СУБД Oracle / Литература / PowerDesigner 9 / GeneralFeatures
.pdfC H A P T E R 9
0DQDJLQJ 2EMHFW 5HSOLFDWLRQV
About this chapter |
This chapter describes the use of object replications in PowerDesigner. |
|
Contents |
7RSLF |
3DJH |
|
||
|
Defining object replications |
336 |
|
Displaying replications |
350 |
|
Working with object replications |
352 |
General Features Guide |
|


&KDSWHU 0DQDJLQJ 2EMHFW 5HSOLFDWLRQV
8QGHUVWDQGLQJ WKH REMHFW UHSOLFDWLRQ FRQFHSW
|
In PowerDesigner you can reuse the definition of an object among several |
|
models by replicating the object in the same model or in different models. |
|
When you replicate an object, you perform a UHSOLFDWLRQ that consists in |
|
creating a local copy called UHSOLFD of the RULJLQDO REMHFW while preserving |
|
the link to it in order to automatically update the replica when the original |
|
object is modified. |
|
An object replication is the ability to make an exact copy of an object and |
|
update this copy when the original object is modified. Attribute changes on |
|
an original object are automatically propagated to the object replica. |
|
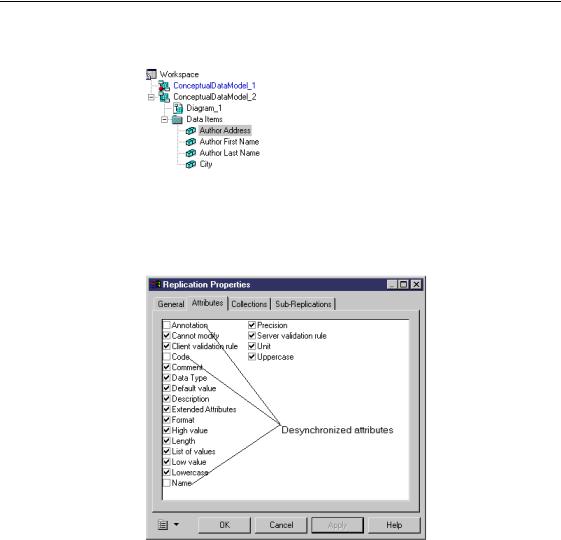
When you replicate an object, all its attributes are by default synchronized in |
|
the replica and appear as read-only in the replica property sheet. You can |
|
desynchronize some attributes using the Version Info page of the replica |
|
property sheet or using the replication property sheet if you want to perform a |
|
partial replication of the original object attributes and thus diverge from the |
|
original object. |
|
For more information on how to desynchronize attributes using the |
|
Version Info page of the replica property sheet, see section Desynchronizing |
|
replicated attributes, replicated collections and sub-replications. |
|
Using object replications means you do not have to duplicate objects. The |
|
replica uses the name, code, type and Id of the target object and is |
|
automatically updated when the definition of the target object is modified. |
Replica |
A UHSOLFD is a copy of an original object or target object. The replica |
|
references its original object in the same or in different models or packages. |
|
It owns a read-only list of synchronized attributes with those of the original |
|
object. |
Referencing model |
A UHIHUHQFLQJ PRGHO or SDFNDJH is where the replica is created. |
Original object |
An RULJLQDO REMHFW is a target object that has one or more replicas in the same |
|
or in different models or packages. |
Replication |
A UHSOLFDWLRQ materializes the link between the replica and the original |
|
object. It has no symbol in the interface but does have a property sheet from |
|
which you can desynchronize replicated attributes and collections. |
|
If you need to access the definition of a target object when it is referenced in |
|
different models, you will choose to perform an object replication and create |
|
a replica that will be an exact copy of the original object. |
General Features Guide |
|

|
|
&KDSWHU 0DQDJLQJ 2EMHFW 5HSOLFDWLRQV |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Which objects |
You can create as many replicas as you want for most of the object types that |
|
||||
support object |
appear under a model diagram or package in the Browser tree view. |
|
||||
replications? |
You can also create replicas of replicas. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
The following table lists objects per module that support replications: |
|
||||
|
0RGXOH |
|
'LDJUDP |
|
2EMHFW |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
CDM (Conceptual Data Model) |
|
— |
|
Entity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Item |
|
|
PDM (Physical Data Model) |
|
Physical |
|
Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
View |
|
|
|
|
|
|
User |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Role |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract Data Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Test Data Profile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Storage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tablespace |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Procedure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trigger Template |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trigger Template Item |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Join Index |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sequence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Database Package |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DataSource |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synonym |
|
|
|
|
Multidimensional |
|
Cube |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Dimension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fact |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DataSource |
|
|
OOM (Object Oriented Model) |
|
Class |
|
Class |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Interface |
|
|
|
|
Use Case |
|
Use Case |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Actor |
|
|
|
|
Sequence |
|
Object |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Actor |
|
|
|
|
Activity |
|
Object State |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Organization Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Object |
|
|
|
|
Component |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
Object |
|
Object |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Deployment |
|
Component Instance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
General Features Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

'HILQLQJ REMHFW UHSOLFDWLRQV
0RGXOH |
'LDJUDP |
2EMHFW |
|
|
Collaboration |
Object |
|
|
|
Actor |
|
|
Statechart |
Event |
|
|
|
Junction Point |
|
BPM (Business process |
— |
Organization Unit |
|
Diagram) |
|
Resource |
|
|
|
Message Format |
|
|
|
Data |
|
All modules |
— |
File |
|
|
|
Business Rule |
|
|
|
Domain |
|
|
|
|
2EMHFW UHSOLFDWLRQ YV VKRUWFXW
<RX XVH VKRUWFXWV ZKHQ You want to reference an object in the same model or in different models or packages in order to share this object representation between models or packages. The shortcut is not a local copy of the target object therefore it cannot be modified independently from its target object.
<RX XVH REMHFW UHSOLFDWLRQV ZKHQ You want to have a local copy of an object that will allow you to reuse the definition of the original object in the same or different models or packages while preserving the link with it.
Besides, an object replication can also diverge from its original object and be customized according to your needs.
5HSOLFDWLRQ REMHFW SURSHUWLHV
As a replication object has no symbol in the interface, you open its property sheet from the List of Replications dialog box.
You must:
♦Select Model→Replications to open the list of replications
♦Double-click a replication in the list to open its property sheet
|
PowerDesigner |
&KDSWHU 0DQDJLQJ 2EMHFW 5HSOLFDWLRQV
The definition of a replication object includes the following general properties:
3URSHUW\ |
'HVFULSWLRQ |
|
Original Object |
Model of the original object. The Properties button lets you |
|
Model |
open the property sheet of the model containing the original |
|
|
object |
|
Original Object |
Full path describing the location of the original object. The |
|
Full Name |
Properties button lets you open the property sheet of the |
|
|
original object |
|
Original Object |
Type of the original object |
|
Type |
|
|
Original Object |
State of the original object model which can be Closed or |
|
Status |
Opened or state of the original object which can be Not |
|
|
Found |
|
Replica Object Full |
Full path describing the location of the replica object. The |
|
Name |
Properties button lets you open the property sheet of the |
|
|
replica object |
|
Generate |
Replication is automatically included among the objects |
|
|
generated from the model when you launch the intermodel |
|
|
generation process. For more information, see section |
|
|
Generating replications. |
|
|
|
0RGHOV ZLWK WKH VDPH QDPH
The List of Target Models shows models containing shortcuts or replicas in the current session. It also allows you to get a model full name to distinguish from another.
For more information on how to use the List of the Target Model, see section Using the list of target models in chapter Managing shortcuts.
A replication definition also includes the following properties:
3URSHUW\ |
'HVFULSWLRQ |
|
Attributes |
List of replicated attributes |
|
Collections |
List of replicated collections |
|
Sub-Replications |
List of replicated sub-objects (for example a column of |
|
|
a replicated table) |
|
|
|
General Features Guide |
|


&KDSWHU 0DQDJLQJ 2EMHFW 5HSOLFDWLRQV
For more information on the definition of the namespace, see section Managing the namespace in models in chapter Managing Models.
The following example illustrates the replication of Entity_1 in a model that already contains an entity named Entity_1. The Entity_1 replica is automatically renamed to Entity_2 in the referencing model:
&UHDWLQJ D UHSOLFD IURP WKH 5HSOLFDWH 2EMHFWV GLDORJ ER[
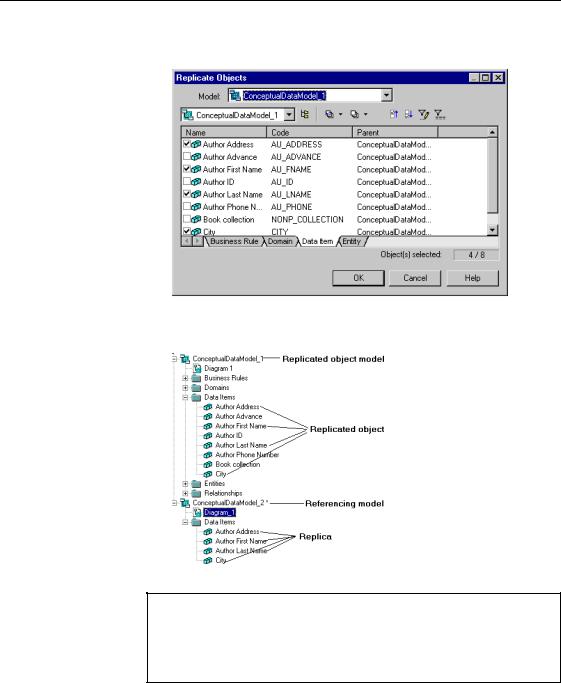
You can replicate objects using the Replicate Objects dialog box from the Edit Menu. It allows you to select one or several objects to replicate in the active model or package.
If you select an object that owns sub-objects (a table that contains columns for example or a class that contains attributes or operations), its sub-objects are also replicated. However, if you want to directly replicate a sub-object, you must use the drag and drop method.
For more information on the drag and drop method to create replicas, see section Creating a replica using the drag and drop feature.
ϖ7R FUHDWH D UHSOLFD IURP WKH 5HSOLFDWH 2EMHFWV GLDORJ ER[
1 Select Edit→Replicate Objects to open the Replicate Objects dialog box.
2 Select a model from the Model dropdown listbox. All available objects of the model are displayed.
3 Select a package from the package selection dropdown listbox. All available objects of the package are displayed.
,QFOXGH 6XE 3DFNDJHV
If you want to display all objects in the model and all objects in packages and sub-packages, click the Include Sub-Packages tool in the list toolbar.
General Features Guide |
|