
12.9. Прогноз и исходы
Важнейшим прогностическим фактором при ВМГ является состояние сознания. У больных с угнетением сознания 8 и менее баллов по ШКГ летальность при травматическихх ВМГ достигает 71% [304].
348
Внутримозговые гематомы
 Детальный
анализ зависимости исходов от уровня
сознания
в группах оперированных и неоперированных
больных, сопоставимых по среднему
возрасту,
представили А.А. Потапов и соавт. [48].
Как видно на рис. 12—16 и 12—17, летальные
исходы начинают
доминировать, когда баллы по ШКГ
снижаются
до 8, а при 5—3 баллах ШКГ погибают все
Детальный
анализ зависимости исходов от уровня
сознания
в группах оперированных и неоперированных
больных, сопоставимых по среднему
возрасту,
представили А.А. Потапов и соавт. [48].
Как видно на рис. 12—16 и 12—17, летальные
исходы начинают
доминировать, когда баллы по ШКГ
снижаются
до 8, а при 5—3 баллах ШКГ погибают все
пострадавшие с ВМГ, независимо от того, подвергались они операции или нет.
Отмечено увеличение летальности с возрастом — у пострадавших старше 50 лет она вдвое выше, чем у лиц молодого возраста [56]. Исходы ухудшаются при локализации ВМГ в височной доле [77, 304], базальных ганглиях [222], прорыве гематомы в же-

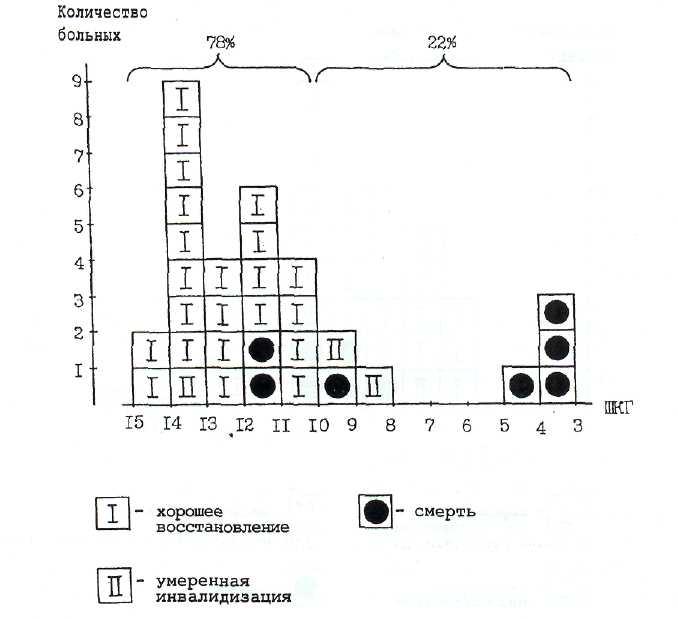
Рис. 12—17. Уровень сознания и исходы у неоперированных больных.
349
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
 лудочки
мозга [249].
На
результаты лечения серьезно
влияют объем В MX,
смещение срединных структур
мозга [249],
состояние
базальных цистерн [48], скорость
развития клинических симптомов [9, 162,
187,
208], наличие светлого промежутка [224]. На
рис.
12—18 и 12—19 [48] представлены соотношения
размеров ВМГ и исходов (раздельно у
оперированных
и неоперированных больных). В обеих
группах
четко прослеживается возрастание
удельного
веса смертности по мере увеличения
диамет-
лудочки
мозга [249].
На
результаты лечения серьезно
влияют объем В MX,
смещение срединных структур
мозга [249],
состояние
базальных цистерн [48], скорость
развития клинических симптомов [9, 162,
187,
208], наличие светлого промежутка [224]. На
рис.
12—18 и 12—19 [48] представлены соотношения
размеров ВМГ и исходов (раздельно у
оперированных
и неоперированных больных). В обеих
группах
четко прослеживается возрастание
удельного
веса смертности по мере увеличения
диамет-
ра внутримозговых гематом. Сравнительный анализ смертности при ВМГ с учетом использования в диагностике КТ показал, что диапазон летальности без се применения варьировал от 27% [144] до 87% [8], а при включении КТ от 15% [208] до 56% [122]. Сопоставление результатов хирургического и консервативного лечения у больных с травматическими ВМГ обнаружило резкое различие по рубрике «хорошее» восстановление у оперированных и неоперированных — 20% и 47%, по ос-
350
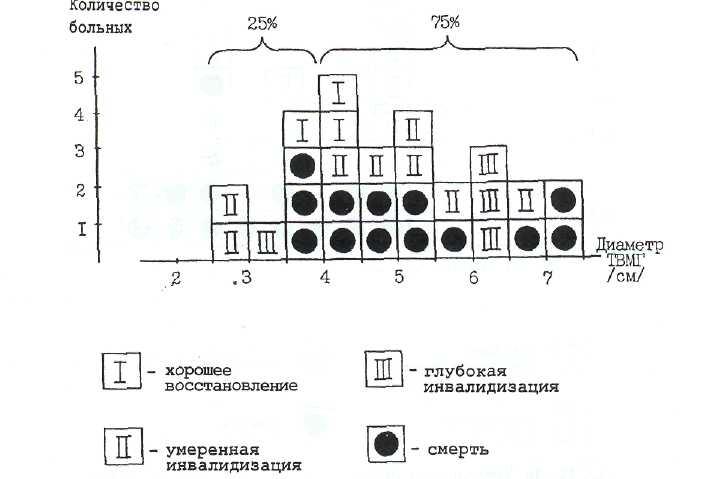
Рис. 12—18. Размер внутримозговых гематом и исходы у оперированных больных.

Рис. 12—19. Размер внутримозговых гематом и исходы у неоперированных больных.
Внутримозговые гематомы
тальным
рубрикам ШИГ разница не существенна
[48,
335].
Е.И. Гайтур и соавторы [9] подробно проанализировали влияние различных факторов на исходы лечения травматических внутримозговых гематом.
В зависимости от срока и метода лечения, пострадавших с ВМГ распределили на три группы: 1 — экстренно оперированные в 1-е сутки после трав-
мы; II — оперированные в течение последующих 2—14 суток; III — леченные консервативно. Исходы оценивали по шкале исходов Глазго. Средний возраст пострадавших, тяжесть их состояния, объем ВМГ и другие данные приведены в табл. 12—1.
Как показал анализ авторов, возраст больных с ВМГ не оказывал существенного влияния на исходы во всех группах больных. Однако у пострадав-
Таблица 12—/
Основные клинические и КТ-показатели в зависимости от метода лечения больных с ВМГ
|
Показатель |
Группы больных | ||
|
I |
II |
III | |
|
Возраст, лет |
36,5 ±4,1 |
29,8 ± 2,4** |
39,2 ±2.3 |
|
ШКГ при поступлении, баллы |
7,2 ± 0,6 |
9,5 ±0,9 |
8,5 ± 0,4 |
|
ШКГ на момент принятия решения*, баллы |
6,8 ±0,6 |
7,8 ± 0,3 |
8,4 + 0,3 |
|
Длительность комы, сутки |
6,0 ± 1,8 |
6,6 ±3,5 |
3,2 ± 0,7** |
|
Объем, мл (миним.-максимальный) |
(52-120) |
(12-60) |
(11-43) |
|
Смещение срединных структур, мм (минимальное-максимальное) |
4,2 ±(0-16)1,3 |
4,5 ± 1,3(0-16) |
1,6±0,3**(0-8) |
|
Сдавление цистерн основания, число больных |
6 (33%) |
4 (33%) |
14(23%)** |
|
Полушарный отек, число больных |
4(22%) |
1 (8%) |
7(11%) |
|
Исход, число больных: |
|
|
|
|
хорошее восстановление |
6 (33%)** |
6 (50%) |
34(56%) |
|
умеренная инвалидизация |
2 (11%) |
2(16,6%) |
10 (16%) |
|
глубокая ишзалидизация |
5 (28%)** |
2(16,6%) |
10 (16%) |
|
смерть |
5 (28%)** |
2(16,6%) |
7(11%) |
Примечания: * — перед операцией или малось решение не оперировать: ** —
при наибольшем ухудшении состояния, когда прини-р <0,05.
ших до 30 лет исходы достоверно коррелировали с объемом патологического очага, смещением срединных структур, сдавлением желудочков мозга и цистерн основания. Это свидетельствует о том, что в молодом возрасте объемные соотношения в полости черепа более жесткие, а их нарушения сильнее сказываются на исходах повреждения. В пожилом и старческом возрасте желудочки мозга и субарахноидальные пространства шире и поэтому объемные зависимости смягчаются.
Тяжесть травмы, которую оценивали по ШКГ при поступлении, оказывала существенное влияние на исходы во всех группах. Исходы у больных, поступивших в коматозном состоянии (8 баллов и менее), достоверно зависели от длительности комы, смещения срединных структур, степени облитерации цистерн основания и выраженности отека мозга. У больных, находившихся в умеренном и глубо-
ком оглушении, исходы были обусловлены только степенью смещения срединных струкур. Следовательно, наиболее прогностически важным КТ-по-казателем для больных ВМГ, уровень сознания которых выше комы, является смещение срединных структур мозга.
Объем ВМГ коррелировал с исходами во всех группах; при этом зависимость смещения срединных структур от объема ВМГ была достоверной при любом положении, кроме локализации гематомы в лобной доле (табл. 12—2).
Как видно из таблицы 12—2, на исходы в группе больных с ВМГ при различной локализации оказывают влияние следующие факторы:
1 — тяжесть состояния пострадавших при поступлении, длительность коматозного состояния и выраженность перифокального отека, которые жестко коррелируют с исходами при всех локализациях;
351
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
Таблица 12—2
Коэффициенты корреляции между исходами и основными показателями при различной локализации ВМГ
|
Показатель |
Преимущественная локализация ВМГ | ||
|
височная (п=33) |
лобная <п=25) |
теменная (п-10) | |
|
Возраст |
0,298 |
0,061 |
0,073 |
|
Тяжесть черепно-мозговой травмы |
0,485* |
0,723* |
0,797* |
|
Длительность комы |
0,4 04 ** |
0,753* |
0,698** |
|
Объем очага |
0,462* |
0,093 |
0.342 |
|
Смещение срединных структур |
0,516* |
0,278 |
0,278 |
|
Выраженность перифокального отека |
0,658* |
0,519* |
0,713* |
|
Состояние базальных цистерн |
0,403** |
0,335 |
0.696** |
Примечания: * — р<0,01, ** — р<0<05.
— объем очага смещения срединных струк тур, которые достоверно коррелируют с исходами при преимущественной локализации субстрата в ви сочной доле;
— сдавление желудочковой системы и цис терн основания, оказывающее достоверное влия ние на исходы при всех локализациях ВМГ, кро ме преимущественного расположения в лобной доле.
Эти данные свидетельствуют о необходимости настороженного отношения к ВМГ любых размеров, располагающихся в височных долях мозга, а также к ВМГ с перифокальным отеком, если они расположены там же, ибо в этих условиях перифо-кальный отек «работает» как дополнительный объем. Перифокальный отек при небольших по объему ВМГ четко коррелирует с исходами при височной локализации ВМГ.
Исходы определялись также и степенью смещения срединных структур. При этом только в группе со смещением более 5 мм исходы зависели от объема ВМГ и степени выраженности перифокального отека. Следовательно, объем патологического очага и степень выраженности перифокального отека как факторы, влияющие на исходы, «включаются» только после смещения срединных структур более чем на 5 мм.
Перифокальный отек достоверно ухудшает исходы у больных с ВМГ. Отдельный корреляционный анализ показал, что чем более выражен отек головного мозга при ВМГ, тем тяжелее была черепно-мозговая травма, длительнее коматозное состояние, больше сдавлены желудочки мозга и цистерны основания, грубее смещение срединных структур. Исходы при отсутствии отека мозга зависели от тяжести травмы и длительности комы; если же появлялся перифокальный отек, то исход зави-
сел только от длительности коматозного состояния. При распространении отека на долю мозга или на его полушарие исходы были обусловлены тяжестью травмы, длительностью коматозного состояния и смещением срединных структур. Распространение отека мозга на оба полушария не выявило никаких достоверных корреляций, однако это может быть связано и с относительно малым числом подобных наблюдений.
Таким образом, развитие отека мозга у больных с ВМГ как вторичный церебральный механизм повреждения оказывает существенное влияние на течение травматической болезни у этих больных, определяя тяжесть клинического состояния, его динамику и исходы.
Отдельный регрессивный анализ показал, что выраженность перифокального отека зависит от степени гиперосмолярного синдрома, а исходы в этой группе больных коррелируют с яркостью клиники гиперосмолярного синдрома (гипергликемии, гипернатриемии) и гипоксемии.
Следовательно, в патогенезе ВМГ развитие гиперосмолярного синдрома жестко детерминирует исходы и коррелирует с выраженностью перифо-калъного отека мозга.
Конечно, качество исходов как при оперативном, так и консервативном лечении ВМГ во многом определяется сопутствующими интракраниальными и внечерепными повреждениями, а также дотравмати-ческой патологией. К благоприятным прогностическим факторам при ВМГ следует отнести состояние сознания, в пределах не выходящих за оглушение, диаметр гематомы не более 4 см, (при отсутствии, разумеется, грубых признаков компрессии ствола, тяжелых сочетанных повреждений, а также соматической отягощен ности).
352
Внутримозговые гематомы
 Литература
Литература
Архангельский В.В. Патогенез и патологоанатомичес- кая характеристика черепно-мозговой травмы. — Руковод ство по хирургии. — М.:Медгиз, 1963, Т. 4.—С. 17—46.
Архангельский В.В. Патологическая анатомия че репно-мозговой травмы. — Руководство по нейротрав- матологии. 4.1. Черепно-мозговая травма. — М.Медици на, 1978. -С. 7-43
Аствацатуров А. И. Травмы центральной нервной системы. - 1 — М,—Л.:Мсдгиз, 1939. — С. 331—348.
Бирючков Ю.В. Наш опыт диагностики и лечения травматических интракраниальных кровоизлияний // Внутричерепные кровоизлияния. — М., 1982. — С. 40—43.
Блинков СМ., Смирнов Н.А. Смешения и дефор мации головного мозга // Москва, 1967.
Васин Н.Я., Шевелев И.Н., Кутин В.А. Некоторые вопросы хирургической тактики при острых внутриче репных травматических гематомах // Внутричерепные кровоизлияния. — М., 1982. — С. 31 — 34.
Васин Н.Я., Шевелев И.Н., Салазкина СИ., Ку тин В.А. О хирургической тактике при острых внутриче репных гематомах // Всесоюзный съезд нейрохирургов, 3-й: Тезисы докладов. — М., 1982. — С. 30—31.
Волковой И.И., Шубрак Ю.И., Егорова E.G., Суво- риков М.Г. Клиника, патологическая анатомия и тактика хирурга при травматических внутримозговых гематомах// Нейрохирургия. — Киев, 1977. — Вып. 10. — С. 39-42.
Гайтур Е.И., Потапов А.А., Лихтерман Л.Б. и др. Травматические внутримозговые гематомы: Сдавление мозга и выбор тактикилечения // Сдавления головного мозга, М, 1998, с. 26-31.
Горя.^ина Г.П. Внутримозговые кровоизлияния в остром периоде закрытой травмы черепа и головного мозга /гистотопографическое исследование/: Автореф. дис. канд.мед.наук. — Л., 1966. — 24 с.
Гриндель О.М. ЭЭГ в остром периоде при травма тических интрацеребральных гематомах. — Электроэн цефалограмма человека при черепно-мозговой травме. — М., Наука, 1988. - С 70-71.
Гук А.Н. Диагностика и хирургическое лечение хронических внутримозговых гематом полушарий голов ного мозга: Дис. канд.мед.наук. — Киев, 1984. — 190 с.
Зотов Ю.В., Щедренок В.В. Основные принципы экспресс диагностики и хирургического лечения трав матических внутричепных кровоизлияний // Внутриче репные кровоизлияния. — М., 1982. — С. 21 — 27.
Зотов. Ю. В. , Шедренок В. В. //Хирургия травма тических внутричерепных гематом и очагов размозже- ния головного мозга. // М.: Медицина, 1984, 198 с.
!5. Иргер И.М. Внутримозговые гематомы и геморрагии. — Многотомное руководство по неврологии. -М.:Медгиз, 1962. - Т. VIII.—С. 272-278.
16. Иргер И.М. Поздние травматические апоплек сии. — Многотомное руководство по неврологии. — М.:Медгиз, 1962. - Т. VIII. - С. 279 - 280.
Исаков Ю.В. Острые травматические внутричереп ные гематомы. — М.:Медицина, 1977. — 263 с.
КандельЭ.И., Переседов В.В. Стереотаксичсское удаление внутримозговых гематом // Вопр. нейрохир. — 1987. №3. - 1 -С. 16-21.
Кариев М.Х. Особенности диагностики и клини ки травматических внутримозговых гематом // Всесо юзный съезд нейрохирургов, 3-й: Тезисы докладов. М., 1982.-С. 53-54.
Кишковский А.Н., Кузнецов СВ. Компьютерная томография при острой закрытой черепно-мозговой травме. Сообщение 1. Диагностика контузионных очагов и внутримозговых гематом // Вести, рептгенол. и ра диол. - 1983. - № 6. - С. 10 - 17.
Коновалов А.Н., Корниенко В.Н. Компьютерная томография в нейрохирургической клинике. — М.Ме дицина, 1985.— 296 с.
Коновалов А.Н., Самотокин Б.А., Васин Н.Я. и соавт. Классификация нарушений сознания при череп но-мозговой травме // Вопр. нейрохир. — 1982. — № 1. — С. 3-6.
23. Корниенко В.Н., Васин Н.Я., Кузьменко В.А. Компьютерная томография в диагностике черепно-моз говой травмы. — М.:Медицина, 1987. — 287 с.
24. Корниенко В.Н., Лихтерман Л.Б. Рентгенологичес кие методы диагностики черепно-мозговой травмы // В книге «Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме», под ред. А.Н. Коновалова, Л.Б. Лихтермана, А.А. Потапова, «Антидор», Москва, 1998, т. 1, с. 472—510.
Корниенко В.Н., Туркин A.M., Лихтерман Л.Б. Магнитно-резонансная томография в диагностике че репно-мозговой травмы // В книге «Клиническое руко водство по черепно-мозговой травме», под ред. А.Н. Ко новалова, Л.Б. Лихтермана, А.А. Потапова, «Антидор», Москва, 1998, т. 1, с. 510-534.
Кузнецов СВ. Возможности компьютерной томог рафии в распознавании черепно-мозговой травмы: Дис. канд.мед.наук.—Л., 1984.—280 с.
Кузьменко В. А. Компьютерная томография в ди агностике острой черепно-мозговой травмы: Дис. канд. мед.наук. — М., 1984. — 1 — 261 с.
Лантух А.В. Диагностика и дифференцированное лечения травматических внутричерепных гематом //Дисс.
канд.мед.наук, ML, I990, 179 с.
Лебедев В. В., Быковников Л.Д. Руководство по нео тложной нейрохирургии. — М. : Медицина, 1987. — 336 с.
Лебедев В.В., Иоффе Ю.С., Сарибекян А. С Ост рый дислокационный синдром и его лечение у больных с внутричерепными кровоизлияниями травматического генеза // В книге «III Всесоюзный съезд нейрохирур гов», М., 1982, с. 62-63.
Лебедев В.В., Сарибекян А.С. Зингерман Л.С. идр. О диагностике вторичного поражения ствола головного мозга при острых внутричерепных гематомах // Журн. невропат, психиатр., 1984, № 2, с. 3.
Лебедев В.В., Шелковский В.Н. Объем хирурги ческого вмешательства при внутричерепных травмати ческих гематомах //Внутричерепные кровоизлияния. — М., 1982.-С. 34-40.
Лихтерман Л.Б. Неврология черепно-мозговой травмы // В книге «Клиническое руководство по череп но-мозговой травме», под ред. А.Н. Коновалова, Л.Б. Лихтермана, А.А. Потапова, «Антидор», Москва, 1998, т. 1, с. 230-268.
Лихтерман Л.Б., Корниенко В.Н., Потапов А.А. и др. Черепно-мозговая травма: прогноз течения и исхо дов // «Книга ЛТД», Москва, 1993, 299с.
Лихтерман Л.Б., Хитрин Л.Х. Травматические внут ричерепные гематомы // Москва, «Медицина», 1973, 295 с.
Логвинов Н.А., Грак Н.Н. Хирургическое лечение травматических внутримозговых гематом // Всесоюзн.- конф.молодых нейрохир., 11-я: Тезисы докладов. — М, 1978.-С. 38.
353
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
37. Мосийчук
Н.М., Григорук П.Т., Швыдкая Д.Г.
Хронические: внутримозговые гематомы// Нейрохирургия. - Киев, 1977.-Вып. 10.-0.51-52.
Мухаметжанов X. Внутричерепная гипертензия в остром периоде тяжелой черепно-мозговой травмы: Ав- тореф. дис. канд. мед.наук. — М., 1987. — 23 с.
Мухаметжанов X. Диагностика внутричерепной гипертензии по данным компьютерной томографии у больных с черепно-мозговой травмой //Пленум.проб- лемн. комиссии «Хирургия»: Тезисы докладов. — Ново сибирск, 1986. — С. 158 - 160.
Науменко В.Г., Греков В.В. Церебральные крово излияния при травме. — М.:Медицина, 1975. — 196 с.
Осна А. И., Хаес Л.Б. Пункционный метод лече ния острых внутричерепных травматических гематом // Матер. 1-й научной конф. 1 нейрохир. Казахстана и рес публик Средней Азии. — Алма-Ата, 1973.— С. 148—149.
Павловец М.В. Клиника, диагностика и хирургиче ское лечение внутримозговых кровоизлияний различной этиологии: Автореф.: дис.докг. мед. наук. — М., 1971.— 26с.
43. Педаченко Е.Г., Макеева Т.К. Множественные травматические внутричерепные гематомы. — Киев: Здо ровья, 1988. — 95 с.
Переседов В.В., Кандель Э.И. Прибор для стерео- таксического удаления внутримозговых гематом // Вопр. нейрохир. - 1983. - № 6. - С. 53-55.
Полишук Н.Е., Лукас Луис Таверас, Альварес Р.А. Диагностика и лечение травматических внутримозговых гематом // Пути повышения эффективнлечебн.меропр. — М., 1979.-С. 62-63.
Потапов А. А. Патогенез и дифференцированное лечение очаговых и диффузных повреждений головного мозга // Дисс. докт.мед.наук, М., 1990, 354 с,
Потаповб&.А., Гайтур Э.И. Биомеханика и основ ные звенья патогенеза черепно-мозговой травмы // В книге «Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме», под ред. А.Н. Коновалова, Л.Б. Лихтермана, А.А. Потапова, «Антидор», Москва, 1998, т. 1, с. 152—165.
Потапов А.А., Лантух А.В., Лихтерман Л.Б., и др. Дифференцированное лечение травматических внутри мозговых гематом // Ж. Вопросы нейрохирургии им. Н.Н.Бурденко, 1992, № 1, с. 5-10.
Ромоданов А.П., Педаченко Г. А. Травматические внутримозговые гематомы. — Руководство по нейротрав- матологии. 4.1. Черепно-мозговая травма. — М.Медици на, 1978. - С. 394 - 396.
Ромоданов А.П., Педаченко Е.Г. Множественные травматические внутричерепные гематомы. — Руковод ство по нейротравматологии. 4.1. Черепно-мозговая трав ма. - М.:Медицина, 1978. -С. 396-401.
Смирнов Л. И. Патологическая анатомия и патоге нез травматических заболеваний нервной системы. 4.2. Частная патологическая анатомия не осложнённой ин фекцией травматической болезни головного мозга. — М., 1949. - 202 с.
Сотрясение головного мозга. — М., 1947. — 135 с.
Стрельников И.И. Внутримозговые травматичес кие гематомы супратенториальной локализации: Дис. канд. мед. наук. — М., 1 1972. — 182 с.
Стрельников И.И. Клиника и диагностика трав матических внутримозговых гематом в остром периоде черепно-мозговой травмы //Ж. невропатол. психиатр. — 1978. - Т. 72, № 6. - С. 801-806.
Таверас Л.Л.М. Клиника, диагностика и лечение травматических внутримозговых гематом: Автореф. дис. канд. мед. наук. — Киев, 1980. -19 с.
56. Таверас Л.Л.М., Полишук Н.Е., Альварес Р.А. Некоторые особенности клинического течения, диаг ностики и лечения посттравматических внутримозговых гематом. // Вопр. нейрохир. — 1981. — № 3. — С. 43—47.
Тикк А. А. Травматические внутричерепные гема томы и гидромы и их клиническая диагностика //Вопр- .клинич. неврологии и психиатр. —Тарту, 1975. — Т. 10.— С. 103-110.
Требелев Э.А. Посттравматические внутри мозжечко вые гематомы // Вопр. нейрохир. — 1965. — № 5. — С. 5—8.
Триумфов А. В. Закрытые травмы головного мозга. — Боевая травма нервной системы. — Киров, 1943. — С. 31-35.
Угрюмов В.М., Васкин И.М., Абраков Л.В. Опе ративная нейрохирургия // под редакцией Маргорин Е.М., Медгиз, Ленинградское отделение, 1959 г., с. 316.
Фраерман А.П. Травматическое сдавление голов ного мозга (клиника, диагностика и хирургическое ле чение): Дис. докт.мед. наук. — Горький, 1981. — 463 с.
Хевсуриани Ш.О., Какауридзе А.И. Клиника, ди агностика и лечение травматических внутримозговых гематом // Всесоюзный съезд нейрохирургов, 3-й: Те зисы докладов. - М, 1982. -С. 117—118.
Чайка Т.Е., Горячкина Г.П. Патоморфология зак рытой черепно-мозговой травмы. — Тяжелая закрытая травма черепа и головного мозга. —Л., 1974. — С. 73—93.
Щербакова Е.Я. Очаги ушиба височной доли го ловного мозга в остром периоде черепно-мозговой трав мы /клиника, диагностика, хирургическое лечение: Ав тореф. дис. докт.мед.наук. — М., 1975. — 52 с.
Щербакова Е.Я. Топическая диагностика внутри черепных гематом острого периода черепно-мозговой травмы: Автореф. дисс. канд.мед.наук. — М— 1962. — 20 с.
Adams JH, Scott G, Parker LS, Graham Dl, Doyle D: The contusion index: a quantitative approach to cerebral contusions in head injury. Neuropath Appi Neurokiol 6:319— 324,1980.
Adams, J. H. (1990) Brain damage in fatal non-mis sile head injury in man, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, vol.13(57), (ed. R. Braakman), Elscvier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp. 43—63.
Adams, J. H. (1992) Head injury, in Creenfield's Neu- ropatholopJ, 5th edn, (eds J.H. Adams and L. M. Ducken), Edward Arnold, London, pp. 106—152.
Adams, J.H., Doyle, D., Graham, D. l.etal. (1986b) Deep intracerebral (basal ganglia) haematomas in fatal non- missile head injury in man. Journal of Neurology, Neurosur- gery and Psychiatry, 9, 1038-1043.
Agnoli A.1L, Zierski J. T in — traumatic 1CH — mea surement of absorlation values // Spontaneous intracerebral haematomas. /Eds.Pia H.W. et al. — Berlin:Springer, 1980. — P.202-215.
Agura Т., Masuzawa H., Mizutanil.et al. Evolution of traumatic intracerebral hematoma // Neurol.Med.-Chir. — 1979. - I V,19, № 6. - P.459-466.
Agycman J.F. Computed tomographical analysis of central cerebral haemorrhage resulting from closed head in jury // Eur. Neurol. - 1982. -V.21,№5. - P.298-304.
Akimoto H., Maki Y. Serial CT study of intracerebral haemorrhage // NeuroI.Surg. - 1979. - V. 7, № 5. - P. 455- 464.
Alexander III E. Intracerebral hematoma after evalua tion of chronic cxtracerebral fluid collections: comments // Neurosurgery. - 1982. - V. 10, № 6. - P.693.
354
Внутримозговые гематомы
Alexander, Ball M. and Laster D.(1987) Subtempo- ral decompression: radiological observations and recurrent surgical experience. British Journal of Neurosurg 1:427— 433.
Andrews B. and Pitts L. Functional recovery after trau matic transtentorial herniation // J. Neurosurg. 29, 1992, p.227—231.
Andrews В., Chiles В., Olsen W. et al. The effect of intracerebral hematoma location on the risk of brain-stem compression and on clinical outcome // J.Neurosurg. 69, 1988, p.518—522.
Aoki N., Mizuguchi K. Chronic encapsulated intracere bral hemaloma in infancy: case report // Neurosurgery. — 1984. — V.14, №5. - P.594-597.
Arseni G., Grigorovici S. L'hcmatomc intracerebral d'origine traumaticque // J.Ghir. — 1961. — V.81, № 3. — P.335-349.
Auer L,H., Endoscope evacuation of intracerebral haemorrhage. Hightcc.-surgical treatment: A new approach to the problem //Acta Neurochir. — 1985. — V.74, № 3—4. — P.124-128.
Auer L.M., Holzer P., Ascher P.W., Heppner F. Endoscopic neurosurgery//Acta Neurochir. — 1988. — V.90, № l.-P. 1-14.
Austarheim K. Delayeed traumatic intracerebral hem orrhage: report on one case with necropsy // Acta Path.Microbiol. ScancL. -1956. - V.38. - P.1977—1985.
Axelbaum S.P., Schellinger D., Luenssenhop A.J. Inlracerebral hematoma. Diagnosis vith automatic comput erized transverse axial (A?TA) scanninh//J.A.M.A. — 1976. — V.235. -P.641-645.
Backlund E.G., von Hoist H. Controlled subtotal evacuation of intracerebral hematomas by stereotactic tech nique//Surf Ncurol. - 1978.-V.9, H2. -P.99-101.
Baratham, G. and Dennyson, W. (1972) Delayed trau matic intracerebral haemorrhage. Journal of Neurology, Neu rosurgery and Psychiatry, 3, 698—706.
Becker D., Grade G., Young H., and Feuerman Т.: Diagnosis and treatment of head injury in adults // in You- mans J., (ed.) Neurological Surgery, 3rd cd., W. B. Saun- ders: Philailelphia, 1990.
Becker D.P., Miller J.D., Ward J.D. ct al. The out come from severe head injury with early diagnosis and in tensive management // J.Neurosurg. — 1977. — V.47, № 4. — P.491-502.
Becker DP, Miller Ю. Sweet RC, et al: Head injury management, 1977. In Neurological Surgery. New York, Raven Press, 1979, p.318-328.
Benes V. Ventricular hemorrhage // Zbi.Neurochir. — 1985. - Bd.46, № 4. — P.283—289.
Bergstrom M., Ericson K., Levander В., Svendsen P. CT of cranial subdural and epidural hematomas: Variation of attennation related to time and clinical events such as rebleeding // J.Comput. Assist.Tomogr. — 1977. — V.I. — P.449-445.
91. Blumberg P.C. (1997) Pathology, in Head injury (ed. P.Reilly and R.Bullock), Chapman&Holl MedicaSl, pp.39-70.
Bobo H. Delayed intracerebral hematoma at the site of a subarachnoid bolt pressure monitor: Case report // J.Neurosurg.1986. - V.64, № 4. - P.673-675.
Bollinger O. Ueber traumatische Spat-Apoplexie. Ein Beilrag zur Lehre von der Hirnerschutterung // Intern. Be- itrage zur Wissenschaft. Med. — Festschrift.Virchow. — Berlin:A. - Hirschwald. - 1891. -V. 2. - S. 457-470.
Borovich В., Gellei В., Plyser E. Massive traumatic hematoma of the basal ganglia // Surg.Neurol. — 1975. — V.3. № 1.- P.25-26.
Bouzarth W.F. «Discussion» in: traumatic intracere bral hematomas: Timing of appearance and indications for operative removal D.Soloniuketal. //J.Trauma. — 1986. — V. 26. — №9. - P.794.
Bricolo A, Turazzi S, Alexandre A, Rizzuto N: De- cerebrate rigidity in acute head injury. / Neu-rosurg 47:680— 698,1977.
Browder J, Turnev MF: Intracerebral hennorrhage of traumatic origin. Its surgical treatment. MS J Med 42:2230— 2235,1942.
Brown, F. D., Muilan; S. and Duda, E. E. (1978) De layed traumatic intracerebral haematomas. Report of three cases, journal of Neurosurgery, 48, 1019—1022.
Brunetti J, Zingesser L, Dunn j, Rovit RL: Delayed intracerebral hemorrhage as demonstrated by CT scanning. Neuroradiology 18:43-46,1979.
Bullock R., and Teasdale G. (1990) Head injuries - surgical management of traumatic intracerebral haematomas, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, vol. 57 — Head injury, (ed. R. Braakman), Elsevier, Amsterdam, ch. 10, pp. 249— 298.
Bullock R., Golek J., Blake G. Traumatic intracere bral hematoma — which patients should undergo surgical evacuation? CT scan features and ICP? monitoring as a basis for decision making// Surg.Neurol. — 1989. — V.32, № 3. — P.I 81 —187.
Bullock, R., Maxwell, W. L., Graham, D. 1. et al. (1991) Glial swelling following human cerebral contusion: an ultrastructurai study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 54, 427—434.
Butzer J.F., Gancilla P.A., Cornele S.H. Computer ized axial tomography of intracerebral hematomas: A clini cal and neuropathological stady // Arch.Heurol. — 1976. — V. 33, №3. - P. 206-214.
Bydder M., PennockJ.M., Porteous R. etal. MRI of intracerebral haematoma at low field (0,15 T) using T2 de pendent partial saturation seguences // Neuroradiology. — 1988. - V. 30. № 5. - P. 367-371.
Byrnes DP: Head injury and the dilated pupil. Am Surg 45:139-143,1979.
Chan K., Mann K. et al. The significance of skull fracture in acute traumatic intracranial haematomas in ado lescents // J. Neurosurg. 72, 1990, p.189.
Clifton L., Grossman R.G., Makela M.E. et al. Neu rological course and correlated computerized tomography findings after severe closed head injury // J.Neurosurg. — 1980. - V. 5 2, № 5. - P.611-624.
Colquhoun, J. R. and Rawlinson, J. (1989) The sig nificance of haematomas of the basal ganglia in closed head injury. Clinical Radiology, 40, 619—621.
Cooper P.R.: Post-traumatic intracranial mass le sions, in Cooper P.R. (ed) Head injury (3d ed). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. 1993:275-329.
Cooper PR, Hagler H, dark WK, Bamett P: En hancement of experimental cerebral edema following decom- pressivc craniectomy: Implications for the management of the severely head injured. Neurosurgery 4:296—300,1979.
Cooper PR. Maravilla K, Moody S, Dark WK: Serial computerized tomographic scanning and the prognosis of head injury. Neurosurgery 5:566—569,1979.
Courville CB: Coup coutre-coup mechanism of cran- iocerebral injuries. Arch Surg 45:19—43, 1942.
355
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
Courville CB: Traumatic intracerebral hemorrhages, With special reference to the mechanisms of their produc tion. Bull Los Angeles Neural Soc 27:22-38,1962.
Custovic K., AhmctspahicJ., DrudaA., SaratlicV. Treat ment of the traumatic intracerebral bematoma // 9-th Intern, Congr.Neurosurgcry. — New Delhi,India. Abstr. 1989. — P.435.
D'Avella D., Blasi F., Ritilio A. et al. Intracerebral hematoma following evacuation of chronic subural hemato- mas//J.Neurosurg. - 1986. - V. 65,№ 5. - P.710—712.
Day J., Koos W., Matula C, Lang J. Color atlas of microneurosurgical approaches. Thieme, Sluttgard, New York, 1977.
De Jong RN: Delayed traumatic intracerebral hem orrhage. Arch Neural Psych 48:257—266, 1942.
De La Paz R.L., New P.P.J., Buonanno F.S. et al. NMR imaging of intracranial hemorrhage // J.Comput. As sist. Tomogr.-1984. - V.8. - P.559-607.
Dejong R.N. Delayed traumatic intracerebral hemor rhage // Arch.Neurol.Psychiat. - 1942. — V.48. - P.257- 266.
Demierre В., Shoenie P.W., Hori A. et al. L'hematome intracerebral secondaire post-traumatic // Neuro-chirurgie. — 1987. -T.33, № 1. - P. 12—16.
DeVct, A. C. (1976) Traumatic intracerebral hae- matoma, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, vol. 24, (eds P. J. Vinken and G. W. Bruyn), Elsevier Science Publishers, pp. 353-368.
Diaz FG,YockDH. Larson D, RockswoldGL: Ear ly diagnosis of delayed post traumatic intracerebral hernato- rnas. / Neunsurg 50:217—223, 1979.
Diemath H.E. Die Bedeutung der Computertomog- raphie fur die Operationscrgeouisse endokranieller trauma- tischer hematomas // Wien Med.Wschr. — 1982. — Bd.132, №6.-5.133-^6.
Doi E.^Moriwaki H., Kornai N.. Iwamoto M. Ste- reotactic evacuation of intracerebral hematomas // NeuroI.Med.-Chir. -1982. - V.22. - № 6. - P.461-467.
Dolinskas C.A., Bilaniuk L.T., Zimmman R., Kuhl D.E. Computed tomography of intracerebral hematoma. Trans mission CT observations on hematoma resolution // Am.J.Roentgenol. -1977. - Y.129,H4. - P. 681-688.
Dongen. K., Braakman a. Computed Tomography in head injury// Progress in Neurol.Surg. — Basel:Karger, 1981. — P.213-219.
Dooms G.C., Uske A., Brant-Zawadzki M Spinecho MR imaging of intracranial hemorrhage // N euro radio log. — 1986. -V.28, №2. - P.132—138.
Dreisbash J., Guberttean 1., Davis K., Taveras J. Eval- ution of extracerebral collections by CT // Intern. Symp. and Course on Computerized Tomography, San Juan, 1976. — P.9.
Driesen W. Post-traumatische intrazerebrale Hamatomc // ICLinische Heurochirurgie. /Hrsgb.Von H.Dietz et al. — N.Y.: Thieme, Stuttgart, 1984. - P.438-439.
Dublin A.B., Ferluch B.N., RennickJ.M. Comput ed tomography in head trauma // Radiology. — 1977. — V. 122, M2. - P. 365-369.
Duff Т., Ayeni S., Levin A. etal. Nonsurgical manage ment of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas //Neurosur- geiy. -1981. - V.9, № 3. - P.387-393.
Eawakami Y., Nakao Y., Tabuchik K. et al. Bilateral intracerebellar calcification associated with cerebellar hemato ma//J.Neurosurg. - 1978. - V.49, № 6. - P. 744-748.
Ebisu Т., Yamaki Т., Kobori N. et al. Magnetic reso nance imaging of brain contusion//Surg.Neurol. — 19S9. — V.31, №4. - P. 261-267.
Edelman R.R., Jomson K., Buxton R. et al. MR of hemorrhage: a new approach //Am.J.Neurorentgen. — 1986. — V. 7, №5.-P.75I-756.
Eisner H., Rigamouto D., Schlegel R., Gorradin G. Delayed intracerebral hematoma (Spat Apaplexie) //Neuro- surgery.—1988. - V.23, № 2. - P.258.
Evans J.P., Scheinker l.M. Histologic studies of the brain following head trauma. II.Post-traumatic petechial and massive intracerebral hemorrhage //J.Neurosurg, — 1946. — V. 3,№2. - P.101-113.
Foroglou G. Posttraumatic intracerebral hematomas, in Advances in Neurotraumatology. Vol. 3. Springer-Verlag. Wien, 1991, pp. 141-166.
French B.N., Dublin A.B. The value of computer ized tomography in the management of 1000 consecutive head injuries//Surg.Neurol.- 1977. - V.7, № 4. - P. 171— 183.
Friedrich P. Therapy of intracerebral hematomas // Zbl.Neurochir. - 1983. - Bd.44, № 3. - S.221-227.
Frowein R.A., HamelT. Role of trauma in ICT: IGH after minor trauma // Spontaneous intracerebral haematomas /Eds. H.W. Piaetal. - Berlin:Springer, 1980.- P.58-71.
Fukamachi A., Kohno K., Nagasaki Y. et al. The incidence of delayed traumatic intracerebral hematoma vith extradural hemorrhages//J.Trauma. — 1985. — V.25, № 2. — P. 145-149.
Fukamachi A., Kohno K., Wakao T. et al. Traumatic intracerebral hematomas; A classification according to the dynamic changes on sequential CT's // Neurol.Med.Chir. — 1979.-V. 19, №1.-P. 1039-1051.
Fukamachi, A., Nagaseki, Y., Kohno, K. et al. (1985) The incidence and developmental process of delayed trau matic intracerebral haematomas. Acta Neurochirurgica, 74,35-39.
Fusco G., Dei Saizo S., Palisi G. et al. L'hematoma intracerebral traumatico // Rass Int.Clin.Then — 1980. — V.60, № 4. - P. 240-255.
Gaab M, Knoblich OE. Fuhrmeister U, Pflughaupt KW, Dietrich K: Comparison of the effects of surgical de compression and resection of local edema in the therapy of experimental brain trauma. Investigation of 1CP, EEC and cerebral metabolism in cats. Child's Brain 5:484—498, 1979.
Gail W.S., Morris J.C. Localisation of intracranial lesions from CT scan //Surg.Neurol.— 1979.-V. U,№1,- P. 35-37.
Galbraith S., Tcasdale G., Prediction the need for operation in the patient with an occult traumatic intracranial hematoma //J.Neurosurg. - 1981. - V.55, № 1. - P. 75-82.
Galbraith S: Misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis in traumatic intracranial haematoma. Br Med ] 1:1438— 1439,1976.
Gindi S.F., Salama M., Tawfik E. et al. A review of 2000 patients with craniocerebral injuries with regard to intra cranial haematomas and other vascular complications // Acta Ncurochir. - 1979. - V. 48, H3-4. - P. 237-244.
Glowacki J. Delayed traumatic apoplexy «Discussion». — Spontaneous intracerebral hematomas / H.W.Pia et al. (eds.) — Berlin:Springer, 1980. - P. 81-82.
Golquhoun I.R., Burrows E.H. The prognostic signifi cance of the third ventricle and basal cisternus in severe closed head injury // Clinical radiology. — 1989. — V. 4Л № 1. — P. 13-16.
152. Gomori J.M, Grossman R.I., Goldterg H.I. et al. Intracranial hematomas: imaging by high-field MR // Radio logy. - 1985. -V.I57,№ I.-P.87-93.
356
Внутримозговые гематомы
Gong R., Zholi C, Shi H. et al. A new method for computerized tomography diagnosis of early transtentoria] hernia // Chin. Med. J. (Engl) 10, 1997, p.778-782.
Gourville C.B. Traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage // Neurol.Soc. - 1962. - V.27, № 1.- P.22-28.
GreenbergM. Handbook of neurosurgery. Greenberg Graphics, Inc, 1997, pp.464.
Gudeman S., Young F., Miller D., Ward J., Beck er D. Indication for operative treatment and operative tech nique in closed head injury // in book «Textbook of head injury» Becker D., Gudeman S., W.B.Saunders, 1989, p.138-181
Gudeman, S Kishore, P., Miller, J. et al. (1979) The genesis and significance of delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma. Neurosurgery, 5, 309—313.
Guillerman P., Lena G., Reynier Y. et al. Leg he- matomes intracerebralux posttraumatiques. A propos d-une serie de 38 cas // Ncuro-chirurgie. 1982. — T.28, № 5. — p.309—314.
Gurdjian E.S., Thomas L.M. Traumatic intracranial hemorrhage // Brock's injuries of the brain and spinal cord and their covering/ Ed.E.H.Feizing. — N.Y.:Springer. 1974. — V.5. -P.203-282.
Gurdjian E.S., Webster J.E. Head injuries; mecha nism, diagnosis and management. — Boston Little Brown, 1958.-269 P.
Gurdjian ES, Gurdjian ES: Cerebral contusions: re- evaluation of the mechanism of their development. J Trauma 16:35-51,1976.
Hamel E., Earimi-Nejad. Traumatic intracerebral he- matomas//Adv.Ncurosurgery. ~ 1978. — V.5, № 1.— P.56—61.
Han JS, Kaufman B, Alfidi RJ, et al: Head trauma evaluated by magnetic resonance and computed tomogra phy: a comp^ison. Radiology 150:71—77,1984.
Hara H., Shiogai Т., Tamagawa T. et al. Three cases of traumatic intracerebral hematoma with ventricular hemor rhage // Neurol.Surg. - 1980. - V. 8, № 3. - p.295-299.
Hayashi Т., Kobayashi J., Yoshida Y. et al. Analysis of the evolution of traumatic intracerebral hematoma // BNeuroI. Med.Ghir. — 1987. - V. 27, № 2. — P. 97-104.
Heiscanen O., Vapalahti M.: Temporal lobe contusion and hematoma//Acta neurochir. (Vienna) 27: 29 35, 1972.
Hensell V., Gerhard 1., Brolsch G. Present limits of neurosurgery // Proc.4—th Europ.Congr.Neurosurgery. — Prague, 1972. - P.128.
Heppner F., Tritibart H., Holzer P. Die operative therapie der traumatishen intrazerebralen Hamatome // Wien.med. Wschr. - 1978. - Bd.122, № 19. - 5.635-636.
Hinck V.C., Glifton G.li. A precise technique for craniotomy localization using computerized tomography. Technical note // Neurosurgery. — 1981. —7.54, № 3. — P. 416-418.
Hindo H., Yoshijima S., Kusaka K., Matsumoto K. Two cases of traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage in the bas al ganglia // Proc. 1-st Conf.Japan Soc.Neurotraumatology. — 1978.-V.I.-P. 101-105.
Hirsh L.F. Delayed traumatic intracerebral hemato ma after surgical decompression // N eurosurgery. — 1979. — V.5, № 5.-P. 653-655.
Hirsh L.F., Spector H.B., BogdanofF B.M. Chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma // Neurosurgery. —- 1981.— V.9, K2.-P. 169-172.
Hofman E., Dressel K., Hadjimi M., Zentrale trau- matische hirnblutungen im computertomogramm // ROFO. — 198Л. - V.143, №2. - P.146-151.
Holbourn H.S. The mechanics of brain injuries // Brit. Med.Bull. - 1934. - V.3. — P. 147-149.
Hondo H., Matsumoto K. CTguied stereotactic evac uation of hypertensive and traumatic intracerebral hemato- mas — experiences with 35 cases // Neurol.Surg. — 1983. — V. 11,№ 1,- P. 35-48.
Ito H., Mukai H., Higashi S. et al. Removal of hyper tensive intracerebral hematoma with stereotactic aquastream and aspirator// Neurol.Surg. - 1989. - V.17, № 10. - P.939-943.
.lamieson K., Yelland J.D.N. Traumatic intracerebral hematoma. Report of 63 surgically treated cases // J.Neuro- surg.-!972. - V.37,H5. - P.528-532.
Jamieson KG: Delayed traumatic intracerebral hem orrhage. (Traurnatische spatapoplexie). Aust New Zeal J Surg 23:300-307, 1954.
179. Jayakumar P.N., Sastry Kolliri V.R., Basavalunar D. et al. Prognosis in traumatic basal ganglia haematoma // Acta Neurochir. - 1989. - V.97, №3-4. - P.I 14-116.
Jellinger K. Delayed traumatic apoplexy. «Discussion». // Spontaneous intracerebral haematomas /Eds.H.W.Pia et al. - Berlin:Springer, 1980. - P.202-215.
Jenkins A., Mendelow A.D., Graham D.J. ct al. Experi mental intracerebral haematoma: the role of blood constituents in early ischaemia // Britisch J. Neurosurg. 4, 1990, p.45—52.
Jennett В., Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. A practical scale // Lancet. — 1975. — V.I.-P. 480-484.
Jennett D., Teasdale G. Aspects of coma after severe head injury//Lancet. - 1977. - V.I. - P. 877-881.
Johnston 1.Н., Harper A.M. The effect of mannitol on cerebral blood How: An experimental study // J.Neurosurg. — 1973. - V.38, №4. - P.461—471.
Kandel E.I., PeresedovV.V. Stereotaxic evacuation of spontaneous intracerebral hematomas //J.Neurosurg. — 1985. -7.62, № 2. - P.206-213.
Karasawa. H., 0giha,ra R., Tomita S. etal. Time course of the — traumatic intracerebral hematomas — Appearance and enlargement // Progress in computer tomography. 1980. — V. 2. - P. 447-453.
187. Karimi-Nejad A., Hamel E. Comparative study of the results in spontaneous and traumatic IGH // Spontane ous intracerebral haematomas / Eds.H.W.Pia et al. — Berlin;Springer, 1980. - P. 202-215.
188. Katz, D. 1., Alexander, M. P., Scliger, G. M. and Bellas, D. N. (1989) Traumatic basal ganglia haemorrhage: clinicopatho- logic features and outcome. Neurology, 39,897—904.
Kaufman HH, Moake JL, Olson JD, Miner ME, du Cret R.P, Piuessner JL, Gildenberg PL: Delayed and recurrent intracranial hematomas related to disseminated intravascular clotting and fibrono-lysis in head injury. Neu rosurgery 7:445-449, 1980.
Kingman A., Mendelow A. et al. Experimental in tracerebral mass: description of model, intracranial pressure changes and neuropathology // J. of Neuropath, and Experim. Neurol. 47, 1988, p. 128-132.
Kirn H., Karaaawa. H., MikabeT., Watabe S. Trau matic intracerebral hematomas. Clinical classification and treatment // 7-th Intern.Congr.Neurol.Surgery. Abstr. — Munchen-N.Y., 1981.- P. 238.
Kobayashi S., Nakazawa S., Otsuka T. Clinical value of serial computed tomography with severe head injury // Surg. Neurol. - 1983. - V.20, № 1. - P.25-29.
Kohi Y., Teasdale G., Murrey L. et al.: Further ex perience with occult traumatic hematoma // The sixth inter national symposium on 1CP. Glasgow, 1985, p. XI—1.
357
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
Kohno К., Fukamachi A.,TazakiT.,WakaoT. Aclini- co-traumatic study of acute traumatic intracerebral hemato- ma by means of CT // Progr.Computer.Tomogr. — 1979. — V. 1.-P. 345-334.
Kolbag R.M. Head, injury management //J.Neurosurg. — 1978. - V.48, № 3. - P.489-490.
Komatsu S., Sato Т., Kagawa S. et al. Traumatic le sions of the corpus callosum // Neurosurgery. — 1979 — V.5, № 1.-P. 32-35.
Krauland W. Uber Hirnshaden durch stunlpfe Ge- walt//Detsch.Zschr.Kervenl - 1949. - Bd.163. - p265.
Krenkel W. Traumatische und nicht-traumatische Hichblatungen // Langenbecks Arch.Klin. Chir. — 1970. — Bd.327. - S.949-954.
!99. Kretschmer H. Traumatische intrazerebrale Ham-atome — Analyse von 88 operative behandelten Eallen // Neurochirurgia.-1979. - V.22, № 1. — P. 35-41.
Kretschmer H. Veriaufsdynamik und Truhprognose traumatischer intrakranieller Blutungen. Illlintrazerebrale Hamatome//Aktual.Traumatol. — 1981. — Y.I 1, № 3. — 7.87-92.
KuroiwaT., KitamuraJ,, Ohta T. Conservative treat ment for the acute stage traumatic intracranial hematoma // Neurol. — Med.-Chir. — 1985. - V.25, № 3. - P. 181 —186.
Kurokawa Y., Hashi K., Ueda T. et al. Enlarging of intracranial heinorrhagie lesions and coagulofibrinolytic abnormalities in multiple-injury patients // Neurol.Surg. — 1989. -V.17, №4. -P. 335-341.
Kwiatkowski S. Traumatic acute intracranial haemato- ma in Manual of neurosurgery. Compiled by J.D.Palmer, Churchill Livingstone, Glasgow, 1996, p.540.
Lamy В., Artru F., Jourdan C. et al. Value of intracra nial pressure monitoring in delayed operative indications in patients with brays hemorragic post traumatic contusion // Agressologie. - $88. - V.29, № 6. - P. 399-404.
Langfitt T.W. Computed tomography, magnetic res onance imaging and positron emission tomography in the stady of brain trauma. Preliminary observatons // J.Neurosurg. — 1986. - V. 64, № 5. - P. 760-767.
206. Laster D.W., Woody D.M., Ball M.R. Resolving intracerebral hematoma; Alteration of the «ring Sing» with steroids //Am.J.Roentgenol. - 1978. - V. 130, № 5. - P.935- 939.
Lee I.I. Organized intracerebral hematoma with acute hemorrhage CT patients and pathologic correlations // Am. J.Roentgen 1986. - V. 147, № 1. - P.I 11-118.
Legros B,, Lapierre F., Fouruier P. et al. Post trau matic intracerebral haematomas // Agressologie. — 1988. — 7.29, № 6. - P. 405-408.
Lesoin F., Viand. C, Glraldon J.M. et al. Les he- matomes intracraniens traumatiques retardes. Intret de l'examen scano-grapbique // Neuro-chirurgie. — 1982. — T.28, № 5. - P. 373-378.
Levander В., Stattin S., Svendsen P. Computer to mography of traumatic infra — and extracerebral lesions // ActaRadiol. -1975. - V.346. - P.107-118.
Levinthal R., Stern W.E. Traumatic intracerebral hematoma with staple neurological deficit // Surg.Neurol. — 1977. _ v. 7, КЗ. - P. 269-273.
212.Upper M.H., Kishore P.R.S., Girevendulis A.K.et al. Delayed intracranial hematoma in patients with severe head injury//Radiology.- 1979 - V.I 33, № 5. - P. 645-648.
213. Lin S.Z., Shin C.J., WangY.C, Tsai S.H. Intracerebral hematoma simulating a new growth // Surg.Neurol. — 1984. - V. 21, № 5. - P. 459-464.
Lindenberg R, Frcytag E: The mechanism of cer ebral contusions. A pathologic-anatomic study. Arch Path 69:440-469,1960.
Lindenberg R. Significance of the tentorium in head injuries from blunt forces // Glin.Neurosurg. — 1966. — V. 12,— P. 129-142.
Lindenberg R., Fisher R.S., Duricher S.H. et al. Le sions of corpus callosum following blunt mechanical trauma, to head//Am.J.Pathol. - 1955. - V.31. - P.297-317.
Lindenberg R., Freytag E. Morphology of cortical contusions//Arch.Pathol. - 1957. - V.63. - P.23-42.
Lindenberg R., Freytag E. The mechanism of cere bral contusion. A pathological anatomic study // Arch.Pathol. — 1960.-V.69.-P.440-469.
Lindgren S. Diagnostic terminology of head injuries — related to severity // Acta Neurochir. — Suppi. — 1986. — V. 36. P.70-80.
Litofsky, N. S., Chin, L. S., Tang, G. et al. (1994) The use of lobectomy in the management of severe closed head trauma. Neurosurgery, 34, 628—633.
Lofgren J. Traumatic intracranial hematomas: Patho- physiological aspects on their course and treatment // Acta Neurochir.- 1986. - V.36,Suppl. - P.151-154.
Macpherson, P., Teasdale, E Dhaker, S. et al. (1986) The significance of traumatic hacmatoma in the region of the basal ganglia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psy chiatry, 49, 29—34.
Makino H, Yamaura A: Assessment of outcome fol lowing large decompressivc craniectoiny in management of serious cerebral contusion. A review of 207 cases. Aria Neuro chir (Suppi) 28:193-194,1979.
Maksymowicz W., Dzewiecko C, Koszewski W., Wa- Icncik A. Posttraumatic intracerebral hematoma // Neurol. Ncuro- surg.Psych.-Pol. — 1987.-V.21, HI. — P.49-53.
Mao Q., Chen J., Li C, et al. The value of serum myelin basic protein in assessment of severity of acute closed head trauma - Hua Hsi I ко Та HsuehPao, 1995, 26, 2:135-7.
Marshall LF. Toole BM, Bowers SA: The national traumatic coma data bank. Part 2: Patients who talk and dete riorate: implications for treatment. / Neumurg 59:285— 288,1983.
Marshall, L. F., Bowers-Marshall, S., Klaubcr, M. R. et al. (1991) A new classification of head injury based on computerised tomography. J. of Neurosurgery, 75, S14-S20.
Massina A.V., Chernik N.L. Computed tomographyt The «resolving» intracerebral hemorrhage // Radiology. — 1976. -V.I 18, №4. - P.609-613.
Masuzawa Т., Saito K., Shimabukuro H. et al. Chronic encapsulated hematomas in the brain // Acta Neuropathol— 1985. -V.66. -p.24-28.
Matsui S., Tanikake Т., Utsurai S. et al. Follow-up studies of cerebral contusion and traumatic intracerebral he matoma by means of CT// Progr.Gomput.Tomogr. — 1979- — V.I. - P.355-360.
Matsui T. Craniotomy based on computerized to mography//Neurol. - Med.-Chir. — 1981. - V.21, № 3. - P.241-250.
Matsumoto K., Hondo H. CT-guided stereotactic evacuation of hypertansive intracerebral hematomas // J.Neurosurg. -1984. - V.61, № 3. - P.440-448.
233. Matsumoto M., Sanpei K., Nishikawa H. et al. Characte ristics of traumatic intracerebral hematomas in children // Neurol.Med.Ghir. - 1988. - V.28, № 9. - P. 1081-1088.
234. Matz P., Weinstein P., Sharp F. Yeme oxygenase-I and heat shock protein 79 induction in glia and neurons
358
Внутримозговые гематомы
throughout
rat brain after experimental
intracerebral
hemorrhage.//Neurosurgery,
1997,40, 1:152-60.
McLaurin RL, Helmer F: The syndrome of tempo ral-lobe contusion. / Neurosurg 23:296—304, 1965.
McLaurin RL, McBride BH; Traumatic intracere bral hemaloma. Review of 16 surgically treated cases. Ann Surg 143:294-305, 1956.
Merino de Villasante J., Taveras J.M. Computerized tomography in acute head trauma //Am.J.Rocntgcnol. 1976. — V.126, №4.-P. 765-778.
Minauf M., Schacht L. Zentrablc Hirnschaden nach Einwirkung stumpfer Gewalt aufden Schadel. lI.Lasionen im Bereich der Stammganglien // Arch.Psychiat. Nerven. Kranken. - 1966. - Bs.208. - S.162-176.
Modesti L.M., Hodge G.J., Barnwell M.L. Intrace rebral hematoma. after evacuation of chronic extracerebral fluid collections // Neurosurgery. — 1982. — V. 10, № 6. — P.689-693.
Mori H., Terabayashi Т., Hitazawa R., Sugiyama Y. Multiple intracerebral hemorrhages immediately after sur gical excision of middle fossa arachnoid cyst and evacuation chronic subdural hydrorna// Neurl. Med. — Chir. — 1989. — V.29, №2.-P. 142-145.
Morin M.A., Pitts F.W. Delayed apoplexy following head injuries // J.Neurosurg. — 1970. — V.33, № 4. — P. 542-547.
Moriyssu N., Tsubokava T. Traumatic intracerebral haematoma factors improving its therapeutic results //Clini cal Res. 1972. -V.49. - P.3409-3417.
Mosberg W.H., Lindenberg R. Traumatic haemor rhage from the anterior chroroidal artery // J.Neurosurg. — 19Л9. - V. 16, № 2. - P. 209-221.
Mosclcy J.I., GianottaS.L., Renandin J.Y. A simple inexpansive^echnique for accurate mass localisation by computerized tomography. Technical note // J.Neurosurg. — 1980. - V.52, № 6. - P.733-735.
Nagaseki Y., Tamura M., Horikoshi S. Evolution of traumatic intracerebral hematoma // Neural.Med.-Ghir. — 1984. -V.24, №5.-P.316- 323.
Nakashima K, Yamashita K, Ucsugi S. et al. Temporal and spatial profile of apoptotic cell death in transient intrac erebral mass lesion jj» the rat. // J Neurotrauma. 1999,16,2:143-51.
Nakazawa S., Kobayashi S., Okada T. The significance of delayed traumatic intracerebral hematoma // 8-th Europ.Oongr. Neurosurgery. Barcellona, Spain, 19 87. — P. 343.
Nath F., Kelly P. et al. Experimental intracerebral haemorrhage: effects on blood flow, capillary permeability and histochemistry // J. Neurosurg. 66, 1987, p.555—560.
Nath P.P., Nicholls D., Fraser R.J.A. Prognosis in intracerebral ha-emorrhage // Acta Neurochir. — 1983. — V. 67, № 1-2. - P, 29-35.
Nehis D., Mendelow A. et al. Experimental intrace rebral haemorrhage: progression of haemodynamic changes after production of a spontaneous mass lesion // Neurosurgery 23, 1988, p.439-442.
Nelson P.В., Rosenbaum A.E., Delayed deteriora tion in the syndrome of temporal lobe contusion: evaluation by computed tomography (CT) // J.Traurntol. — 1982. — V.22, № 1.-P. 39-42.
New P.F.J., Aronow S. Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography // Radiology. -Г6. - V. 121, №4. - P.635-640.
Niizuma H., Otsuki Т., Johkura H. et al. CT-guided stereotactic aspiration of intracerebral hematoma result of a
hematoma lysis method using urokinase // Appl.Neurophysiol. — 1985. - V.48, № 1-6. - P.427-430.
Ninchoji Т., Uemura K., Shirnoyama 1. et al. Trau matic intracerebral haematoraas of delayed onset // Acta Neurochir.-1984. -V.71,№ 1-2. - P.69-90.
Ogura K., Yamamoto К., Нага M, et al. CT of the traumatic hematoma in the corpus callosum // Neurol.Surg. — 1982. - V.10, № 12. - P.1299-1301.
Ohmori H., Miyazaki S., Munckatak et al. On — the patogenesis of traumatic intracere'bral hematoma with a se quential study of computerized tomography // Progr.Comput. tomogr, - 1984. - V. 3 P. 181 -184.
Ommaya AK, Gennarelli T: Cerebral concussion and traumatic unconsciousness. Correlation of experimental and clinical observations on blunt head injuries. Brain 97:633— 654,1974.
Oro J. Comment on Terada Т., Okuno Т., Moriwaki H. et al. Chronic encapsulated, intracerebral hematoma during infancy; case report // Neurosurgery. — 1985 — V.I6,Кб. — P. 835.
Ovul 1., Ouer K. Intracerebral hematoma after evac uation of chronic subdural hematoma // Neurochirurgia. — 1988. - V.31. № 5. - P.160-162.
Paillas J.F. Sedan R., Combalbert A., Lavieille J. L'hematome intracerebral traumatique (Apropos de 20 ob servations) // Marseille Ohir. - 1962. - V. 2. - P. 111-120.
Pan D.H.C., Lee I.S., Chen M.S. et al. Modified Screw-and-Sucti on technique for stereotactic evacuation of deep intracerebral hematomas// Surg.Neurol. — 1986. — V.25, № 6. - p.540-544.
Papo I., CaruselH G., Scarpelli M. Time course in intracerebral traumatic hematomas // Intracranial Pressure IV/Eds. K.Shulman etal. — Berlin-Hcidelberg-N.Y.:Springer, 1980. - P. 33-35.
PariekJ., Malec R., Sercl M. et al. Pourazova krvace- ni a infarkty bazalnich ganglii u deti // Geskosl.Neurol. Neu- rochir.-1984. - V.47, № 6. - P. 370-376.
Parkinson D., Newry E.G., Taylor J. Trauma in in tracerebral hematomas // Spontaneous intracerebral haemato- mas/Eds.H.W. Pia ct al. - Berlin:Springer, 130. - P. 317— 319.
Parkinson D., Newry E.G., Tubman D. Indications and operative treatment of traumatic ICH // Spontaneous intracerebral haematomas /Eds.H.E.Pia. etal. — Berlin: Sprin ger, 1980.—P.317—319.
Parkinson D., Newry E.G-., West M. Prognosis in traumatic ICH // Spontaneous intracerebral haematomas / Eds.H.W.Pia et al. - Berlin:Springer, 1980. - P.202-213.
Paxton R., Ambrose J. The EMI scanner. A brief re view of the first 650 patients // Br.J.Radiol. —1974. -V. 47.— P. 530-565.
Penning L. CT localization of a convexty brain tumor on the scalp. Technical note // J.Neurosurg. — 1987. — V.66, K4. - P. 474-476.
Peters G. Schadigungen des Zentralnervensystem durch Ultrastrahl // Handbuch der Speziellen pathologis- chen Anatomie und Histologie. — Berlin:Springer, 1955. — Bd.33»reil3.-S. 84-91.
Peystcr R.S., Hoover E.D. CT in head trauma // J.Trauma.. — 1982. -V.22, № 1. - P.25-38.
Picard L., HermannsN., Rogert L. etal. Indications de la tomodensitomctrie dans les traumatismes cranions graves //J.Neuroradiol. - 1983. -V.10. - P.149-153.
Pineda A. Computed tomography in intracerebral haemor rhage // Surg.Neurol. - 1977, - V.8. — KI. - P.55-58.
359
Клиническое руководство по черепно-мозговой травме
Piskun.V.S., Stevens E.A., Lamorgese J.R. ctal. A simple method of CT assisted localization and biopsy of intracranial lesions // Surg.Neurol. - 1979. - V. 11, № 6. - P.413-417.
Possatt E., Giuliani G., Gaist G. et al. Chronic expan ding intracerebral hematoma// J.Neurosurg. — 1986. — V.65. №5.-P. 611-614.
Pretorius I.E., Kaufman H.H. Rapid onset of de layed traumatic intracerebral hematoma with diffuse intra- vascular coagulation and fibrunolisis // Acta Neurochir. — 1982.-V.65, № 1—2.P. 103-109.
Probst G., Schubinger 0. Localisation de petits pro- cessus sous-corticaux situes au nivcau de zones fonctionellcs importantes par tomodensitometrie preoperatoire //Neuro- chirurgie. 1987. - T.33, № 4. - P.244-247.
Raufman H., Sadhu H., Clifton V.K. et al. Delayed intracerebral hematoma due to traumatic aneurysm caused by a shotgun wound. A problem in prophylaxis // Neurosur- gery. - J980. - V. 6, №2. - P.181—184.
Reilly PL, Graham Dl, Adams JT, et al: Patients with head injury who talk and die. Lancet 2:375—377, 1975.
Rivano C, Borzone M., Carta, Michelozzi G. Trau- rflatic intracerebral hematomas. 72 cases surgically — treated //J.Neurosurg.Sci. — 1980. — V.24, № 2. — P.77-84.
Roberson F.C., Kishore P.R.S., Miller J.D. et al. The value of serial computerized tomography in the man agement of severe head injury // Surg.Neurol. — 1979. — V.12, №3. - P. 161 — 167.
Roob G., Kleinert R., Seifert Т., et al. Indications of cerebral microhemorrhage in MRI. Comparative histological findings and possible clinical significance. //Nervenartz 1999, 70, 12: 1082-7.
Sakamoto Т., Kinoshita Y., Yoshioka T. ct al. Delayed surgery for traumatic intracerebral hematoma//Neurol.Mcdi. Chir.-1988.-^28, №2. - P. 164-169.
Sautreayx J.L., Binnert D., Thierry A. et al. La scan- ographic en traumatologie cranienne. Etude critiaque de 100 cas.//Neurochirurgie. — 1982. — T.28, № 4. — p.263-270.
Saweda, Y, Sadomitsu, D., Sakmoto, T. ct al. (1984) Lack of correlation between delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma and disseminated iniravascular coagulation. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 77,1125—1127.
Schacht L., Minauf M. Zentrale Hirnschaden nach Einwir-kung Strumpfer Gewalt a-uf den Schadel. I.Bakken- lasionen //Arch, Psychiat.Nervcn.Krank. — 1965. — Bd.207. — 3.416-427.
Schazfctter F. Intracerebral hematoma: indication for surgical treatment // Ther.Umsch. — 1981, — Bd. 38, № 8. -3.762-766.
Scheinker I.M. Vasoparalysis of the central nervous system. Characteristic vascular syndrome—significance in the pathology of centra] nervous system//Arch.Neurol.Psychiat. — 1944.V.52.-P.43-56.
Schmidek H., Sweet W. (eds): Operative neurosurgi- cal techniques. 1st ed., Grune and Stratton: Ney York, 1982.
Schneider RC, Lemmen LJ, Bagchi BK: The syndrome of traumatic intrace rebel la r hematoma. With contrecoup su- pratcntorial complications. / Ncurosurg 10—122—137,1953.
Schonauer M, Schisano G, Cimino R, Viola L: Space occupying contusions of cerebral lobes after closed brain injury. Considerations about 57 cases. / Neurosurg Sci 23:279—288, 1979.
Schulz W., Harms L., linger R.R., Synowitz H.J. Ein einfaches Hilfsmittel fur die Lokalisation von intrak- raniellen Prozessen im zerebraien Gomputertomogramm // ZhI.Neurochir. -1986.-V.47, № 1. - P.72-75.
292. Schutz H.J., Lochucr В., Agnoli A., Hufnagel A. Welche Voitcile bictet dia Magnctresonanziomographie gegenu- ber der computertomographie bei der Darstcllung spontaner Himblutungen? // Nervenarzt. - 1988. - Bd. 59, № II. - p.654-660.
293. Scott W.R., Miller B.R. Intraccrebral hemorrhage with rapid recovery// Arch.Neurol. - 1985. - V.42. — P. 133-136.
Scott W.R., New P.F.J., Davis K.R., Schur J.A. Computerized axial tomography of intracerebral and mtraven- tricular hemorrhage // Radiology. — 1974. — V.I 12, № I. — P.73-80.
Shallat R., Taekman M., Nagel R. Delayed compli cation of cranioccrebral trauma-: Case report // Neurosur gery. - 1981.-V. 8.-№5. - P. 569-573.
Shigemori M., Kojyo N., Yuge Т., Tolcutomi T. Massive traumatic haematoma of the corpus callosuin // Acta Neurochir. -1986. - V.8I, № 1-2. - P.36-39.
Shigemori M., Tokutomi Т., Shirahama M. ct al. Massive traumatic hematoma localized in the basal ganglia // Neurol. Med.Chir. - 1981. - V.2I,H8. - P.697-700.
Shiroyama Y., Ikeyama Y., Aoki H. et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage immediately following the operation for chronic subdural hematoma// Neurol.Surg. — 1989. — V.I7, № 8. — P. 759-762.
Sipponcn J.T., Sepponen R.E., Sivula A. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging of intracerebral hem orrhage in the acute and resolving phases // J.Gomput. Assist. Tomogr. - 1983. - V.7.-P. 954-959.
300.Sipponcn J.T., Sepponen R.E., Tauttu J.I., SivulaA. Intracranial hematomas studied by MR imaging at 0,17 and 0.02 T//J.Gomput. Assist. Tomogr. - 1985. - V. 9. - p.698-704.
Skriver E.B., Olscn T.S. Tissue damage at computed tomography following resolution of intracerebral hematomas //ActaRadiol.Biagn. - 1986. - V. 27, № 5. - P. 495-500.
Smith D.R., DuckerT.B., Kempe L.G. Experimen tal in vivo microcirculatory dynamics in brain trauma // J.Neurosurg.-1969. - V.30, № 5. - P.664-672.
Sokol JH, Rowed DW: Traumatic intracerebellar haemotoma. Surg Neurol 10:340-341, 1978.
Soloniuk, D., Pitts, L. H., Lovely, M. et al. (1986) Traumatic intracerebral haematomas: timing of appearance and indications for operative removal. Journal of Trauma, 26, 787-794.
Swensen S.J., Keller P.L., BerquistT.H. ctal. Magnet ic resonance imaging of hemorrhage // Am. J. Roentgen. - 1985 - V.145, № 5. - P.921-927.
Symonds CP: Delayed traumatic intracerebral haem orrhage. BrMedJ 1:1048-1051,1940.
Takahashi N., Kikuchi H., Kobayashi K., Kaeasawa J. Multicular encapsulated intracerebral hematoma // Neurol.Surg. -1983. - V.I 1, № 8. - P.739-743.
Tandon S.C., Gupta S.K. Traumatic intracerebellar haematomas // 9-th Intern.Congr.Neurol.Surg. — New Del hi, 1989. —P.348.
Taneda M., Irino T. Enlargement of intracerebral haematomas following surgical removal of epidural haemato mas//Acta Neurochir. - 1979 - V.51, № 1-2. - P.73-82.
Tanikawa Т., Amano K., Kawamura H. ct al. CT- guided stercotactic surgery for evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematoma // Appl.Neurophysiol, — 1985, - V.48, № l-гб. - P.431-439.
Tanizaki Y., Sugita, K., Toriyama Т., Hokama M. New CT-guided stereotactic apparatus and clinical experi ence with intracerebral hematomas // Appl.Neurophysiol. — 1985.-V.48, № 1-6.-P.
360
Внутримозговые гематомы
Teasdale E., Cardosa E., Galbraith S., Tcasdale G. CT scan in severe diffuse head injury: physiological and clin ical correlations//J.Neurol.Neurosurg.Psychiat. — 1984. — V.47, №6.-P. 600—603.
Teasdale G., Galbraith S., Jennett B. Operate or observe ICP and the management of the «silent» traumatic intracranial haematoma. // Intracranial Pressure IV. — Berlin ctc.;Springcr, 1980. - P.36-38.
Teasdale G., Galbraith S., Murray L. et al. Manage ment of traumatic intracranial haematoma // Br.Med.J. — 1982. - V. 285. - P. 1695-1697.
Teasdale G., Galbrith S., Jennett В.: Operate, ob serve? ICP and the management of the silent traumatic in tracranial hematoma // In Shulman K., Marmarou A., Mill er J. Et al. (eds): Intracranial pressure IV, Berlin, Springer- Verlag, 1980, pp.36—38.
Terada Т., Okuno Т., Moriwaki H. et al. Chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma during infancy: case report//Neurosurgery. - 1985. — V.16, № 6. — P. 833—835.
Thierry A., Binnert D., Foissac J.G. et al. Contrast medium exstravasation in traumatic intracerebral haemato ma // Neuroradiology. - 1973. - V.5, № 2. - P. 178-180.
318. Toczek, Morrell, Silverberg G. et at.: Cercbellar Hemorrhage Complicating Temporal Lobectomy: Report of Four Cases. J Neurosurg.85; 718-22,1996.
Todzawa Т., «Discussion» conservative treatment for the acute stage traumatic intracranial hematoma, Kuroiwa T. et al. // Neurol.Med.-Chir. - 1985. - V.25,K3. - P.181-186.
Tsai P.Y., Huprich J.E., Gardner F.C. et al. Diag nostic and prognostic implications of computed, tomogra phy of head trauma // J.Gomput.Assist.Tomogr. — 1978. — V.2. - p.323-331.
Tsementzis S.A. Surgical management of intracere bral hematoi^as // Neurosurgery. — 1985. — V.16, № 4. — P.562—572>
Tsubokawa RT., Ueno Y., Kondoh T. et al. Bleeding mechanism of delayed traumatic intracerebral hematomas // Shinkei Saisho. - 1980.-V.3.- P. 147-153.
Tsubokawa Т., Jones U. Treatment of traumatic intracerebral hematoma//Nihon.Univ. J.Med. — 1976. — Y.I8, №4. - P.305-321.
Tsubokawa Т., Sidican S.E., Yamada J., Moriuyasu N. New classification of traumatic intracerebral hematoma // MihonUniv. J.MecL. - 1979. - V.21, №4. - P.309-320.
Tsubokawa Т., Two types of delayed post-traumatic intracerebral hematoma // Heurol.Med.-Ghir. — 1981. — V. 21, H7. - P. 669-675.
Tsubokawa Т., Yamada J., Tomizawa N. et al. Classifica tion of traumatic intracerebral hematoma by repeated CT scan and clinical course // Neurol.Med.-Ghir. — 1979. — V.19,Mil.-P. 1127-1137.
Tsukahara Т., Nishikawa M., Iwama M., Kirn S. Trau matic intracerebra! midline haematoma // Acta Neurochir. — 1982. - V.62, № 1-2. - P.73-77.
Ueda S., Ebisdani D., Ban M. et al. Frontobasalis injuries CT findings in delayed traumatic intracerebrai he matoma // Ptoc.4-th Conf. Japan. Soc. Neurotraumatology. — 1981,V.4—P. 1-9.
Ugrumov VM, Zotov YV, Shchedryonok VV: Early surgical treatment of traumatic intracranial haematomas and laceration foci as the main factor for favourable prognosis. Acta Neurochir (Suppl) 28:199-200,1979.
330. Vara-Thorbeck R. Delayed traumatic apoplexy //Spon taneous intracerebrai haematomas /Eds.H.W.Pia et al. - Beriin:Springer, 1980. — P.77—82.
Vigouroux R.P., Guillermain P. and Rabehauta P. Cerebral contusions and lacerations // Advances in Neurn- traumatology 3, 1991, p.91-99.
Wagner K., Xi G., Hua Y. et al. Lobar intracerebral hemorrhage model in pigs: rapid edema development in peri- hematomal white matter. // Stroke, 1996,27,3:490-7.
Wardlaw J., Statham P. How often is haemosiderin not visible on routine MRI following traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage? // Neuroradiology, 2000,42,2:81-4.
Weigcl K., Ostertag СВ., Mundinger F. CT follow- up control of traumatic intracerbral hemorrhage // Adv.Neurosurgery. 1978. - V.5. - P.62—67.
Yamamoto M., Jimbo M., lde M. Conservative treat ment of traumatic intracerebral hematoma // Ncurol.Surg. — 1984.-V. 12, № 10.-P. 1131-1138.
Yamamoto M., Suginza M., Yochida S. et al. Com puterized tomography of acute severe head, trauma // Neurol.Med.-Chir. -1979. - V.19, № 17. - P.27.
Yamanaka R., Salon S. Comparison of stereotactic aspiration, craniotomy and conservative treatment for puta- menal hemorrhage // Neurol.Med.-Ghir. - 1988. - V.28, № 10.- P.986-990.
Yamaura A, Uemura K, Makino H: Large decompre- sivc craniectomy in management of severe cerebral contusion. A review of 207 cases. Neurol MldChlr (Tokyo) 19:717-728,1979.
Yokota H., Kobayashi S., Yajima K. ct al. Clinical study of traumatic intracercbcllar hemorrhage // Neurol.Mcd. — Chir. - 1985. - V.25, № 10. - P.844-849.
Yokote H., Kornai N., Nakai E. et al. Stereotactic eva cuation of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage using plasminogen activator //Neurol.Surg. - 1989. - V.17, № 5. - P. 421-425.
Young, H., Cleave, ]., Schmidex, H. and Gregory, S. (1984) Delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma; a report of 15 cases operatively treated. Neurosurgery, 14,22—25.
Zhang Y. Non-operative therapy for acute traumatic intracranial hematoma // 9-th Intern. Congr.Neurol. Surgery. — Abstr-Ncw Delhi, India, 1989. - P.337.
Zimmerman R.A., Bilaniuk 1.Т., Gennarelli T. et al. Cranial computed tomography in diagnosis and management of acute head trauma // Am.J.Rocngenol. — 1978. — V.131, №1.-P. 27-34.
Zimmerman R.A., Bilaniuk L.T., Grossman R.I. et al. Resistive NMR of intracranial hematomas // Neuroradi ology.-1985. -V.27, № 1.- P.16-20.
Zimmerman R.A., Bilaniuk L.T., Hockney D.B. et al. Head injury: early results of comparing CT and high-field MR //Am.J.Roentgenol. - 1986. - V.147, № 6. - P. 1215—1222.
Zimmerman R.A., Bilaniuk li.T. Computer tomog raphy of traumatic intracerebral hemorrhagic lesions: the change in density and mass effect with time //Neuroradiol ogy. - 1978. - V. 16, № 3. - P. 320-321.
Zimmerman R.A., Leeds N.E., NaidichT.P. Ring blush Associated with intracerebral hematoma // Radiology». — 1977.-V. 122.-H3. -P.707-71 1.
Zimmerman R.D. Intracranial hematomas: imaging by high-field MR // Radiology. - 1986. - V.159, № 2. - p.565-566.
Zimmerman R.D., Heier L.A., Snow R.B. e-bal. Acute intracranial hemorrhage: Intensity changes on sequential MR scan at 0,5 T//Am.J.Roentgenol. - 1988. - 7.150, № 3.— P.651—661.
350. Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Dolinskas C, Gennarelli T. Bruce D, Uzzell B: Computed tomography of acute intracerebral hemorrhagic contusions. // Comp Axial Tomogr 1:271-280, 1977.
361
