
- •3219 Методичні вказівки
- •Immunity
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Give the explanation of following terms:
- •2 Say what type of immunity is spoken about:
- •Organs of the Immune System
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Find in the text English equivalents for the following sentences:
- •2 Make up a dialogue.
- •3 Give the explanation of following terms:
- •4 Discuss the picture given in the text.
- •Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Answer the questions:
- •2 Respond to the following tasks:
- •Myths about hiv and aids
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Explain with your own words why myths about hiv are dangerous.
- •2 Say what group of myths is spoken about:
- •3 Look at the statements and say whether they are true or false. But don’t answer only «It’s true», or «It’s false», try to give your own explanation to the given statement.
- •Hiv Treatment
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Give full answer to given survey questions:
- •2 Respond to the following tasks:
- •3 Answer the following:
- •4 Find in the text English equivalents for following sentences:
- •Allergy
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Translate the following terms and use them in making sentences of your own:
- •2 Translate the following:
- •3 Respond to the given assignments:
- •Endocrine System
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Give the meaning of the following:
- •2 Choose the proper continuation:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •4 Give the explanation of following terms:
- •Endocrine System Disorders
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Respond to the following tasks:
- •2 Find in the text English equivalents for the following sentences:
- •3 Describe the symptoms of one of the endocrine system disorders for other students to guess.
- •4 Render the text Endocrine System Disorders.
- •Respiratory System
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Answer the questions:
- •2 Say what organ is spoken about:
- •Unit 10
- •Respiration
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Explain the mechanisms of inhalation and exhalation using the picture given in the text.
- •2 Respond to the following tasks:
- •Unit 11
- •Respiratory System Disorders
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Give the explanation of following terms:
- •2 Match the definition of the disease in column I with the name of the disease in column II:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Unit 12
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Match the definition of the disease in column I with the name of the disease in column II:
- •2 What myths about asthma do you know? Try to disprove them. Unit 13
- •Nervous System
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Answer the questions:
- •2 Retell the stages of neurotransmittion using the picture given in the text. Unit 14
- •Nervous System Disorders
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Match the definition of the disease in column I with the name of the disease in column II:
- •2 Translate the following:
- •Unit 15
- •The Brain
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Say what part of brain is spoken about:
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Unit 16
- •Human Sense Organs
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Translate the following:
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •Unit 17
- •The Human Eye
- •Visual purple
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Describe the structure of the human eye using the picture in the text.
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Unit 18
- •The Human Ear
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Describe the structure of the human ear using the picture in the text.
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Unit 19
- •The Human Skin
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Describe the structure of the human skin using the picture in the text.
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Unit 20
- •Dermatitis
- •Post-text assignments
- •1 Match the definition of the disease in column I with the name of the disease in column II:
- •2 Answer the questions:
- •3 Translate the following:
- •Список літератури
- •Методичні вказівки
Post-text assignments
1 Match the definition of the disease in column I with the name of the disease in column II:
I |
II |
1 Disease affects people during or after physical activity. |
a) nocturnal Asthma |
2 Disease is induced by triggers that exist in a person’s workplace. |
b) cough-variant asthma |
3 Disease is triggered by allergens, such as pet dander, food preservatives, mold, or pollen. |
c) Exersice Indused asthma |
4 The symptoms of this disease worsen at night |
d) non-allergic asthma |
5 Disease is triggered by irritants in the air that are not related to allergies. |
e) occupational asthma |
6 Disease is characterized by one symptom, a persistent dry cough |
f) allergic asthma |
2 What myths about asthma do you know? Try to disprove them. Unit 13
Pre-text assignment
Learn the key words and phrases:
stimuli, spinal cord, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic system, parasympathetic system, acetylcholine, norephinephrine, serotonin, motor nerves, involuntary, neurotransmitter.
Nervous System
The nervous system is composed of all nerve tissues in the body. The functions of nerve tissue are to receive stimuli, transmit stimuli to nervous centers, and to initiate response. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord and serves as the collection point of nerve impulses.
The peripheral nervous system includes all nerves not in the brain or spinal cord and connects all parts of the body to the central nervous system. The peripheral (sensory) nervous system receives stimuli, the central nervous system interprets them, and then the peripheral (motor) nervous system initiates responses.
The somatic nervous system controls functions that are under conscious voluntary control such as skeletal muscles and sensory neurons of the skin.
The autonomic nervous system, mostly motor nerves, controls functions of involuntary smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands. The autonomic nervous system provides almost every organ
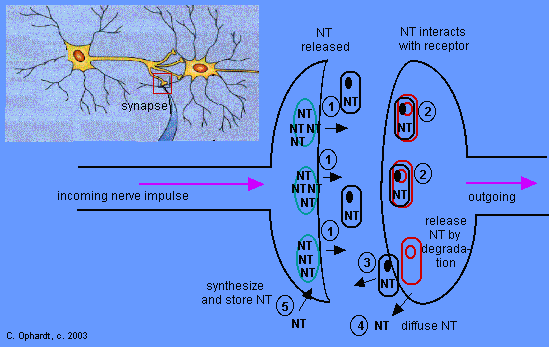
Figure 5 – Neurotransmitter (NT) in Synapse
with a double set of nerves - the sympathetic and parasympathetic. These systems generally but not always work in opposition to each other.
The sympathetic system activates and prepares the body for vigorous muscular activity, stress, and emergencies. While the parasympathetic system lowers activity, operates during normal situations, permits digestion, and conservation of energy.
The two systems generally act in opposition to each other. For example, a stimulation by the sympathetic system on the heart would increase contractions, while a stimulation by the parasympathetic system would decrease heart contractions. Where dual control of an organ exists, both systems operate simultaneously although one may be operating at a higher level of activity than the other. The operation is similar to the operation of a car with both the accelerator and brake pedals depressed.
In the peripheral nervous system, a chemical neurotransmitter carries the nerve impulses from neuron to neuron across a synapse (space between neurons). The neurotransmitters are acetylcholine, norephinephrine, serotonin, and others.
Neurotransmitters
The events in a neurotransmission in the synapse are summarized in the graphic in the text.
1 Release of Neurotransmitter: Transmission of nerve impulses is accomplished when a nerve impulse causes the rupture of vesicles containing the chemical transmitter from the nerve ending.
2 Interaction with Receptor: The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and interacts with receptors located on the membrane of the next neuron. This interaction may produce membrane permeability changes which result in an excitatory response.
3 Degradation of Neurotransmitter: After each impulse it is necessary to inactivate or terminate the neurotransmitter's action. This may be accomplished by degradation as in the hydrolysis of acetylcholine. OR
4 Diffusion from the Receptor: The NT may simply diffuse from the receptor site after a short period of time.
5 Resynthesize or restore NT: The neurotransmitter may be retaken back into the storage site or new NT is synthesized.
And so on and so on and so on.
Remind you of anything?
How about a relay of dominoes in which one standing domino falls and trips the next and the next and the next.
