
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Unit 5- igneous rocks 96
- •Part 2 - continental crust 172
- •Unit 1 geology
- •1. Comprehension
- •Fig. 1. James Hutton (1726-1797)
- •2. Reading comprehension Read the text «What is Geology?»
- •2. 1 Vocabulary
- •Text: What is Geology?
- •2.2 Exercises
- •2.2.2 Translate into Russian:
- •2.2.3 Complete the sentences:
- •2.2.6 Match the word phrases in right column with the word phrases in the left one and compile your own sentences.
- •2.2.7 Give the English equivalents to the Russian words:
- •2.2.8 Read the text and find the English equivalents to the following terms and phrases.
- •2.2.9 Match the science with the description of what it studies:
- •2.2.10 Choose the correct variant.
- •3. Discussion
- •4. Wordlist
- •4.1 Pronunciation
- •4.2 Terms
- •Unit 2 fossils
- •1. Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •3. Pay attention to the underlined terms and expressions in the text:
- •Channel канал
- •2. Exercises
- •2.1 Mark the stressed syllable on the following words from the text:
- •2.3. Give the Russian equivalents to the following word combinations and phrases:
- •2.4 Read the text below and think of the word that best fits each space. Use only one word in each space. There is an example at the beginning.
- •2.5 Form nouns from the following verbs and find the sentences in the text with these new words.
- •2.6 Put a preposition in each of the numbered spaces:
- •2.7 What are the corresponding words?
- •2.8 Choose between the alternatives to complete these sentences:
- •(1) Petrify (2) organ (3) decompose (4) effect (5) cover (6) compact (7) lithify (8) reduce (9) react (10) fossil
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •3.1. Detailed reading: Relative Dating: Using Rocks
- •3.2.1 How to Treat a Fossil in Geological Fieldwork
- •4.1 Read the following text and pay special attention to the pronunciation of the geological periods. The Geological Column
- •Geologic Time Scale
- •History of the time scale
- •Terminology
- •Table 1. Geologic Time Scale
- •4.2 Read the texts “Geological Time Scale» in self-study booklet, pg. 58) Choose one period and using the following plan, make a short report.
- •5. Listening comprehension
- •5.1. You will hear a radio report about fossils. Answer statements 1-10 by writing t (for True) and f (for False):
- •5.2. Listen to the report once more. Then, for statements 11-20, complete the notes that summarize what the speaker says. You will need to write a word or a short phrase in each box.
- •6. Discussion (r.P – 2.1)
- •Communicative formulas
- •7. Wordlist
- •7.1. Pronunciation
- •7.2 Terms
- •7.3 Words and phrases
- •Unit 3 sizing up the earth
- •1. Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •1.2 Read the text «Our layered planet» and pay attention to the terms in bold (r.P – 3.4, 3.5) our layered planet
- •Fig. 7. Differentiation of early Earth
- •2.4 State whether the following statements are true or false.
- •3.1.2 Read the text once more and fill in the chart with the necessary information. Then label the diagram and give an explanation what each item means.
- •3.2 Detailed reading - Earth’s size and shape
- •Isostasy
- •Fig. 10. Relative abundance of elements in whole Earth
- •Fig. 11. Relative abundance of elements in Earth’s crust
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •4.3. You will hear a lecture on the Earth’s origin. For statements 16-20, choose the best answer a, b, c, d.
- •5. Discussion: (r.P – 3.1, 3.3)
- •1. Situational game-
- •2. The earth
- •6. Wordlist
- •6.1 Pronunciation
- •6.2 Terms
- •Unit 4 rocks and minerals
- •1. Comprehension
- •Definitions
- •Fig. 12. Rock cycle
- •1.3 Read the following text and fulfill the after task exercises the rock cycle
- •Vocabulary
- •2. Exercises
- •2.3 Spelling dictation
- •2.4 Read the following definition and fill in the gaps with the missing words and then give a short outline of this definition. (r.P – 8.2.12)
- •Fig. 13. Rock cycle
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •3.1 Scanning: Earth’s building blocks (r.P – 4.2)
- •3.1.1 Pay attention to the pronunciation of the following minerals:
- •3.1.2 Find the information you need to complete the following diagram from the text below.
- •Table 2. Chemical Grouping and Composition of Some Common Minerals
- •3.1.3 Complete the following chart. Give examples of each type of rock forming mineral.
- •3.2 Informative reading- Minerals and their physical properties.
- •Part 1 Minerals
- •3.2.2 Read the text and fulfill the after-reading exercises. (r.P – 4.3, 4.6) Physical Properties
- •Table 3 Mohs Hardness Scale
- •Fig. 18. Pyrite cube showing metallic luster (Photo by John Bett) Fig. 19. Vitreous luster on quartz crystal faces (Photo by John Bett)
- •3.2.2.3 Give examples of the following physical properties of minerals
- •Fig. 24. Conglomerate – sedimentary rock
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •5. Discussion
- •5.1 Complete the mind map. Discuss the following questions:
- •5.2 Exploratory speaking (short talk)
- •Use the mind-maps and the table below. Don’t forget communicative formulas. Communicative formulas
- •Table 4. Rocks and minerals
- •6. Wordlist
- •6.1 Pronunciation
- •6.2 Terms
- •6.3 Words and phrases
- •Igneous rocks
- •1. Comprehension Read the following text «Anatomy of a volcano»
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •1.2 Anatomy of a volcano Pay attention to the following terms in bold. (r.P. – 5.3)
- •2. Exercises
- •2.1 Read the text (once) more carefully and choose the correct alternative for these words:
- •Round-formed opening
- •2.2 Use two words from the corresponding line to complete each sentence.
- •2.3. Give the Russian equivalent the following phrases:
- •2.4 Match the words in the right column with the words in the left one.
- •2.5 Use the terms and fill in the gaps
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •3.1 Scanning - Igneous rocks (r.P. -5.5)
- •Fig. 26. Classification of igneous rocks
- •3.1.1. Correct the following statements where necessary (Igneous rocks)
- •3.1.2. You have one minute to read this part of the text -Classification and chemical differentiation of igneous rocks
- •3.2 Informative reading – Igneous Rocks (r.P.-5.4)
- •Fig. 27. Various modes of occurrence of igneous rocks
- •3.2.2 Can these terms and phrases be understood without translating? Why?
- •3.2.3 State, which sentences, is t (true) or f (false) according to the text.
- •3.2.6 Complete the following sentences, using words and phrases from the text.
- •3.2.7 Answer the following questions and give more / extra information.
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •4.1 You will hear a radio report about volcanic rocks. Answer statements 1-10 by writing t (for True) and f (for False):
- •4.3 Listen to the lecture in geology at the Aberdeen University. The topic of the lecture is intrusive igneous rocks. Complete the following chart with the missing information.
- •Igneous Rocks- Intrusive
- •4.4. Listen to the lecture once more. Look at the diagram and describe the features produced by intrusive rocks, using the given definitions:
- •5. Discussion
- •Fig. 28. Shapes of volcanoes
- •6. Wordlist
- •6.1 Pronunciation
- •6.2 Terms
- •Unit 6 sedimentary rocks
- •Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •1.2 Read the text and fulfill the after reading exercises (r.P – 6.1)
- •Fig. 29. Breccia
- •Exercises
- •2. 2 Read the following phrases, write down the word. Read the word and find sentences with this word.
- •2.3 Match the verb with the noun. (Add the preposition where necessary)
- •2.4 Complete the following sentences, by unscrambling the bolded words. Spell the word. Give its definition.
- •2.5 There is a spelling mistake in each line. Write the correct word in the space provided. Prepare for a spelling dictation.
- •2.6 Fill in the space with the appropriate word or phrase.
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •3.1 Scanning
- •3.1.1 Rocks from living things
- •3.1.2 Rocks from chemicals
- •1. Match the words with the Russian equivalent.
- •2. Translate the following word combinations and phrases.
- •3. Compose questions to the text, using the following Wh-words: what, which, where, when, how
- •3.2 Informative reading- Rocks from fragments
- •3.2.1 Read the text (Part 1, Part 2) and for statements 1-12, choose the best answer: a, b, c or d. Then explain the words in bold. Part 1
- •Fig.33. Ferruginous sandstone Part 2
- •B. No bigger than sand grain
- •A. Medium-grained
- •B. Greywacke
- •3.2.2 Read the text once more and fill in the charts with the necessary information from part 1 and part 2. Sedimentary rocks
- •Types of sedimentary rocks
- •3.2.3 Give detailed information to the following questions.
- •3.2.4 Use the following, so as to write a description of sedimentary rocks. Label each description (conglomerate / breccia / rudite)
- •3.3 Detailed reading
- •Text 1 - Sedimentary Rocks
- •Table 5. Classification of Common Sedimentary Rocks
- •3.3.2. Match the English terms with the Russian ones in the right column
- •3.3.3. Match the words from column a with the words in column b.
- •3.3.4. Fill in the blanks with the correct word.
- •3.3. 5. Compile sentences using the following phrases.
- •3.3.6. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- •3.3.7. Answer the following questions.
- •Fig. 36. Sedimentary stages in the rock cycle
- •Fig. 37. Continental, shoreline and marine sedimentary environments
- •Read the following text and fill in the missing words.
- •3.3.9. Complete the following sentences.
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •4.2 You will hear a lecture. You will hear it twice. For questions 6-10 choose the best answer a, b or c.
- •B. Destruction of sedimentary rocks
- •5.2 You have to give a lecture on sedimentary rocks. Use the following diagram.
- •5.3 Group discussion
- •6. Wordlist
- •6.1 Pronunciation
- •6.2 Terms
- •Unit 7 metamorphic rocks
- •1. Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •3. Read the following word formations and remember their pronunciation:
- •1.2 Read the text and fulfill the after reading exercises. (r.P – 7.2, 7.3) metamorphic rocks
- •Fig. 38. Gneiss Fig. 39. Marble
- •Fig. 40. Grade and facies describe metamorphism
- •Table 6. Classification of Common Metamorphic Rocks
- •2. Exercises
- •2.1 Define the following terms with their similar meaning in Russian
- •2.2 Match the English equivalents to the Russian terms.
- •2.4 Fill in the gaps using the word formations.
- •2.7 State whether the following statements are true or false.
- •3. Readng comprehension
- •3.1 Detailed reading: Occurrence and classification of metamorphic rocks
- •3.1.1. State whether the following sentences are t (true) or f (false), according to the information from the text
- •3.2 Informative reading: Metamorphic rocks
- •Fig. 41. Metamorphic facies
- •4. Revision
- •4.1 Choose the correct variant
- •5. Listening comprehension
- •5.1 You will hear part of a lecture. For statements 1- 10, complete the notes, which summarize what the speaker says. You will need to write a word or short phrase in each box.
- •5.2 You will hear a conversation between a student and a teacher in Geology at Aberdeen University. For statements 1-10, choose the best answer a, b, or c.
- •6. Discussion: task 1
- •Communicative formulas
- •7. Wordlist
- •7.2 Terms
- •7.3 Words and phrases
- •Unit 8 the restless crust part 1: oceanic crust
- •1. Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •1.2 Read the text «The Ocean Floor». Pay attention to the diagram. Fulfill the exercises after the text. (r.P – 8.1.1)
- •Fig. 42. Ocean floor
- •2. Exercises
- •2.1 Look at the geographical map and point out the oceans. Name them.
- •2.2 Look at the diagram below and answer the following questions (r.P.- 8.2.1)
- •Fig. 43. Ocean areas and depths
- •2.3 Match the English term with the Russian one.
- •2.6 Look at the (r.P – 8.1.1) cross section of an imaginary ocean. The vertical scale is exaggerated for effect. Name the 10 major features of an ocean floor. Point them out.
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •3.1 After-reading tasks.
- •3.1.1. Look through the text and pick out the terms, which have the following definition.
- •3.1.3. Spreading ridge evolves several stages. Put the words according to the stages. Compose sentences to describe the process. (r.P – 8.1.2, 8.1.3)
- •3.1.4. Put the facts in the correct order which shows how sea floor spreading develops.
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •6. Discussion (r.P – 8.1.5)
- •Earth’s changing surface
- •Fig. 45. Three types of plate boundaries
- •1. Comprehension
- •1.1 Vocabulary
- •1.2 Mountain building (r.P – 8.2.7, 8.2.8, 8.2.9)
- •Fig. 46. Mountain building
- •Fig. 47. Ocean-ocean subduction zone
- •Fig. 48. Ocean-continent boundary
- •Fig. 49. Continent-continent collision
- •2.3 Complete the following short description of mountain building. Scan the text once more.
- •3. Reading comprehension
- •Informative reading: How continents evolve
- •4. Listening comprehension
- •5. Discussion
- •3.1 Comprehension: faults
- •3.1.2 Fault terminology (r.P – 8.3.1.3, 8.3.1.2)
- •Fig. 50. Fault anatomy
- •Fig. 51. Three types of fault motion
- •3.1.3 Exercises
- •1. Match the English term with the Russian variant. (text: Fault terminology)
- •3. Match the term with its definition and then find its translation.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with the missing words.
- •5 Read the following fault types. The look at the diagrams and then try to draw them by heart. And draw a diagram. (r.P – 8.3.1.3, 8.3.1.4)
- •Fig. 52. Fault types
- •6. Here are six definitions. Read the definition, then name the term and give its translation (r.P – 8.3.1.3, 8.3.1.4)
- •3.1.4 Listening comprehension
- •3.2 Comprehension: folds
- •3.2.1 Vocabulary
- •Word formation
- •Fold terminology (r.P. - 8.3.2.1, 8.3.2.3)
- •Fig. 54. Folding structure
- •4. Discussion
- •5. Wordlist
- •5.1 Pronunciation
- •5.2 Terms
- •Appendix test 1 (unit 1- Geology)
- •B. Isaac Newton d. James Hutton
- •Test 2 (unit 2-Fossils)
- •B. Found in
- •Permeation
- •A. How old the rocks are
- •A. Crust rock
- •Test 3 (unit 3-Earth)
- •Test 4 (unit 4 - Rocks and Minerals)
- •Test 5 (unit 5-Igneous Rocks)
- •B. Central
- •A. Circular
- •A. Mafic lava
- •C. Felsic lava
- •Test 6 (unit 6- Sedimentary Rocks)
- •Test 7 (unit 7- Metamorphic Rocks)
- •C. Burial metamorphism
- •Test 8-1 (unit 8- Restless Crust)
- •Test 8-2 (unit 8- Restless Crust)
- •A. Faults
- •References
Isostasy
3.3 SCANNING- Earth’s building blocks
You are looking for specific information. Don’t read every word. Run your eye down the text and stop when you find the relevant (важный; существенный) words. You have 3-4 minutes.
1. building blocks-
2. abundance of elements-
3. elements-
4. silicate-
5. crystal-
6. mineral identification-
Earth’s building blocks are elements and minerals of our planet. Of 92 naturally occurring elements, eight account for 98% of the weight of the Earth’s crust – the rocky layer that scientists know best. Nearly 3/4 of its weight lies in two non-metals – oxygen and silicon; most of the rest consists of the six metals-aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium and magnesium.
Within the crust most elements occur as minerals- natural substances that differ chemically and have distinct atomic structures. The Earth’s crust holds about 2000 kinds of minerals. A few (including gold) occur as just one element; most comprise two or more elements chemically joined as compounds.
Silicates (minerals containing silicon and oxygen) are the most abundant minerals in crust and mantle, which make up 4/5 of our planet’s volume.
Most minerals formed from fluids that solidified – a process that arranged their atoms geometrically producing crystals. Scientists identify six crystal systems based on axes-imaginary lines passing through the middle of a crystal. Each system yields crystals with distinctive symmetry. Within each system, each mineral crystal grows in a special shape or habit, though this can be modified by temperature, pressure and impurities.
Traditional tests identify by hardness, color, streak (color of the powered mineral), luster, specific gravity, cleavage, fracture, form, tenacity (resistance to bending, breaking and other forces), odor, taste and feel.
(Lambert “The Field Guide to Geology” 1988, Cambridge University Press)
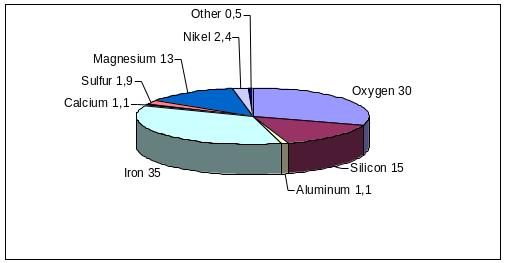
Fig. 10. Relative abundance of elements in whole Earth
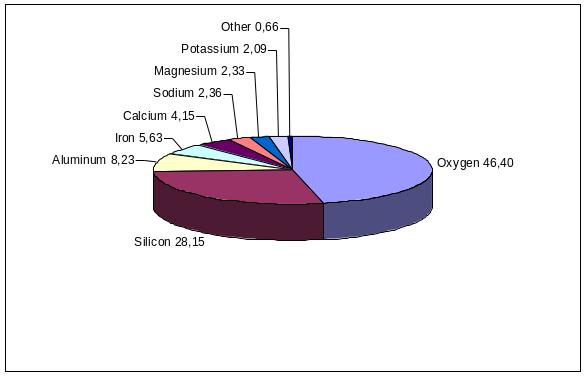
Fig. 11. Relative abundance of elements in Earth’s crust
4. Listening comprehension
4.1 You will hear a lecture. After the lecture you will hear some statements. The lecture and questions will be spoken just one time. When you hear a statement, read the three possible answers, and decide which one would be the best answer to the statement you have heard.
1. The crystal rind is covered by
A. condensed atmosphere components
B. volatile atmosphere components
C. ocean volatile components
2. The mantle lies under
A. oxide rich shells
B. rocky exterior
C. concentric shells
3. They are
A. constructing blocks
B. constructing rocks
C. constructing layers
4. The main factor is
A. sunlight only
B. the Earth itself
C. physicochemical evolution
5. The following systems
A. protection
B. interconnected
C. biological
4.2 You will hear part of a radio report about the earth as a planet of our solar system. For statements 6- 15, complete the notes that summarize what the speaker says. You will need to write a word or a short phrase in each box.
Earth is a |
|
6 |
The Earth is the third planet to |
|
7 |
The planets don’t fly into space because of |
|
8 |
Life on Earth is due to |
|
9 |
Each rotation produces |
|
10 |
The Moon completes |
|
11 |
while Earth completes |
|
12 |
This is an Earth’s |
|
13 |
The Earth is separated from the other bodies by |
|
14 |
So, the solar system comprises |
|
15 |
