
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgments
- •Introduction
- •Cardiac Tissue Engineering
- •Objectives and Scopes
- •Organization of the Monograph
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •The Heart and Cardiac Muscle Structure
- •Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure
- •Congenital Heart Defects
- •Endogenous Myocardial Regeneration
- •Potential Therapeutic Targets and Strategies to Induce Myocardial Regeneration
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Human Embryonic Stem Cells
- •Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- •Direct Reprogramming of Differentiated Somatic Cells
- •Cardiac Stem/Progenitor Cells
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Basic Biomaterial Design Criteria
- •Biomaterial Classification
- •Natural Proteins
- •Natural Polysaccharides
- •Synthetic Peptides and Polymers
- •Basic Scaffold Fabrication Forms
- •Hydrogels
- •Macroporous Scaffolds
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Biomaterials as Vehicles for Stem Cell Delivery and Retention in the Infarct
- •Introduction
- •Stem Cell Delivery by Biomaterials
- •Cardiac Stem/Progenitor Cells
- •Clinical Trials
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Myocardial Tissue Grafts Created in Preformed Implantable Scaffolds
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Bioreactor Cultivation of Engineered Cardiac Tissue
- •Mass Transfer in 3D Cultures
- •Bioreactor as a Solution for Mass Transfer Challenge
- •Perfusion Bioreactors
- •Inductive Stimulation Patterns in Cardiac Tissue Engineering
- •Mechanotransduction and Physical/Mechanical Stimuli
- •Mechanical Stimulation Induced by Magnetic Field
- •Electrical Stimulation
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Prevascularization of the Patch by Incorporating Endothelial Cells (ECs)
- •The Body as a Bioreactor for Patch Vascularization
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Decellularized ECM
- •Injectable Biomaterials
- •Injectable hydrogels based on natural or synthetic polymers
- •Injectable Decellularized ECM Matrices
- •Mechanism of Biomaterial Effects on Cardiac Repair
- •Immunomodulation of the Macrophages by Liposomes for Infarct Repair
- •Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Macrophage Response after MI
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography
- •Introduction
- •Evolution of Bioactive Material Approach for Myocardial Regeneration
- •Bioactive Molecules for Myocardial Regeneration and Repair
- •Injectable Systems
- •Sulfation of Alginate Hydrogels and Analysis of Binding
- •Injectable Affinity-Binding Alginate Biomaterial
- •Summary and Conclusions
- •Bibliography

9.7. IMMUNOMODULATION OF THE MACROPHAGES 131
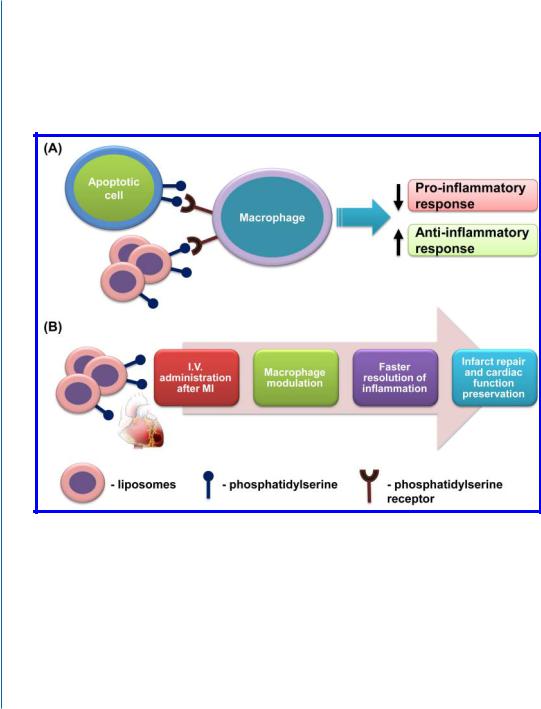
9.7IMMUNOMODULATION OF THE MACROPHAGES BY LIPOSOMES FOR INFARCT REPAIR
Biomaterials mimicking natural processes after MI may be used to influence infarct repair. In this section, we present a new biomaterial-based strategy for the modulation of cardiac macrophages to a reparative state, at a predetermined time after MI, in aim to promote resolution of inflammation and elicit infarct repair.
9.7.1INFLAMMATION, APOPTOSIS, AND MACROPHAGE RESPONSE AFTER MI
Inflammation has emerged as a critical biological process contributing to nearly all aspects of cardiovascular diseases including MI. After MI, cardiomyocyte death triggers a cascade of inflammatory pathways. For the heart, an organ with limited regeneration ability, post-MI remodelling comprises a series of structural and functional changes, all of which have been linked to the activation of the inflammatory pathways. Inadequate or excessive inflammatory response may lead to improper cellular repair, tissue damage, and dysfunction. Thus, the modulation of inflammation as a therapeutical strategy for cardiac repair after MI has become an active research field.
Our group focussed on macrophage modulation as a strategy for inducing cardiac tissue repair. After MI, resident and recruited macrophages remove necrotic and apoptotic cells, secrete cytokines, and modulate angiogenesis at the infarct site. As such, the macrophage is a primary responder cell involved in the regulation of post-MI infarct wound healing at multiple levels [34]. Apparently, different macrophage populations are responsible for these activities; during the early inflammatory phase (phase 1), proinflammatory macrophages dominate the injury site and phagocytose the apoptotic/necrotic myocytes, whereas during inflammation resolution (phase 2), the dominant macrophage population is the reparative macrophages, which promote infarct repair [35, 36]. The duration and extent of the early inflammatory phase have major implications on infarct size and ventricular remodelling.
Thus, we hypothesized that immunomodulation to control the duration of the different inflammation phases following MI could be a therapeutic target to improve infarct healing and repair. Until our study, most, if not all, investigated immunomodulation strategies for myocardial repair relied on the delivery of various growth factors or activated cells (macrophages, apoptotic cells, stem cells) [37, 38]. Such approaches are less clinically relevant, less safe, and certainly not as reproducible and accessible as an acellular system, and therefore have less potential to serve as a treatment for inflammation associated with MI in patients.
9.7.2PS-PRESENTING LIPOSOMES AS APOPTOTIC CELL-MIMICKING PARTICLES FOR EFFECTIVE IMMUNOMODULATION AND INFARCT REPAIR
We conceived a novel strategy for controlling the duration and extent of the inflammatory phase following MI, in aim to reduce myocardium damage, preserve infarct size, and prevent ventricle
132 9. ACELLULAR BIOMATERIALS FOR CARDIAC REPAIR
remodeling. Our strategy exploits the principle underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of apoptotic cells, which are known to actively suppress inflammation by inhibiting the release of proinflammatory cytokines from macrophages while augmenting the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as TGFβ and interleukin-10 (IL-10) [39]. Macrophages recognize the apoptotic cells via surface ligands, among them phosphatidylserine (PS), and “silently” clear the cells [40, 41, 42]. In humans, apoptosis after MI occurs mainly in the border zones and in the remote areas of ischemia, which may lead to only minor resolution of inflammation [43].
Figure 9.2: The modulation of macrophages by PS-presenting liposomes as an effective strategy for infarct repair. A. Nature-mimicking mechanism of macrophage modulation and phenotype switch by PSpresenting liposomes. B. Treatment strategy and proposed mechanism of infarct repair by PS-presenting liposomes.
Our strategy is based on the exogenous administration of PS-presenting liposomes, designed to mimic the apoptotic cells and their anti-inflammatory effects (Fig. 9.2).
At first, we demonstrated that following the uptake of PS-presenting liposomes by macrophages in vitro, the cells secreted high levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines, TGFβ and IL-10, and upregulated the expression of the mannose receptor CD206 (a surface marker of repar-
