
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Related Documents
- •Typographic and Syntax Conventions
- •Creating HDL Modules for CDBA Cellviews
- •Creating HDL Data as You Save CDBA Cellviews
- •Creating HDL Data from Pre-existing CDBA Cellviews
- •Quick-Start Tutorial
- •The Circuit
- •AMS Designer Tools
- •Setting Up the Tutorial
- •Running from a Script
- •Running within the AMS Environment
- •Opening the Command Interpreter Window
- •Netlisting and Compiling
- •Elaborating and Simulating the Design
- •Summary
- •Setting Up the AMS Environment
- •Overview
- •The hdl.var File
- •The ams.env Files
- •AMS Designer Supports Design Management
- •Specifying the Text Editor to Use
- •Specifying Fonts for the Cadence Hierarchy Editor
- •Preparing to Use AMS Designer from the Hierarchy Editor
- •Netlisting
- •Netlisting Modes Supported by the AMS Netlister
- •Automatic Netlisting of a Cellview
- •Netlist Updating and Netlisting of Entire Designs
- •Netlisting from the UNIX Command Line
- •Library Netlisting
- •Netlisting of Cells in Response to Changes in CDF
- •Preparing Existing Analog Primitive Libraries for Netlisting
- •Specifying the Behavior of the Netlister and Compilers
- •Opening the AMS Options Windows
- •Setting Netlister Options from the Hierarchy Editor
- •Opening the CIW AMS Options Window
- •Setting Compiler Options
- •Viewing the AMS Netlister Log
- •Understanding the Output from the AMS Netlister
- •How Inherited Connections Are Netlisted
- •Inherited Signal Connections
- •Inherited Terminal Connections
- •Instance Values for Inherited Connections
- •Third-Party Tools and Other Cadence Tools
- •How Aliased Signals Are Netlisted
- •How m-factors (Multiplicity Factors) Are Netlisted
- •How Iterated Instances Are Netlisted
- •Passing Model Names as Parameters
- •Effect of the modelname, model, and modelName Parameters
- •Handling of the model* and componentName Parameters
- •Precedence of the model* and componentName Parameters
- •Specifying Parameters to be Excluded from Netlisting
- •Ignoring Parameters for Entire Libraries
- •Example: Specifying Parameters to Ignore
- •Ensuring that Floating Point Parameters Netlist Correctly
- •Working with Schematic Designs
- •Setting Schematic Rules Checker Options for AMS Designer
- •Creating Cellviews Using the AMS Environment
- •Preparing a Library
- •Creating the Symbol View
- •Using Blocks
- •Descend Edit
- •Inherited Connections
- •Global Signals in the Schematic Editor
- •Inherited Connections in a Hierarchy
- •How Net Expressions Evaluate
- •Net and Pin Properties
- •groundSensitivity and supplySensitivity Properties
- •Making Connect Modules Sensitive to Inherited Connection Values
- •Using External Text Designs
- •Overview of Steps for Using External Text Designs
- •Bringing Modules into a Cadence Library
- •Specifying the Working Library
- •Compiling into Libraries
- •Compiling into Temporary Libraries
- •Listing Compiled Modules
- •Using Text Blocks in Schematics
- •Using Modules Located in a Cadence Library
- •Preparing for Simulation
- •Using Analog Primitives
- •Using SPICE and Spectre Netlists and Subcircuits
- •Preparing to Use SPICE and Spectre Netlists and Subcircuits
- •Placing SPICE and Spectre Netlists and Subcircuits in a Schematic
- •Using Test Fixtures
- •Creating and Using a Textual Test Fixture
- •Creating a Textual Test Fixture
- •Using a Test Fixture
- •Example: Creating and Using a Test Fixture
- •Using Design Configurations
- •Ensuring HDL Design Unit Information Is Current
- •Preparing a Design for Simulation
- •Overview of AMS Design Prep
- •What AMS Design Prep Does to Prepare a Design for Simulation
- •When to Use AMS Design Prep
- •Specifying the Behavior of AMS Design Prep
- •Setting Options for Global Design Data
- •Specifying Global Signals
- •Specifying Design Variables
- •Specifying Model Files to Use During Elaboration
- •Running AMS Design Prep
- •The cds_globals Module
- •Global Signals
- •Design Variables
- •Setting Elaborator Options
- •Setting Simulator Options
- •Setting Waveform Selection Options
- •Creating Probes
- •Selecting Instances from the Virtuoso Schematic Editing Window
- •Selecting Buses
- •Selecting Instances from the Scope Navigator
- •Copying and Pasting Within Tables
- •Elaborating and Simulating
- •Viewing Messages
- •Plotting Waveforms After Simulation Ends
- •Starting the SimVision Waveform Viewer
- •Plotting Waveforms Selected on a Schematic (Direct Plot)
- •Using the amsdesigner Command
- •Examples
- •Producing Customized Netlists
- •Producing Customized Netlists
- •Identifying the Sections of a Netlist
- •Using ams.env Variables to Customize Netlists
- •Using Netlisting Procedures to Customize Netlists
- •Examples: Problems Addressed by Customized Netlists
- •Example: Adjusting Parameter Values to Account for Number of Fingers
- •Example: Using Symbols that Represent Verilog Test Code
- •Data Objects Supported for Netlisting
- •Netlister Object
- •Formatter Object
- •Cellview Object
- •Parameter Object
- •Instance Object
- •SKILL Functions Supported for Netlisting
- •Default Netlisting Procedures
- •Netlisting Helper Functions
- •Variables for ams.env Files
- •How AMS Designer Determines the Set of Variables
- •Why AMS Designer Uses ams.env Files, Not .cdsenv Files
- •List of ams.env Variables
- •Detailed Descriptions of ams.env Variables
- •aliasInstFormat
- •allowDeviantBuses
- •allowNameCollisions
- •allowSparseBuses
- •allowUndefParams
- •amsCompMode
- •amsDefinitionViews
- •amsEligibleViewTypes
- •amsExcludeParams
- •amsExpScalingFactor
- •amsLSB_MSB
- •amsMaxErrors
- •amsScalarInstances
- •amsVerbose
- •analogControlFile
- •bindCdsAliasLib
- •bindCdsAliasView
- •cdsGlobalsLib
- •cdsGlobalsView
- •checkAndNetlist
- •checkOnly
- •checktasks
- •compileAsAMS
- •compileExcludeLibs
- •compileMode
- •connectRulesCell
- •connectRulesCell2
- •connectRulesLib
- •connectRulesView
- •detailedDisciplineRes
- •discipline
- •excludeViewNames
- •hdlVarFile
- •headerText
- •ieee1364
- •ifdefLanguageExtensions
- •incdir
- •includeFiles
- •includeInstCdfParams
- •initFile
- •instClashFormat
- •iterInstExpFormat
- •language
- •lexpragma
- •logFileAction
- •logFileName
- •macro
- •maxErrors
- •messages
- •modifyParamScope
- •ncelabAccess
- •ncelabAnnoSimtime
- •ncelabArguments
- •ncelabCoverage
- •ncelabDelayMode
- •ncelabDelayType through ncelabMessages
- •ncelabMixEsc
- •ncelabModelFilePaths
- •ncelabNeverwarn through ncelabVipdelay
- •ncsimArguments
- •ncsimEpulseNoMsg through ncsimExtassertmsg
- •ncsimGUI
- •ncsimLoadvpi through ncsimStatus
- •ncsimTcl
- •ncsimUnbuffered through ncsimUseAddArgs
- •ncvhdlArguments
- •ncvlogArguments
- •ncvlogUseAddArgs
- •netClashFormat
- •netlistAfterCdfChange
- •netlistMode
- •netlistUDFAsMacro
- •neverwarn
- •noline
- •nomempack
- •nopragmawarn
- •nostdout
- •nowarn
- •paramDefVals
- •paramGlobalDefVal
- •pragma
- •processViewNames
- •prohibitCompile
- •runNcelab
- •runNcsim
- •scaddlglblopts
- •scaddltranopts
- •scale
- •scalem
- •scannotate
- •scapprox
- •scaudit
- •sccheckstmt
- •sccmin
- •sccompatible
- •scdebug
- •scdiagnose
- •scdigits
- •scerror
- •scerrpreset
- •scfastbreak
- •scgmin
- •scgmincheck
- •schomotopy
- •sciabstol
- •scic
- •scicstmt
- •scignshorts
- •scinfo
- •scinventory
- •sclimit
- •sclteratio
- •scmacromod
- •scmaxiters
- •scmaxnotes
- •scmaxrsd
- •scmaxstep
- •scmaxwarn
- •scmethod
- •scmodelevaltype
- •scmosvres
- •scnarrate
- •scnotation
- •scnote
- •scopptcheck
- •scpivabs
- •scpivotdc
- •scpivrel
- •scquantities
- •screadic
- •screadns
- •screlref
- •screltol
- •scrforce
- •scscale
- •scscalem
- •scscftimestamp
- •scscfusefileflag
- •scskipcount
- •scskipdc
- •scskipstart
- •scskipstop
- •scspeed
- •scstats
- •scstep
- •scstop
- •scstrobedelay
- •scstrobeperiod
- •sctemp
- •sctempeffects
- •sctitle
- •sctnom
- •sctopcheck
- •sctransave
- •scusemodeleval
- •scvabstol
- •scwarn
- •scwrite
- •simRunDirLoc
- •simVisScriptFile
- •status
- •templateFile
- •templateScript
- •timescale
- •update
- •use5xForVHDL
- •useDefparam
- •useNcelabNowarn
- •useNcelabSdfCmdFile
- •useNcsimNowarn
- •useNowarn
- •useScaddlglblopts
- •useScaddltranopts
- •useScic
- •useScreadic
- •useScreadns
- •useScwrite
- •useSimVisScriptFile
- •useProcessViewNamesOnly
- •verboseUpdate
- •vlogGroundSigs
- •vloglinedebug
- •vlogSupply0Sigs
- •vlogSupply1Sigs
- •wfDefaultDatabase
- •wfDefInstCSaveAll
- •wfDefInstCSaveLvl
- •wfDefInstSaveCurrents
- •wfDefInstSaveVoltages
- •wfDefInstVSaveAll
- •wfDefInstVSaveLvl
- •wfDefInstVSaveObjects
- •Updating Legacy SimInfo for Analog Primitives
- •The ams Fields
- •Special Handling of model, modelName, modelname, and componentName
- •Converting an Existing Analog Primitive Library
- •Designing for Virtuoso AMS Compliance
- •Terminals
- •Buses
- •Component Description Format
- •Parameters
- •Using Inherited Parameters
- •Using Cell Parameters
- •Parameterized Cells
- •VHDL-AMS Component Declarations
- •Properties
- •Properties to Avoid Completely
- •Avoid the portOrder Property Unless Required by Special Circumstances
- •Properties to Use Only in AMS Compatibility Mode
- •Properties That Have No Special Meaning in the AMS Environment
- •Properties Fully Supported by the AMS Environment
- •SKILL Functions
- •amsCheckCV
- •amsIsPresent
- •amsNetlist
- •amsProcessCellViews
- •amsUIOptionsForm
- •amsUIRunNetlisterForm
- •ddsCvtAMSTranslateCell
- •ddsCvtAMSTranslateLib
- •ddsCvtToolBoxAMS
- •vmsUpdateCellViews
- •Customization Variables
- •schHdlNotCreateDB
- •schHdlUseVamsForVerilog
- •vmsAnalysisType
- •vmsCreateMissingMasters
- •vmsNcvlogExecutable
- •vmsPortProcessing
- •vmsRunningInUI
- •vmsTemplateScript
- •vmsVerboseMsgLevel
- •Compiling Cadence-Provided Libraries
- •Purpose of the amsLibCompile Tool
- •Running the amsLibCompile Tool Manually
- •Example

Virtuoso AMS Environment User Guide
Preparing a Design for Simulation
Editing an Analog Model File
To edit the contents of a model file listed in the table,
Highlight the row that lists the model file you want to edit, and clickEdit.
The model file opens in your selected editor.
Running AMS Design Prep
To run AMS Design Prep,
1.Choose AMS – Design Prep from the Cadence hierarchy editor. The AMS Design Prep window appears.
April 2004 |
221 |
Product Version 5.3 |

Virtuoso AMS Environment User Guide
Preparing a Design for Simulation
The settings in this window determine when netlisting and compilation occur as you work with the CDBA cellviews in your design hierarchy.
Setting |
Behavior |
|
|
Netlist |
Enables netlisting |
Incremental |
Netlists CDBA cellviews in the hierarchy only if their HDL |
|
data is not synchronized with their CDBA data |
All |
Netlists all CDBA cellviews in the hierarchy, regardless of |
|
whether their HDL data is synchronized with their CDBA |
|
data |
Compile |
Enables compilation |
When netlisting |
Specifies that thencvlog compiler is to create or update |
|
the cellview’s compiled data only if the cellview is netlisted |
|
when you click Run |
All |
Specifies that, for each cellview used in the design, the |
|
ncvlog or ncvhdl compiler is to compile the cellview, |
|
whether or not the cell is netlisted in this run. |
|
|
2.Set the appropriate options.
3.Click Run.
In accordance with your selections, AMS Design Prep performs some or all of the following tasks:
Creates or updates netlist data
Creates or updates compiled data
Creates or updates the cds_globals module for global signals
Declares or updates design variables
Reports information, warnings, and errors in the log file and in the hierarchy editor message pane
April 2004 |
222 |
Product Version 5.3 |
Virtuoso AMS Environment User Guide
Preparing a Design for Simulation
While AMS Design Prep is running, the AMS Run Info progress indicator appears.
You can stop the AMS Design Prep run by clicking Stop.
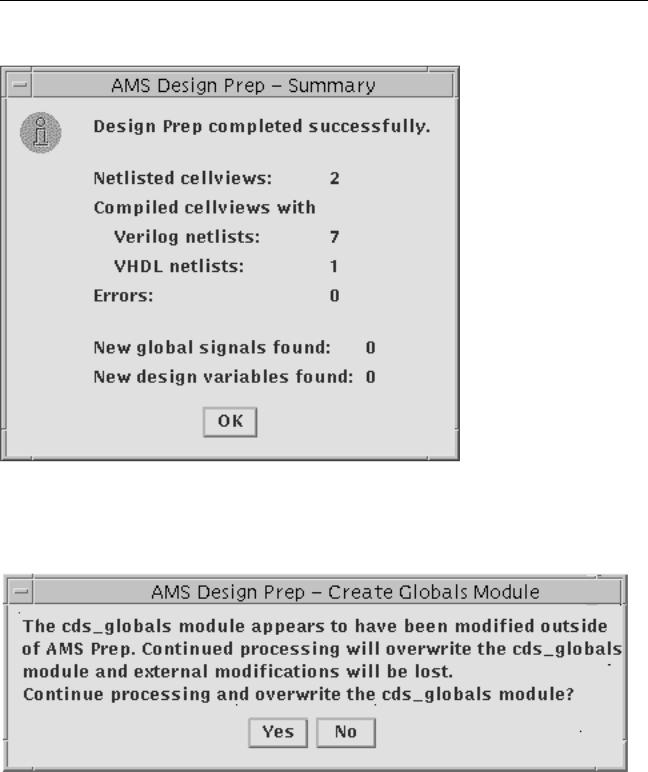
After AMS Design Prep finishes, the AMS Design Prep - Summary window appears, displaying the following information:
■Success or failure of the design preparation
■How many design units were netlisted
■How many errors were found in the design
■How many new global signals were found
April 2004 |
223 |
Product Version 5.3 |
Virtuoso AMS Environment User Guide
Preparing a Design for Simulation
■How many new design variables were found
AMS Design Prep detects whether you have generated or edited the cds_globals module. If you try to run AMS Design Prep when the data in the cds_globals module has been edited outside the hierarchy editor or has an error, AMS Design Prep issues a warning and asks for confirmation, as shown below.
April 2004 |
224 |
Product Version 5.3 |

Virtuoso AMS Environment User Guide
Preparing a Design for Simulation
Messages and Log Files
When AMS Design Prep runs, it displays messages in the Cadence hierarchy editor window.
For example, the hierarchy editor messages might look like this.
Netlisting amslib top schematic
Compiling verilog.vams in cellview amslib top schematic.
ncvlog: v3.150.(a1): (c) Copyright 1995 - 2000 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. Netlisting amslib comparator schematic.
Compiling verilog.vams in cellview amslib comparator schematic.
ncvlog: v3.150.(a1): (c) Copyright 1995 - 2000 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. Creating cds_globals module in amslib cds_globals top_config.
Compiling verilog.vams in cellview amslib cds_globals top_config.
ncvlog: v3.150.(a1): (c) Copyright 1995 - 2000 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. Design preparation has completed successfully.
You can watch the hierarchy editor messages to see current information about the AMS Design Prep run. If errors are reported that you want to fix, you can stop the AMS Design Prep run by clicking Stop in the AMS Run Info progress indicator.
AMS Design Prep does not create it’s own log file. However, tools running under the control of AMS Design Prep do create log files. The AMS netlister creates a log file called, by default, ams_direct.log, and the NC Verilog and NC VHDL compilers create the ncvlog.log and ncvhdl.log files. You can view these log files easily by choosingAMS – Netlister Log File or AMS – Simulator Log Files from the hierarchy editor menu.
For example, the contents of a netlister (ams_direct.log) file might look like this.
@(#)$CDS: amsdirect version 4.4.6 04/05/2000 17:39 (machine) $ Copyright (c) 1999 Cadence Design Systems. All Rights Reserved.
Run date: Thu Apr 13 14:09:52 2000 Run time options used:
-mpshost machine.Cadence.COM -mpssession sudeshna -pid 2443
Info: Processing ("amslib" "top" "schematic") ...
Info: Verilog-AMS netlist successfully written to /mnt3/sudeshna/eureka/alpha/AMS_lib/amsLib/top/schematic/verilog.vams.
Info: Found 0 errors and 0 warnings.
Info: Processing ("amslib" "comparator" "schematic") ...
Info: Verilog-AMS netlist successfully written to /mnt3/sudeshna/eureka/alpha/AMS_lib/amsLib/comparator/schematic/
verilog.vams.
Info: Found 0 errors and 0 warnings.
How AMS Design Prep Handles Global Signals and
Design Variables
The values of global signals and design variables must be available throughout a design, not just within a single module. AMS Design Prep enables this capability by collecting global signals and design variables into a module called cds_globals.
April 2004 |
225 |
Product Version 5.3 |
