
- •English for medical students
- •Preface
- •Medicine as a science. Branches of medicine
- •Branches of medicine
- •Basic sciences
- •Diagnostic specialties
- •Clinical disciplines
- •Human organism human anatomy
- •The cell
- •Properties of cells:
- •Cell membrane: a cell's protective coat
- •Cytoskeleton: a cell's scaffold
- •Genetic material
- •Organelles
- •Cell nucleus (a cell's information center)
- •Ribosomes (the protein production machine)
- •Mitochondria and Chloroplasts (the power generators)
- •Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus (macromolecule managers)
- •Lysosomes and Peroxisomes (the cellular digestive system)
- •Centrioles
- •Vacuoles
- •The tissue
- •Human organ systems
- •The anatomical position
- •Relative directions
- •Median and sagittal plane
- •Coronal plane
- •Transverse plane
- •Special cases
- •Body cavities
- •Digestive system
- •Introduction
- •Ingestion
- •Digestion: stomach
- •Digestion and absorption: small intestine
- •Absorption: large intestine
- •Answer the questions
- •Ulcerative colitis
- •Urinary system
- •Introduction
- •Kidneys: location and structure
- •Kidneys: function
- •Urine production
- •Answer the questions
- •Cystitis
- •Reproductive system
- •Introduction
- •Male reproductive organs
- •Female reproductive organs
- •Development of sex cells
- •Answer the questions
- •Vaginismus
- •Prostatitis
- •Nervous system
- •Introduction
- •Cns: neurons, brain, spinal cord
- •Pns: somatic (voluntary) nervous system, autonomic (involuntary) nervous system
- •Sense organs
- •Answer the questions
- •Ischemic stroke
- •Immediate treatment
- •Cardiovascular system
- •Introduction
- •Components of blood
- •How blood clots
- •How red blood cells carry oxygen
- •Blood pressure
- •The heart (the pump)
- •Answer the questions
- •Mitral stenosis
- •Respiratory system
- •Introduction
- •Lungs and air passages
- •Gas exchange
- •Respiration
- •Answer the questions
- •Lymphatic system
- •Introduction
- •Capillary hydrostatic pressure: fluid diffusion and reabsorption
- •Lymph vessels
- •Lymph organs: nodes, nodules, spleen, thymus gland, tonsils
- •Answer the questions
- •Lymphadenitis and lymphangitis
- •Skeletal system
- •Introduction
- •Axial skeleton
- •Appendicular skeleton
- •Ossification and reconstruction
- •Bone marrow
- •Answer the questions
- •Osteoarthritis
- •Muscular system
- •Introduction
- •Cardiac muscle
- •Smooth muscle
- •Skeletal muscle
- •Muscle fibers and exercise
- •Answer the questions
- •Myasthenia gravis
- •Skin (integumentary system)
- •Introduction
- •Skin: epidermal layers
- •Skin: dermal layers
- •Sudoriferous (sweat) and sebaceous (oil) glands
- •Hair and nails
- •Skin color
- •Answer the questions
- •Endocrine system
- •Introduction
- •Glands and neural components
- •Homeostatic feedback mechanisms
- •Pituitary gland
- •Thyroid gland
- •Adrenal glands
- •Ovaries and testes
- •Answer the questions
- •Type 1 diabetes
- •Insulin
- •Vascular disease
- •I. What is cancer?
- •II. Terminology of cancer
- •III. History of oncology
- •IV. Oncological diseases
- •1. Laryngeal cancer
- •Symptoms:
- •Diagnosis:
- •Treatment:
- •2. Lung cancer
- •Causes:
- •Symptoms:
- •Diagnosis:
- •Treatment:
- •3. Colon cancer
- •Causes, incidence, and risk factors:
- •Symptoms:
- •Signs and tests:
- •Treatment:
- •4. Brain tumor
- •Causes, incidence, and risk factors:
- •Symptoms:
- •Signs and tests:
- •Treatment :
- •Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
- •I. Diagnostic radiology
- •II. Therapeutic radiology
- •III. Interventional radiology
- •Answer the questions
- •Pharmacology
- •For the gastrointestinal tract or digestive system
- •For the cardiovascular system
- •For the central nervous system
- •For musculo-skeletal disorders
- •Why we need vitamins
- •Vitamin deficiencies
- •Analgesics
- •Paracetamol and nsaiDs
- •Opiates and morphinomimetics
- •Combinations
- •Topical or systemic
- •Psychotropic agents
- •Addiction
- •Antibiotics
- •Side effects
- •Antibiotic resistance
- •Vaccines
- •Origin of vaccines
- •Developing immunity
- •Potential for adverse side effects in general
- •Answer the questions
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 1
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 2
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 3
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 4
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 5
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 6
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 7
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 8
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 9
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 10
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 11
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 12
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 13
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 14
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 15
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 16
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 17
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 18
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 19
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 20
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 21
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 22
- •I. Learn new combining forms and their meanings
- •II. Do basic exercises
- •III. Do additional exercises
- •IV. Get ready for the test
- •V. Write test 23
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are on top of each kidney. Each gland has a cortex (outer region) and a medulla (inner region). The cortex secretes glucocorticoids such as cortisol, mineralocorticoids, and small amounts of androgens and estrogens responsible for some secondary sex characteristics. Glucocorticoids raise blood sugar levels by increasing gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from amino acid). This action ensures glucose supplies for the body when it is under stress. Mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone promote sodium (salt) reabsorption by stimulating the kidneys to absorb more sodium from the blood.
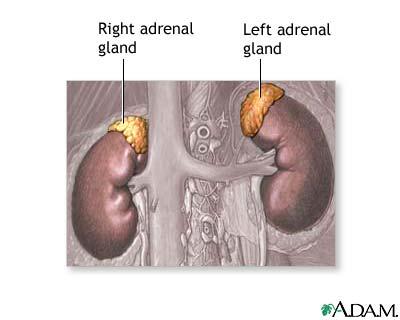
The medulla "emergency gland" develops from nervous tissue; the autonomic nervous system controls its secretions. The medulla secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), chemicals that raise the blood levels of sugar and fatty acids. These hormones also increase the heart rate and force of contraction. These effects prepare the body for the "Fight or Flight" response (instant physical activity), enabling the individual to think quicker, fight harder, and run faster. These hormones also constrict the blood vessels supplying the skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other areas of the body not needed for the response.

Ovaries and testes
The ovary is the site of estrogen and progesterone synthesis. Estrogen is required to form the ovum (egg) during oogenesis and prepares the uterus for implanting a fertilized egg. Progesterone prepares the breasts for lactation during pregnancy and works with estrogen to regulate the menstrual cycle.
The testes produce the hormone testosterone. Testosterone is required for sperm formation during spermatogenesis, the development of male external genitalia, and secondary sexual traits such as beard growth, chest hair, and enlarged thyroid cartilage.

Answer the questions
What are the two types of feedback mechanisms?
What happens when calcium amount decreases?
How big is the pituitary gland?
Name tropic hormones.
What is the cause of acromegaly?
Why do the adrenal glands are called “adrenal”?
What hormone prepares the breasts for lactation during pregnancy?
What can be regarded as “chemical messengers”?
How do hormones travel to their destination?
What is a duct?
Why are the endocrine system and the nervous system collectively called the neuroendocrine system?
What gland does the hypothalamus send messages to?
Describe the action of negative feedback mechanisms.
What do positive feedback mechanisms control?
What is FSH?
Do prolactin and growth hormone affect specific organs?
Where are the parathyroid glands situated?
Where does estrogen and progesterone synthesis take place?
What hormone makes beard grow?
How does the endocrine system maintain various body functions?
Give the names of the main glands.
What is the term for “a stable internal environment”?
Which glands are called “ductless”?
What is the "master switchboard"?
