
- •Textbook Series
- •Contents
- •1 Air Information Publications
- •Introduction
- •Format of an AIP
- •Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS)
- •Aerodrome Communication Facilities
- •Aerodrome Radio Navigation and Landing Aids
- •Other Sources
- •Search and Rescue
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •2 Fuel Policy and Fuel Monitoring
- •Universal Application of Fuel Policy
- •Realistic Trip Fuel
- •Reserve Fuel
- •Calculation of Contingency Fuel
- •Fuel Monitoring
- •Special Cases 1 – Decision Point Procedure
- •Special Cases 2 – Isolated Aerodrome Procedure
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •3 Nautical Air Miles
- •Nautical Air Miles
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •4 Single-engine Piston Aeroplane (SEP)
- •Introduction
- •Single-engine Piston Aeroplane
- •Cruise Power Settings Tables
- •Range Profile Figure
- •Endurance
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •5 Multi-engine Piston Aeroplane (MEP)
- •Introduction
- •MEP 1-Fuel, Time and Distance to Climb Data
- •MEP 1-Range at Standard Temperatures
- •MEP 1-Cruise Power Setting and Fuel Flow
- •MEP 1-True Airspeed
- •MEP 1-Endurance
- •MEP 1-Descent Fuel, Time and Distance
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Introduction
- •Aeroplane Data and Constants
- •Optimum Cruise Altitude
- •Short Distance Cruise Altitude
- •Answers to Simplified Flight Planning
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •En Route Climb
- •Cruise/Integrated Range Tables
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Descent Table
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Answers to Integrated Flight Planning
- •8 MRJT Additional Procedures
- •ETOPS – CAP 697 MRJT1
- •Non-normal Operations
- •Fuel Tankering
- •Answers
- •9 Topographical Chart
- •Introduction
- •World Geodetic System of 1984 (WGS84)
- •Aeronautical Information
- •Topographical Information
- •Miscellaneous
- •Establishment of Minimum Flight Altitudes
- •The Minimum Grid Area Altitudes (Grid MORA)
- •Choosing Cruising Levels
- •Altimeter Errors and Corrections
- •Exercise 1
- •VFR Exercise 2
- •Answers
- •Exercise 1 Answers
- •VFR Exercise 2 Answers
- •10 Airways
- •Introduction
- •Air Traffic Services (ATS) Routes/Standard Routes
- •Area, Low and High Level Charts
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Answers to Examples/Exercises
- •Answers Exercise 1
- •Answer Airways Exercise 2
- •Projection
- •Track Direction/Magnetic Variation/Distance
- •Grid Navigation
- •Exercise 1
- •Answers to Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Answers
- •AT(H/L) 1 & 2 Information
- •Exercise 3
- •12 ATC Flight Plan
- •Introduction
- •Definitions
- •Annexes to This Chapter
- •Specimen CA48
- •Item 19: Supplementary Information
- •Item 15
- •Use of DCT (Direct)
- •Exercise 1
- •Exercise 2
- •Exercise 3
- •Exercise 4
- •Answers
- •Annex 2
- •13 Point of Equal Time (PET)
- •Introduction
- •Derivation of Formula
- •The Effect of Wind on the Position of the PET:
- •Single Sector All-engine PET
- •Engine Failure PET
- •14 Point of Safe Return (PSR)
- •Introduction
- •Derivation of the Formula
- •Transposing the Formula to the Navigation Computer
- •The Effect of Wind on the Location of the PSR
- •Single Leg PSR
- •Derivation of the Formula for Variable Fuel Flows
- •15 Revision Questions
- •Revision Questions
- •Answers to Revision Questions
- •Specimen Examination Paper
- •Answers to Specimen Examination Paper
- •Explanations to Specimen Examination Paper
- •16 Index

Chapter
3
Nautical Air Miles
Nautical Air Miles . . . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
43 |
Questions . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
46 |
Answers . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . |
|
.48 |
41

3 |
|
Nautical Air Miles |
|
||
|
|
|
Miles Air Nautical 3
42
Nautical Air Miles |
|
3 |
|
||
|
|
|
Nautical Air Miles
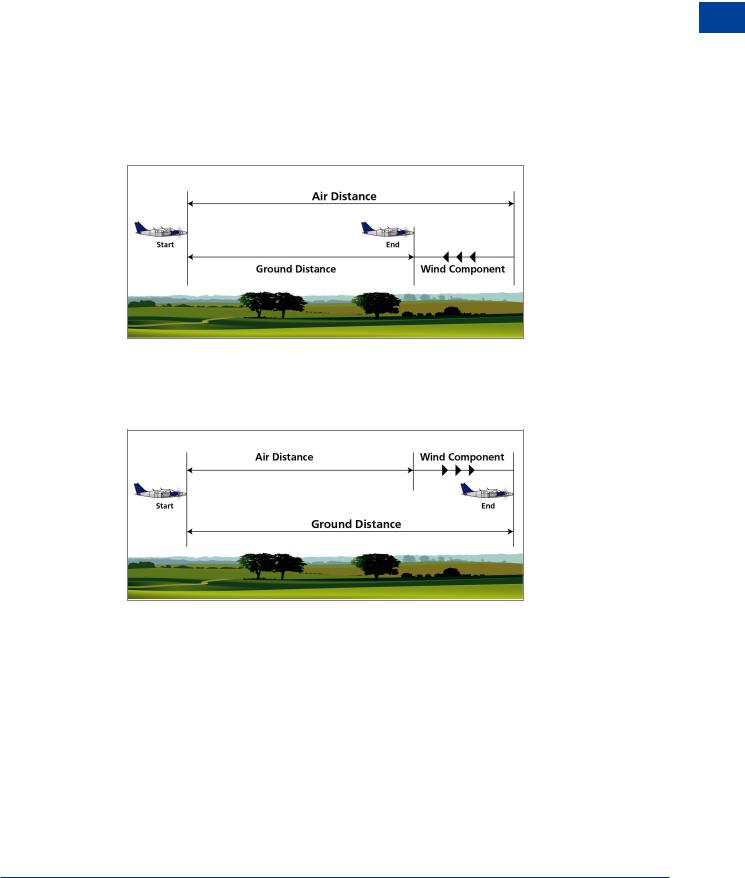
Many of the graphs for the Single-engine Piston (SEP), Multi-engine Piston (MEP) and, later, the Medium Range Jet Transport (MRJT) aircraft, refer to nautical air miles (NAM). They are a measure of the air distance flown by an aircraft, i.e. the distance flown at the True Airspeed (TAS). In still air (or when there is no wind component along the aircraft’s heading vector) the NAM flown are equal to the Nautical Ground Distance (NGM) flown. NGM is the distance flown by the aircraft over the ground, as may be measured on a chart.
Usually the air is moving and an aircraft flying through this moving air will fly a different distance over the ground. If the air is moving in the opposite direction to the aircraft (a headwind, or minus wind component) then the aircraft will fly more NAM than NGM. (See Figure 3.1.)
Figure 3.1 NAM greater than NGM
Similarly, if the wind is blowing in the direction that the aircraft is flying, (a tailwind or plus wind component ) the NAM will be less than NGM. (See Figure 3.2.)
Figure 3.2 NAM less than NGM
The relationship between NAM, NGM, TAS, GS (ground speed ) and wind component (WC) is:
NAM = TAS
NGM GS
Nautical Air Miles 3
43
3 |
|
Nautical Air Miles |
|
||
|
|
|
Miles Air Nautical 3
Example
An aircraft flies at TAS 142 kt for 63 NAM. If the WC is -20 kt, how many NGM does it fly?
NAM |
= |
TAS |
||
NGM |
GS |
|||
|
||||
63 |
|
= |
142 |
|
x |
122 |
|||
|
||||
x = 122/142 × 63 = 54
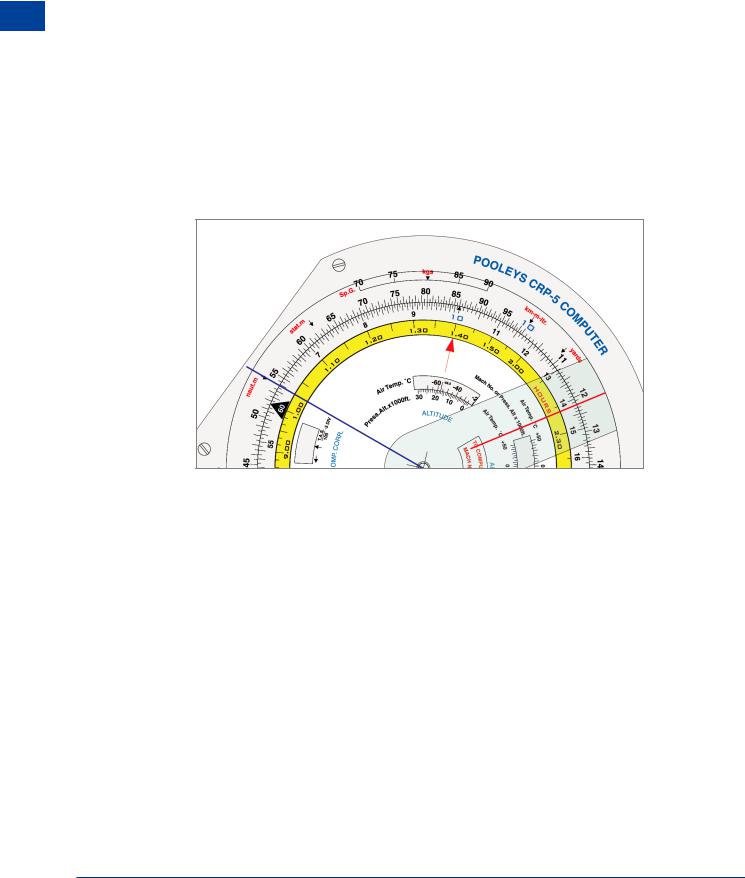
OR on your Navigation Computer
Red cursor: 142 on the inner scale is set against 122 on the outer. Blue cursor: 63 is read on the inner scale against 54 on the outer.
Figure 3.3 NAM to NGM using navigation computer
If the TAS (or GS) are not known, for example in a climb or descent, the conversion can still be carried out.
Consider an aircraft with a TAS of 100 kt:
In one hour it would fly 100 NAM. But in that hour the air has been moved by the wind component. If the WC is -25 (25 head), then the air has moved 25 NM in the direction from which the aircraft came. So the ground distance flown is:
100 - 25 = 75 NGM
Similarly, if the WC is +25 (25 tail) the ground distance is:
100 + 25 = 125 NGM
44

Nautical Air Miles |
|
3 |
|
||
|
|
|
We can see that the difference between air and ground distance is the +/- WC per minutes flown, or:
+/- WC |
× |
minutes flown |
|
||
60 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
This gives the formula: |
( |
|
|
|
) |
|
60 |
|
|||
NGM = NAM +/- |
|
|
WC |
× sector time |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Example
An aircraft climbs to cruising level in 11.5 minutes, covering 23.5 NAM. If the wind component is -30 kt, how many NGM are flown in the climb?
NGM = 23.5 - ( 3060 × 11.5 )
Nautical Air Miles 3
=23.5 – 5.75
=17.75 ( or 18 ) NGM
45
