- •Предисловие
- •History and Development of Automatic Control
- •Introduction to Control Systems
- •From the History of Automatic Control Theory
- •Управление
- •Elements and Structure of Automatic Control Systems
- •Automation
- •Business Systems
- •Comparing Feed forward and Feedback Controllers
- •Types of Feedback Control Systems
- •History of the word "cybernetics"
- •The History of Cybernetics
- •Cybernetics
- •Сфера кибернетики
- •The heritage and revival of cybernetics
- •Distributed Control System (dcs) History
- •Servomechanism, Regulator and Process Control
- •Data acquisition
- •Methodology Source
- •Signals
- •Daq hardware
- •Daq software
- •Алгоритмы функционирования технологических объектов, управляемых асутп
- •What is Artificial Intelligence?
- •Составление реферата
- •Hart-коммуникация
- •Беспроводные интерфейсы
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •Artificial Intelligence
- •Robot programming and interfaces
- •Writing a Summary
- •Experimental modeling and adaptive power control of a 750mw once-through boiler
- •I. Industrial robot
- •II. Robot types, features
- •III. Defining parameters
- •IV. End –of-arm Tooling
- •V. Controlling Movement
- •VI. Robotics
- •Функции асу тп
- •Grammar Reference Passive Voice
- •Сопоставление русских и английских времен в Passive
- •The Infinitive
- •Forms of the Infinitive
- •Functions of the Infinitive
- •2) Частью сказуемого.
- •The Complex Object
- •The Complex Subject
- •The Participle
- •The Absolute Participle Construction
- •The Gerund
- •Forms of the Gerund
- •Functions of the Gerund
- •Supplementary Texts Types of control systems
- •History of Cybernetics and Systems Science
- •The Search for New Tools
- •Industrial Robots
- •An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- •Applications of ai
- •Artificial intelligence
- •Open and closed – loop systems
- •Inputs and Outputs
- •Interface
- •Technological revolution in Russia
- •Асу тп сегодня
- •Microprocessor
- •External Processor Interfaces and Operation
- •Trigonometry. Units of Measurement
- •Figure 1 - a radian defined
- •Interrupts
- •Programs
- •Other microcontroller features
- •Higher integration
- •What Is a Control Engineer?
- •Специальность «Автоматизация и управление»
- •Linear versus Nonlinear Control Systems
- •Principles of Automatic Emergency Control
- •Сети следующего поколения
- •Список литературы
- •Содержание
- •Предисловие
- •History and Development of Automatic Control
- •Introduction to Control Systems
- •From the History of Automatic Control Theory
- •Управление
- •Elements and Structure of Automatic Control Systems
- •Automation
- •Business Systems
- •Comparing Feed forward and Feedback Controllers
- •Types of Feedback Control Systems
- •History of the word "cybernetics"
- •The History of Cybernetics
- •Cybernetics
- •Сфера кибернетики
- •The heritage and revival of cybernetics
- •Distributed Control System (dcs) History
- •Servomechanism, Regulator and Process Control
- •Data acquisition
- •Methodology Source
- •Signals
- •Daq hardware
- •Daq software
- •Алгоритмы функционирования технологических объектов, управляемых асутп
- •What is Artificial Intelligence?
- •Составление реферата
- •Hart-коммуникация
- •Беспроводные интерфейсы
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •Artificial Intelligence
- •Robot programming and interfaces
- •Writing a Summary
- •Experimental modeling and adaptive power control of a 750mw once-through boiler
- •I. Industrial robot
- •II. Robot types, features
- •III. Defining parameters
- •IV. End –of-arm Tooling
- •V. Controlling Movement
- •VI. Robotics
- •Функции асу тп
- •Grammar Reference Passive Voice
- •Сопоставление русских и английских времен в Passive
- •The Infinitive
- •Forms of the Infinitive
- •Functions of the Infinitive
- •2) Частью сказуемого.
- •The Complex Object
- •The Complex Subject
- •The Participle
- •The Absolute Participle Construction
- •The Gerund
- •Forms of the Gerund
- •Functions of the Gerund
- •Supplementary Texts Types of control systems
- •History of Cybernetics and Systems Science
- •The Search for New Tools
- •Industrial Robots
- •An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- •Applications of ai
- •Artificial intelligence
- •Open and closed – loop systems
- •Inputs and Outputs
- •Interface
- •Technological revolution in Russia
- •Асу тп сегодня
- •Microprocessor
- •External Processor Interfaces and Operation
- •Trigonometry. Units of Measurement
- •Figure 1 - a radian defined
- •Interrupts
- •Programs
- •Other microcontroller features
- •Higher integration
- •What Is a Control Engineer?
- •Специальность «Автоматизация и управление»
- •Linear versus Nonlinear Control Systems
- •Principles of Automatic Emergency Control
- •Сети следующего поколения
- •Список литературы
- •Содержание
- •Предисловие
- •History and Development of Automatic Control
- •Introduction to Control Systems
- •From the History of Automatic Control Theory
- •Управление
- •Elements and Structure of Automatic Control Systems
- •Automation
- •Business Systems
- •Comparing Feed forward and Feedback Controllers
- •Types of Feedback Control Systems
- •History of the word "cybernetics"
- •The History of Cybernetics
- •Cybernetics
- •Сфера кибернетики
- •The heritage and revival of cybernetics
- •Distributed Control System (dcs) History
- •Servomechanism, Regulator and Process Control
- •Data acquisition
- •Methodology Source
- •Signals
- •Daq hardware
- •Daq software
- •Алгоритмы функционирования технологических объектов, управляемых асутп
- •What is Artificial Intelligence?
- •Составление реферата
- •Hart-коммуникация
- •Беспроводные интерфейсы
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •The End of a Monopoly Era
- •Artificial Intelligence
- •Robot programming and interfaces
- •Writing a Summary
- •Experimental modeling and adaptive power control of a 750mw once-through boiler
- •I. Industrial robot
- •II. Robot types, features
- •III. Defining parameters
- •IV. End –of-arm Tooling
- •V. Controlling Movement
- •VI. Robotics
- •Функции асу тп
- •Grammar Reference Passive Voice
- •Сопоставление русских и английских времен в Passive
- •The Infinitive
- •Forms of the Infinitive
- •Functions of the Infinitive
- •2) Частью сказуемого.
- •The Complex Object
- •The Complex Subject
- •The Participle
- •The Absolute Participle Construction
- •The Gerund
- •Forms of the Gerund
- •Functions of the Gerund
- •Supplementary Texts Types of control systems
- •History of Cybernetics and Systems Science
- •The Search for New Tools
- •Industrial Robots
- •An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
- •Applications of ai
- •Artificial intelligence
- •Open and closed – loop systems
- •Inputs and Outputs
- •Interface
- •Technological revolution in Russia
- •Асу тп сегодня
- •Microprocessor
- •External Processor Interfaces and Operation
- •Trigonometry. Units of Measurement
- •Figure 1 - a radian defined
- •Interrupts
- •Programs
- •Other microcontroller features
- •Higher integration
- •What Is a Control Engineer?
- •Специальность «Автоматизация и управление»
- •Linear versus Nonlinear Control Systems
- •Principles of Automatic Emergency Control
- •Сети следующего поколения
- •Список литературы
- •Содержание
Microprocessor
A silicon chip that contains a CPU. In the world of personal computers, the terms microprocessor and CPU are used interchangeably. At the heart of all personal computers and most workstations sits a microprocessor. Microprocessors also control the logic of almost all digital devices, from clock radios to fuel-injection systems for automobiles.
Three basic characteristics differentiate microprocessors:
- Instruction set: The set of instructions that the microprocessor can execute.
- bandwidth: The number of bits processed in a single instruction.
- clock speed : Given in megahertz (MHz), the clock speed determines how many instructions per second the processor can execute.
In both cases, the higher the value, the more powerful the CPU. For example, a 32-bit microprocessor that runs at 50MHz is more powerful than a 16-bit microprocessor that runs at 25MHz.
In addition to bandwidth and clock speed, microprocessors are classified as being either RISC (reduced instruction set computer) or CISC (complex instruction set computer).
External Processor Interfaces and Operation
The way that the processor "talks" to other parts of the system is in many ways as important a factor in indicating system power as how it works internally. The processor controls the entire PC, and uses dedicated control pathways called "buses" to send information between itself and the system cache, memory and other devices. These are the processor's external interfaces, which can be different even for otherwise similar CPUs.
There are several different types of buses on a modern PC. The section on System Bus Function and Features provides the basic details on the various bus types, the hierarchy of buses, and general explanations of bus size and bandwidth. You can also find there descriptions of the I/O system buses such as PCI and ISA. At the processor level, the important buses are the processor bus and memory bus, which we discuss in more detail here.
Do the following tasks:
- Read the text.
- Broad the information in each paragraph.
- Speak of microprocessor charachteristics.
Trigonometry. Units of Measurement
by Bob Connell
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with functions that describe angles. Although knowledge of trigonometry is valuable in surveying and navigation, in control systems engineering its virtue lies in the fact that trigonometric functions can be used to describe the status of objects that exhibit repeatable behavior. This includes the motion of the planets, pendulums, a mass suspended on a spring, and perhaps most relevant here, the oscillation of process variables under control.
The most common unit of measurement for angles is the degree, which is 1/360 of a whole circle.
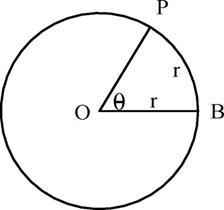
A lesser used unit is the radian. Although the radian is not ordinarily used in angular measurement, it should be understood because when differential equations, which occur in control systems engineering, are solved, the angles emerge in radians.
On the circumference of a circle, if an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle is marked off, then the arc will subtend, at the center of the circle, an angle of 1 radian. The angle θ (or POB) in Figure 1, illustrates this.