
- •2. Evolution of the marketing concept
- •3. Implementing the marketing concept
- •Evolution of customer orientation
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Questions and assignments:
- •VI. Find in the text and pinpoint (выделите) the main idea(s) of each of its
- •VII. Speak on the following:
- •VIII. Read and translate this additional information: major marketing functions
- •Vocabulary
- •IX. Translate into English:
- •Unit 2 marketing
- •Generalities
- •2. A marketing mix
- •3. A marketing strategy
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian.
- •II. Find the English equivalents..
- •III. Fill in the blanks.
- •IV. Translate into English.
- •V. Questions and assignments.
- •VI. Speak on the following.
- •Unit 3 marketing environment
- •1. Marketing strategy and the marketing environment
- •2. Strategic market planning
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English in writing:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •VI. Speak on the following:
- •Unit 4 a product in marketing generalities
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian.
- •II. Find the English equivalents
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •2. Price and nonprice competition
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •VI. Agree or disagree with these statements. Use the following phrases:
- •VII. Speak on the following:
- •IX. Translate the sentences and indicate (укажите) the points (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) to which the following statements refer:
- •Part II unit 1 categories of product
- •Consumer product classifications
- •2. Industrial product classifications
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Find out to what category these consumer products refer (относятся) according to the following examples.
- •VI. Find out to what categories these industrial products refer according to the following examples.
- •VII. Questions and assignments:
- •VIII. Agree or disagree with the statements. Use the following phrases:
- •IX. Make up a written abstract (аннотацию) of the above text.
- •4. Business analysis
- •5. Product development
- •6. Test marketing
- •7. Commercialization
- •8. Why do products fail?
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Questions and assignments:
- •VI. Briefly describe the seven new product development phases (by writing down one or two definitions for each phase).
- •2. Growth
- •3. Maturity
- •4. Decline
- •Using the product life cycle
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •V. Find out to what stages of the product life style these statements refer:
- •V. Questions and assignments:
- •VI. Agree or disagree with the statements. Use the following phrases:
- •VII. Make up a written abstract of the above text.
- •5. Multiple channels for consumer goods
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into russian:
- •Consumer Buying Decision Process and Possible Influences on the Process
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Translate into Russian:
- •II. Find the English equivalents:
- •III. Fill in the blanks:
- •IV. Questions and assignments:
- •V. Translate into English in writing:
V. Questions and assignments:
1. How many phases does a new product go through before it is introduced?
2. List (перечислите) the seven phases of a product development.
3. Who do product ideas may come from?
4. Why may management reject a good idea in the screening phase?
5. Pinpoint (выделите) the main aim (цель) of concept testing.
6. Briefly describe the main objective (конечную цель) of business analysis.
7. What must a company find out in the product development phase?
8. What is the aim of test marketing?
9. With what can marketers experiment in different test areas in test marketing phase?
10. Do new advertising, pricing, and packaging give buyers a chance to researches the product?
11. What may the results of test marketing tell the marketers during commercialization?
12. Are new products usually introduced nationwide overnight?
13. In what way most new products are marketed?
14. Why may a new product fail?
VI. Briefly describe the seven new product development phases (by writing down one or two definitions for each phase).
VII. Retell your written abstract.
UNIT 3
THE PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
In a way, products are like people. They are born, they live, and they die. Every product progresses through a product life cycle, which is a series of stages in which its sales revenue and profit increase, reach a peak, and then decline. A firm must be able to launch, modify, and delete products in response to changes in product life cycles. Otherwise, the firm's profit will disappear and the firm will fail. Depending on the product, life cycle stages will vary in length.
STAGES OF THE PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
Centrally the product life cycle consists of four stages— introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Some products go through these stages rapidly, in a few weeks or months. Others may take years to go through each stage.
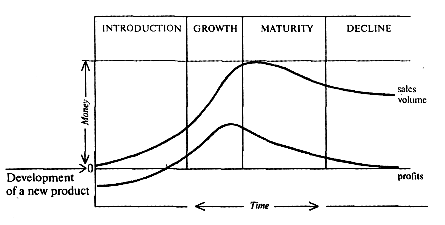
1. INTRODUCTION
In the introduction stage, customer awareness and acceptance of the product are low. Sales rise gradually, but initially high marketing costs result in low profit, or even in a loss. There are relatively few competitors. The price is sometimes high, and purchasers are primarily people who want to be «the first» to own the new product. The marketing challenge at this stages is to make potential customers aware of the product's existence and its features, benefits, and uses.
A new product is seldom an immediate success. Marketers must be prepared to modify the new product if necessary. The product should be priced so as to attract the particular market segment that has the greatest desire and ability to buy the product. The product itself, the initial price, distribution channels, and promotional efforts must be adjusted quickly to maintain sales growth during the introduction stage.
2. Growth
In the growth stage, sales increase rapidly as the product becomes well known. Other firms have probably begun to market competing products. The competition and lower unit costs (due to mass production) result in a lower price, which reduces the profit per unit. Note that profits reach a peak and begin to decline during this stage. To meet the needs of the growing market, the firm offers modified versions of its product and expands its distribution.
Management's goal in the growth stage is to stabilize and strengthen the product's position. To beat the competition, the company may further improve the product or expand the product line to attract specialized market segments. Management may also compete by lowering prices if increased production efficiency has resulted in savings for the company. As the product becomes more widely accepted, marketers may be able to broaden the network of distributors. During this period it is necessary to build brand loyalty among customers.
