
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgments
- •Introduction
- •Cardiac Tissue Engineering
- •Objectives and Scopes
- •Organization of the Monograph
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •The Heart and Cardiac Muscle Structure
- •Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure
- •Congenital Heart Defects
- •Endogenous Myocardial Regeneration
- •Potential Therapeutic Targets and Strategies to Induce Myocardial Regeneration
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Human Embryonic Stem Cells
- •Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- •Direct Reprogramming of Differentiated Somatic Cells
- •Cardiac Stem/Progenitor Cells
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Basic Biomaterial Design Criteria
- •Biomaterial Classification
- •Natural Proteins
- •Natural Polysaccharides
- •Synthetic Peptides and Polymers
- •Basic Scaffold Fabrication Forms
- •Hydrogels
- •Macroporous Scaffolds
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Biomaterials as Vehicles for Stem Cell Delivery and Retention in the Infarct
- •Introduction
- •Stem Cell Delivery by Biomaterials
- •Cardiac Stem/Progenitor Cells
- •Clinical Trials
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Myocardial Tissue Grafts Created in Preformed Implantable Scaffolds
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Bioreactor Cultivation of Engineered Cardiac Tissue
- •Mass Transfer in 3D Cultures
- •Bioreactor as a Solution for Mass Transfer Challenge
- •Perfusion Bioreactors
- •Inductive Stimulation Patterns in Cardiac Tissue Engineering
- •Mechanotransduction and Physical/Mechanical Stimuli
- •Mechanical Stimulation Induced by Magnetic Field
- •Electrical Stimulation
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Prevascularization of the Patch by Incorporating Endothelial Cells (ECs)
- •The Body as a Bioreactor for Patch Vascularization
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Decellularized ECM
- •Injectable Biomaterials
- •Injectable hydrogels based on natural or synthetic polymers
- •Injectable Decellularized ECM Matrices
- •Mechanism of Biomaterial Effects on Cardiac Repair
- •Immunomodulation of the Macrophages by Liposomes for Infarct Repair
- •Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Macrophage Response after MI
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Evolution of Bioactive Material Approach for Myocardial Regeneration
- •Bioactive Molecules for Myocardial Regeneration and Repair
- •Injectable Systems
- •Sulfation of Alginate Hydrogels and Analysis of Binding
- •Injectable Affinity-Binding Alginate Biomaterial
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography

9.8. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 133
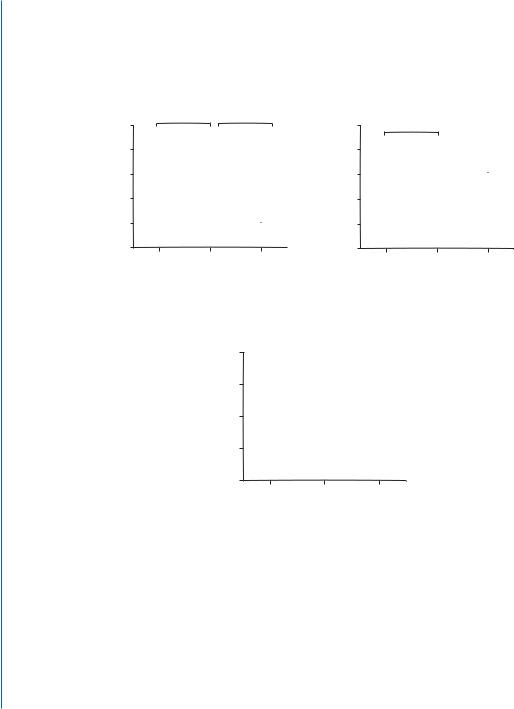
ative macrophages), concomitant with down-regulation of the surface marker of pro-inflammatory macrophages, CD86. An intramyocardial injection of PS-presenting liposomes induced cardiac macrophages to secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines (TGFβ and IL-10) and reduced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) as early as three days after treatment, one day earlier than without treatment (Fig. 9.3A).
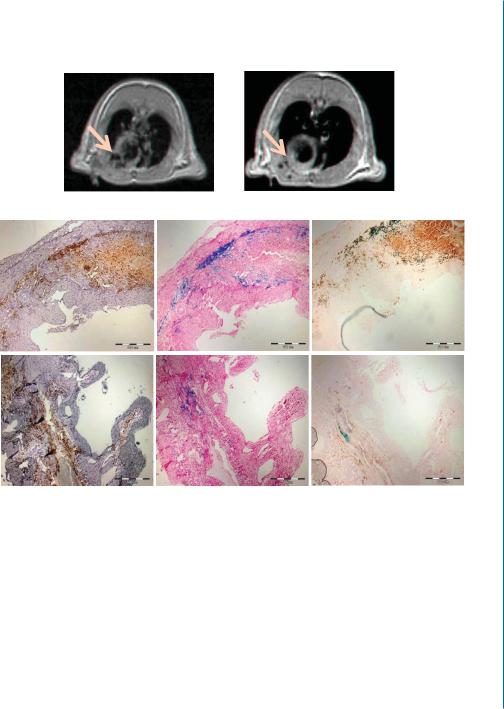
We then demonstrated the ability of PS-presenting liposomes to target the infarct after i.v. injection and be engulfed by cardiac macrophages using liposomes containing iron-oxide and their follow-up by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and immuno-staining of cross-sections for ED-1 (macrophage marker, brown stain) and for iron (blue stain). The liposomes were injected through the femoral vein, 48 h after MI induction in rats. MRI scans and histology of the hearts 4 d later revealed the presence of resident and/or infiltrating macrophages at the infarct that had taken up PS-presenting liposomes and accumulated in the infarct (Fig. 9.3B).
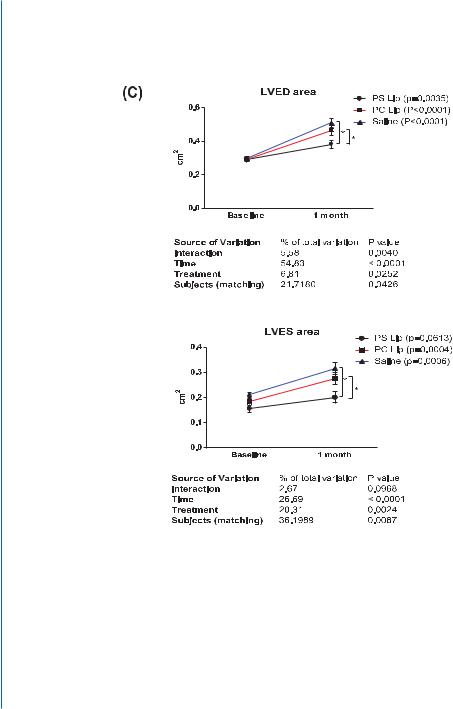
The finding that PS-presenting liposomes can be targeted to the infarct after i.v.administration and be taken up by cardiac macrophages prompted us to test the efficacy of this strategy to improve infarct repair after MI. The treatment was performed 48 h after MI induction because at this time point the macrophages are found in greater numbers at the infarct than immediately after MI. Treatment with PS-presenting liposomes by i.v. administration enhanced angiogenesis at the infarct compared to infarcts treated with PS-lacking liposomes or saline; it preserved infarct thickness to a better extent and prevented infarct expansion. Echocardiography studies showed that LV end systolic and diastolic areas (LVES and LVED areas) were more preserved after the treatment with PS-presenting liposomes, suggesting that this treatment is capable of preventing the LV remodeling associated with MI (Fig. 9.3C) [44].
Our results suggest that the modulation of recruited or resident cardiac macrophages by applying PS-presenting liposomes is feasible, leading to attenuation in left ventricle remodeling and prevention of heart dilatation. Its nature-mimicking mechanism, defined composition, and plausible delivery options make this strategy a unique and applicable approach for MI treatment. With respect to translation into the clinics, the strategy of using autologous apoptotic cells to treat chronic heart failure has been clinically tested (ACCLAIM trial) showing some benefit for the treatment [37]. Yet, there are concerns using autologous apoptotic cells because this treatment can ameliorate autoimmune diseases, for example, via the release of auto-antigens. The use of welldefined PS-presenting liposomes abrogates the concerns associated with apoptotic cell treatment, while still benefiting from their anti-inflammatory effect and positive effects on infarct repair.
9.8SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
Acellular biomaterials and scaffolds in various forms were shown to be effective for myocardial repair, by creating a more favorable environment for healing, while simultaneously providing mechanical support to the infarcted wall. The clinical applicability of the acellular biomaterial strategy has been intensified with the development and use of injectable forms of biomaterials, delivered as hydrogels
134 9. ACELLULAR BIOMATERIALS FOR CARDIAC REPAIR
$
QJ PO
D |
,/ 6HFUHWLRQ |
3 |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
7*)Ε6HFUHWLRQ |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QJ PO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 OLS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
6DOLQH |
|
|
3& OLS |
|
|
|
6DOLQH |
36 OLS |
3& OLS |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
F
QJ PO
71) 6HFUHWLRQ
|
|
|
|
3 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6DOLQH |
36 OLS |
3& OLS |
Figure 9.3: PS-presenting liposomes as an effective strategy for immunomodulation and infarct repair. A. Immunomodulation of cardiac macrophages after MI. MI was induced in mice, followed by intramyocardial injections of either PS-presenting liposomes (PS lip), PS-lacking liposomes (PC lip), or saline. Three days later, macrophages were isolated from the infarcted hearts, cultured for 24 h and the collected culture medium was analyzed by the respective ELISAs using antibodies against anti-inflammatory (IL10 (a) and TGFβ (b)), and pro-inflammatory (TNFα (c)) cytokines. * denotes statistically significant difference.
9.8. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 135
% |
D |
36 /LSRVRPHV |
6DOLQH |
E |
(' |
,URQ |
(' ,URQ |
|
36 OLS |
36 OLS |
36 OLS |
6DOLQH |
6DOLQH |
6DOLQH |
Figure 9.3: PS-presenting liposomes as an effective strategy for immunomodulation and infarct repair. B. In vivo uptake and accumulation of PS-presenting liposomes in cardiac macrophages after i.v. administration to rats, 48 hours after MI induction. a. MRI scans of in vivo uptake and accumulation of PS-presenting liposomes, 4 days after injection. The dark areas in the coronal sections represent macrophages, which have uptaken PS-presenting liposomes containing the iron oxide. b. Histology/immuno-histochemistry of cross-sections from mice hearts. Four days after liposome injection, the animals were sacrificed and hearts were fixated and sliced for histology and immuno-staining for ED1 (a marker for resident macrophages, brown) and iron oxide (blue). Bar = 500 μm.
136 9. ACELLULAR BIOMATERIALS FOR CARDIAC REPAIR
Figure 9.3: PS-presenting liposomes as an effective strategy for immunomodulation and infarct repair. C. Effect of i.v. injected PS-presenting liposomes on LV remodeling after MI. Results of echocardiography study for measured LV end systolic and diastolic (LVES and LVED) areas. * denotes statistically significant difference [44].
