps
material to stop macrocracks.
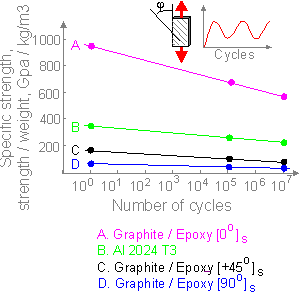 Unique
properties of a composite can be obtained by proper choice of
filament, fiber content, layer orientation, etc.
Unique
properties of a composite can be obtained by proper choice of
filament, fiber content, layer orientation, etc.
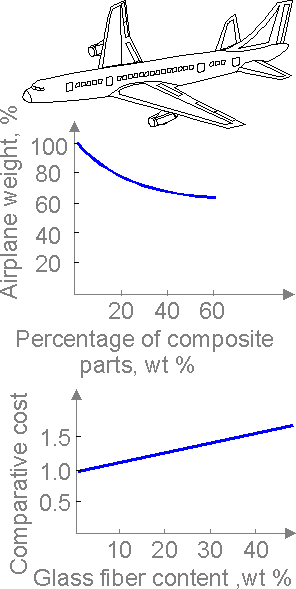 The
use of composite materials decreases the weight of a passenger
airplane by 20 - 40%.
Use of composite materials
decreases cost of many engineering structures. Fiber content increase
does not excessively raise the cost of the composite.
The
use of composite materials decreases the weight of a passenger
airplane by 20 - 40%.
Use of composite materials
decreases cost of many engineering structures. Fiber content increase
does not excessively raise the cost of the composite.
 One
of the most important stages of composite structure manufacturing is
nondestructive testing:
A. Ultrasonic testing can reveal
porosity, voids, incorrect volume fraction, foreign inclusions,
translaminar cracks, delaminations, disbonds in adhesive, poor fillet
in honeycomb construction.
B. Eddy currents technique is
limited to materials with a conducting phase.
C. Thermography
can be used as rapid technique for inspecting large-scale composite
structures.
D. Holography is very expensive technique with
restricted list of discovered defects, such as disbonding and
delamination.
E. Radiography is used in testing of boron or
glass reinforced composites, not carbon fiber reinforced composites.
Ultrasonic testing is the most widely used technique for
many composite materials.
Group fiber breakage is the
most dangerous defect in a composite. It can be revealed by one of
the nondestructive methods from the above list.
One
of the most important stages of composite structure manufacturing is
nondestructive testing:
A. Ultrasonic testing can reveal
porosity, voids, incorrect volume fraction, foreign inclusions,
translaminar cracks, delaminations, disbonds in adhesive, poor fillet
in honeycomb construction.
B. Eddy currents technique is
limited to materials with a conducting phase.
C. Thermography
can be used as rapid technique for inspecting large-scale composite
structures.
D. Holography is very expensive technique with
restricted list of discovered defects, such as disbonding and
delamination.
E. Radiography is used in testing of boron or
glass reinforced composites, not carbon fiber reinforced composites.
Ultrasonic testing is the most widely used technique for
many composite materials.
Group fiber breakage is the
most dangerous defect in a composite. It can be revealed by one of
the nondestructive methods from the above list.
