
- •Unit 1 commercial paper.
- •Types, parties and basic concepts
- •Study these vocabulary notes
- •Purposes of Commercial Paper
- •Assignment
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text:
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •III. Answer the following questions.
- •Text b Kinds of Commercial Paper
- •Promissory Note. A promissory note is an instrument by which the maker promises to pay a sum of money to another party (the payee).
- •Promises to Pay and Orders to Pay
- •Demand and Time Instruments
- •Assignment
- •Unit 2 parties to commercial paper
- •Text a Parties to Commercial Paper
- •The acceptor
- •Indorsers
- •Holders
- •Assignment
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text.
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions
- •Text b Types of Indorsements
- •Assignment
- •Give the definition of:
- •II. Speak on:
- •Unit 3 commercial documents Study these vocabulary notes
- •Commercial Documents
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text.
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •III. Answer the following questions.
- •IV. Speak on:
- •Unit 4 insurance documents Study these vocabulary notes
- •Insurance Documents
- •Assignment
- •I. Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text.
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •Unit 5 bill of lading Study these vocabulary notes
- •Text a Bill of Lading
- •Liner Bill of Lading
- •Assignment
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text.
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •Text b Sea Waybill, Air Way Bill Study these vocabulary notes
- •Air waybill (also called an air consignment note or air freight note)
- •Assignment
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Speak on:
- •Unit 6 financial documents Study these vocabulary notes
- •Financial Documents
- •Sometimes, the exporter might draw two bills of exchange on the foreign
- •The advantages of using bills of exchange in international trade
- •Promissory Note
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text.
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •The advantages of using bills of exchange in international trade.
- •Unit 7 shipping terms and incoterms
- •Study these vocabulary notes
- •Shipping Terms and Incoterms
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text:
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •Unit 8 collections Study these vocabulary notes
- •Procedures and Definitions
- •Clean collections and documentary collections
- •The Parties to a Collection
- •Clean collection
- •Documentary collections: d/p and d/a
- •Documentary collection
- •Assignment
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text:
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •30 Days’ sight d/p; 60 days’ sight d/a. Unit 9 documentary credit Study these vocabulary notes
- •Documentary Credit
- •Documentary credits as a method of payment
- •Assignment
- •Suggest the Ukrainian for the following words and word combinations from the text:
- •Find in the text English equivalents for the following words:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Speak on:
- •Part II sipplementary reading Text 1 Collections: Advantages and Disadvantages
- •Text 2 Standby Credits
- •Text 3 Revolving Credits
- •Text 4 Documentary Credits as a Means of Finance
- •Text 5 Export Credit Insurance
- •Text 6 The short-term Guarantee
- •Text 7 Insurance for Overseas Investments
- •Text 8 Eurocommercial paper
- •Part III documents
- •North bank plc
- •International Division
- •North bank plc
- •International Division
- •Heritage teas premium services
- •Heritage teas premium services
- •Diagram 1
- •Diagram 2
- •Clean or documentary foreign bills for acceptance or collection or negotiation
- •P X lease follow instructions which I/we have marked below
- •Glossary
- •Список рекомендованої літератури
- •Contents
The Parties to a Collection
The parties to a collection are as follows.
The principal. This is a customer who entrusts the operation of collection to his bank. For our purposes, this might be
(a) an exporter in the UK entrusting the collection to his UK bank; or
(b) a foreign supplier of goods to a UK company entrusting the collection to a bank in his own country.
The remitting bank. This is a bank to which the principal has entrusted the operation of collection. For example, if a UK exporter entrusts a collection to his UK bank, this bank will be the remitting bank in the collection.
The collecting bank. This is any other bank, apart the remitting bank, involved in processing the collection orders. In our example of the UK exporter, this will be an overseas bank to which the UK remitting bank sends a collection order.
The presenting bank. This is a collecting bank which makes the presentation to the drawee. (The drawee is defined as “the one to whom presentation is to be made according to the collection order.)
-
Exporter

-
Remitting bank
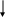

-
Collecting bank
May be the same bank
-
Presenting/collecting bank
-
Buyer
For a clean collection, the commercial documents are sent direct by the exporter to the overseas buyer. The remitting bank which, in turn, will use the services of the collecting/presenting bank) will be asked to arrange for:
(a) payment of a bill of exchange on sight, or payment of a promissory note or cheque; or
(b) acceptance of a term bill of exchange. The bank will then be instructed to arrange for the payment to be obtained when the bill matures.
Clean collection

The only advantage of a clean collection involving a bill of exchange rather than a cheque is that the presentation of the bill to the buyer by a bank might prompt the buyer into paying. The exporter might have difficulty in prompting the buyer to pay if he relies on the buyer to initiate payment by sending a cheque or promissory note. At least with the bill of exchange, the bill is drawn by the exporter who therefore initiates payment himself and enlists the aid of his bank in obtaining acceptance/payment.
Documentary collections: d/p and d/a
For a documentary collection, the bank may be instructed to release the commercial documents to the buyer only against payment for the goods. This form of collection is referred to as D/P or documents against payment.
When a bill of exchange is the financial document, it will be either (a) a sight bill or (b) a term bill (usance bill) which has previously been accepted and has now reached its maturity date for payment. (In trade with buyers in the Far East, in particular, documents of title may not be handed over until payment of a term bill.)
Alternatively with a documentary collection, the bank may be instructed to release the commercial documents to the buyer only against immediate acceptance by the buyer of a bill of exchange, drawn on him by the exporter. This form of payment is referred to as D/A or documents against acceptance. The bill of exchange will be a term bill (also known as a tenor bill or usance bill).
A bill of exchange which is accompanied by commercial documents of title to the goods is known as a documentary bill.
