
- •Features
- •Pin Configuration
- •Overview
- •ATtiny11 Block Diagram
- •ATtiny12 Block Diagram
- •Pin Descriptions
- •Port B (PB5..PB0)
- •XTAL1
- •XTAL2
- •RESET
- •Status Register
- •Internal RC Oscillator
- •Crystal Oscillator
- •External Clock
- •External RC Oscillator
- •Register Description
- •Memories
- •I/O Memory
- •Register Indirect
- •I/O Direct
- •Flash Program Memory
- •EEPROM Data Memory
- •Register Description
- •Sleep Modes
- •Sleep Modes for the ATtiny11
- •Idle Mode
- •Power-down Mode
- •Sleep Modes for the ATtiny12
- •Idle Mode
- •Power-down Mode
- •Reset Sources
- •External Reset
- •Watchdog Reset
- •Register Description
- •Interrupts
- •Reset and Interrupt
- •Interrupt Handling
- •Interrupt Response Time
- •External Interrupt
- •Pin Change Interrupt
- •Register Description
- •I/O Port B
- •Register Description
- •Port B as General Digital I/O
- •Alternate Functions of Port B
- •Timer/Counter0
- •Timer/Counter Prescaler
- •Register Description
- •Watchdog Timer
- •Register Description
- •Analog Comparator
- •Register Description
- •Fuse Bits in ATtiny11
- •Fuse Bits in ATtiny12
- •Signature Bytes
- •ATtiny11
- •ATtiny12
- •ATtiny11/12
- •High-voltage Serial Programming
- •Low-voltage Serial Downloading (ATtiny12 only)
- •Data Polling
- •Electrical Characteristics
- •Absolute Maximum Ratings
- •External Clock Drive ATtiny11
- •External Clock Drive ATtiny12
- •Register Summary ATtiny11
- •Register Summary ATtiny12
- •Instruction Set Summary
- •Ordering Information
- •ATtiny11
- •ATtiny12
- •Packaging Information
- •Table of Contents

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ATtiny11/12 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Electrical Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Absolute Maximum Ratings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*NOTICE: |
Stresses beyond those ratings listed under |
||||||||
|
Operating Temperature.................................. |
|
-55°C to +125°C |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
“Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause perma- |
||||
|
Storage Temperature ..................................... |
|
-65°C to +150°C |
|
|
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
only and functional operation of the device at |
||||
|
Voltage on any Pin except |
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
these or other conditions beyond those indicated |
|||||||
|
with respect to Ground ................................ |
|
-1.0V to VCC+0.5V |
|
|
in the operational sections of this specification is |
|||||||||||||
|
Voltage on |
|
with respect to Ground |
-1.0V to +13.0V |
|
|
not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rat- |
||||||||||||
|
RESET |
|
|
ing conditions for extended periods may affect |
|||||||||||||||
|
Maximum Operating Voltage |
|
|
|
6.0V |
|
|
device reliability. |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
DC Current per I/O Pin ............................................... |
|
|
40.0 mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
DC Current VCC and GND Pins................................ |
|
|
100.0 mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
DC Characteristics – Preliminary Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
TA = -40°C to 85°C, VCC = 2.7V to 5.5V for ATtiny11, VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V for ATtiny12 (Unless otherwise noted) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Symbol |
|
Parameter |
|
Condition |
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
|
Units |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIL |
|
Input Low Voltage |
|
Except (XTAL) |
|
-0.5 |
|
(1) |
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0.3 VCC |
|
|||||||||||||
|
VIL1 |
|
Input Low Voltage |
|
XTAL |
|
-0.5 |
|
(1) |
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 VCC |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIH |
|
Input High Voltage |
|
Except (XTAL, RESET) |
|
VCC + 0.5 |
|
V |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
0.6 VCC |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
VIH1 |
|
Input High Voltage |
|
XTAL |
|
(2) |
|
VCC + 0.5 |
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
0.7 VCC |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
VIH2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input High Voltage |
|
RESET |
|
VCC + 0.5 |
|
V |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
0.85 VCC |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
VOL |
|
Output Low Voltage(3) |
|
IOL = 20 mA, VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
Port B |
|
IOL = 10 mA, VCC = 3V |
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
V |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
VOL |
|
Output Low Voltage |
|
IOL = 12 mA, VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
PB5 (ATtiny12) |
|
IOL = 6 mA, VCC = 3V |
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
V |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
Output High Voltage(4) |
|
I |
= -3 mA, V = 5V |
|
4.3 |
|
|
|
|
V |
||||||
|
VOH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Port B |
|
IOH = -1.5 mA, VCC = 3V |
|
2.3 |
|
|
|
|
V |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
IIL |
|
Input Leakage Current |
|
VCC = 5.5V, Pin Low |
|
|
|
8.0 |
|
µA |
||||||||
|
|
I/O Pin |
|
(Absolute value) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
IIH |
|
Input Leakage Current |
|
VCC = 5.5V, Pin High |
|
|
|
8.0 |
|
µA |
||||||||
|
|
I/O Pin |
|
(Absolute value) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
RI/O |
|
I/O Pin Pull-Up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
122 |
|
kΩ |
||||
59
1006F–AVR–06/07

DC Characteristics – Preliminary Data (Continued)
TA = -40°C to 85°C, VCC = 2.7V to 5.5V for ATtiny11, VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V for ATtiny12 (Unless otherwise noted)
Symbol |
Parameter |
Condition |
|
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Active 1 MHz, VCC = 3V |
|
|
1.0 |
mA |
||
|
|
(ATtiny12V) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Active 2 MHz, VCC = 3V |
|
|
2.0 |
mA |
||
|
|
(ATtiny11L) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Active 4 MHz, VCC = 3V |
|
|
2.5 |
mA |
||
|
|
(ATtiny12L) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Active 6 MHz, VCC = 5V |
|
|
10 |
mA |
||
|
|
(ATtiny11) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Active 8 MHz, VCC = 5V |
|
|
10 |
mA |
||
|
|
(ATtiny12) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle 1 MHz, VCC |
= 3V |
|
|
0.4 |
mA |
|
|
|
(ATtiny12V) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICC |
Power Supply Current |
Idle 2 MHz, VCC |
= 3V |
|
|
0.5 |
mA |
|
(ATtiny11L) |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Idle 4 MHz, VCC |
= 3V |
|
|
1.0 |
mA |
|
|
|
(ATtiny12L) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle 6 MHz, VCC |
= 5V |
|
|
2.0 |
mA |
|
|
|
(ATtiny11) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle 8 MHz, VCC |
= 5V |
|
|
3.5 |
mA |
|
|
|
(ATtiny12) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Down(5), VCC |
= 3V, |
|
9.0 |
15 |
µA |
|
|
|
WDT enabled |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Down(5), VCC |
= 3V. |
|
<1 |
2 |
µA |
|
|
|
WDT disabled (ATtiny12) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Down(5), VCC |
= 3V. |
|
<1 |
5 |
µA |
|
|
|
WDT disabled (ATtiny11) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VACIO |
Analog Comparator |
VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
|
40 |
mV |
Input Offset Voltage |
VIN = VCC/2 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
IACLK |
Analog Comparator |
VCC = 5V |
|
|
-50 |
|
50 |
nA |
Input Leakage Current |
VIN = VCC/2 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
TACPD |
Analog Comparator |
VCC = 2.7V |
|
|
|
750 |
|
ns |
Propagation Delay |
VCC = 4.0V |
|
|
|
500 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Notes: 1. “Max” means the highest value where the pin is guaranteed to be read as low.
2.“Min” means the lowest value where the pin is guaranteed to be read as high.
3.Although each I/O port can sink more than the test conditions (20 mA at VCC = 5V, 10 mA at VCC = 3V) under steady state conditions (non-transient), the following must be observed:
1] The sum of all IOL, for all ports, should not exceed 100 mA.
If IOL exceeds the test condition, VOL may exceed the related specification. Pins are not guaranteed to sink current greater than the listed test conditions.
4.Although each I/O port can source more than the test conditions (3 mA at VCC = 5V, 1.5 mA at VCC = 3V) under steady state conditions (non-transient), the following must be observed:
1] The sum of all IOH, for all ports, should not exceed 100 mA.
If IOH exceeds the test condition, VOH may exceed the related specification. Pins are not guaranteed to source current greater than the listed test condition.
5.Minimum VCC for Power-down is 1.5V. (On ATtiny12: only with BOD disabled)
60 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
External Clock Drive
Waveforms
Figure 32. External Clock
VIH1
VIL1
External Clock Drive ATtiny11
|
|
VCC = 2.7V to 4.0V |
VCC = 4.0V to 5.5V |
|
||
Symbol |
Parameter |
Min |
Max |
Min |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1/tCLCL |
Oscillator Frequency |
0 |
2 |
0 |
6 |
MHz |
tCLCL |
Clock Period |
500 |
|
167 |
|
ns |
tCHCX |
High Time |
200 |
|
67 |
|
ns |
tCLCX |
Low Time |
200 |
|
67 |
|
ns |
tCLCH |
Rise Time |
|
1.6 |
|
0.5 |
µs |
tCHCL |
Fall Time |
|
1.6 |
|
0.5 |
µs |
External Clock Drive ATtiny12
|
|
VCC = 1.8V to |
VCC = 2.7V to |
VCC = 4.0V to |
|
||||||
|
|
|
2.7V |
|
4.0V |
|
5.5V |
|
|||
Symbol |
Parameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min |
|
Max |
Min |
|
Max |
Min |
|
Max |
Units |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1/tCLCL |
Oscillator |
0 |
|
1.2 |
0 |
|
4 |
0 |
|
8 |
MHz |
Frequency |
|
|
|
||||||||
tCLCL |
Clock Period |
833 |
|
|
250 |
|
|
125 |
|
|
ns |
tCHCX |
High Time |
333 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
ns |
tCLCX |
Low Time |
333 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
ns |
tCLCH |
Rise Time |
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
0.5 |
µs |
tCHCL |
Fall Time |
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
0.5 |
µs |
Table 29. External RC Oscillator, Typical Frequencies
R [kΩ] |
C [pF] |
f |
|
|
|
100 |
70 |
100 kHz |
|
|
|
31.5 |
20 |
1.0 MHz |
|
|
|
6.5 |
20 |
4.0 MHz |
|
|
|
Note: R should be in the range 3-100 kΩ, and C should be at least 20 pF. The C values given in the table includes pin capacitance. This will vary with package type.
61
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11 Typical
Characteristics
The following charts show typical behavior. These figures are not tested during manufacturing. All current consumption measurements are performed with all I/O pins configured as inputs and with internal pull-ups enabled. A sine wave generator with rail- to-rail output is used as clock source.
The power consumption in Power-down Mode is independent of clock selection.
The current consumption is a function of several factors such as: operating voltage, operating frequency, loading of I/O pins, switching rate of I/O pins, code executed and ambient temperature. The dominating factors are operating voltage and frequency.
The current drawn from capacitive loaded pins may be estimated (for one pin) as CL*VCC*f where CL = load capacitance, VCC = operating voltage and f = average switching frequency of I/O pin.
The parts are characterized at frequencies higher than test limits. Parts are not guaranteed to function properly at frequencies higher than the ordering code indicates.
The difference between current consumption in Power-down Mode with Watchdog Timer enabled and Power-down Mode with Watchdog Timer disabled represents the differential current drawn by the Watchdog timer.
Figure 33. Active Supply Current vs. Frequency
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T = 25 |
˚ |
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 6V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 5.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 4.5V |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
= 4V |
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.6V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 2.7V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
VCC = 2.1V |
VCC = 2.4V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
VCC |
= 1.8V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
||
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
||||||||||||||
Frequency (MHz)
62 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 34. Active Supply Current vs. VCC
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
FREQUENCY = 4 MHz
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC (V)
Figure 35. Active Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by Internal Oscillator
(mA) cc
I
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc DEVICE CLOCKED BY 1.0MHz INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR
6
5
TA = 25˚C
4
TA = 85˚C
3
2
1
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
63
1006F–AVR–06/07
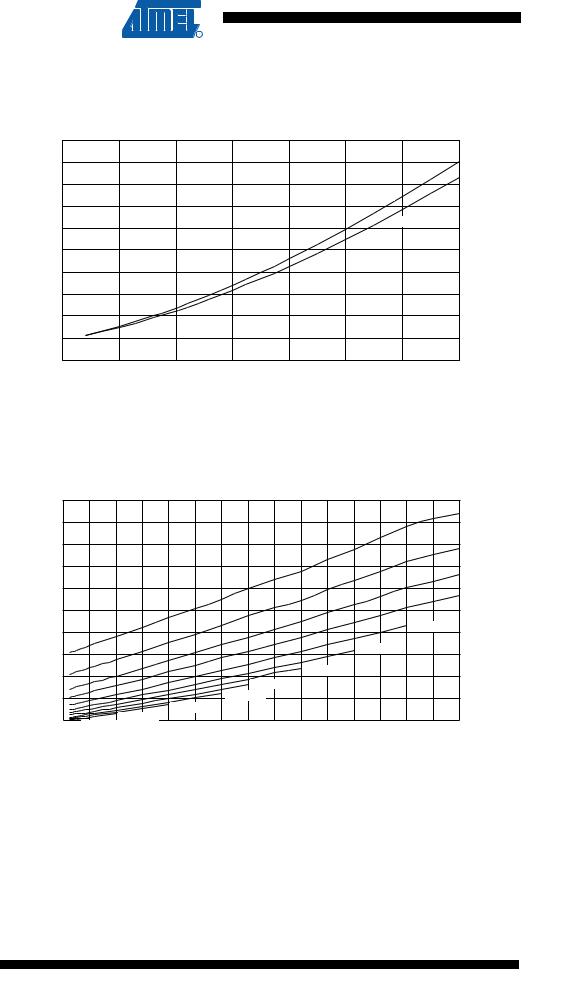
Figure 36. Active Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by External 32kHz Crystal
(mA) cc
I
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc DEVICE CLOCKED BY 32KHz CRYSTAL
5
4.5
4
TA = 25˚C
3.5
3 TA = 85˚C
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
Figure 37. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T = 25 |
˚ |
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 6V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 5.5V |
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 4.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 4V |
|
|
I |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.6V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 3.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
VCC = 2.4V |
|
VCC = 2.7V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
VCC = 2.1V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
0 |
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
= 1.8V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
Frequency (MHz)
64 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 38. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
FREQUENCY = 4 MHz
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC (V)
Figure 39. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by Internal Oscillator
(mA) cc
I
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
DEVICE CLOCKED BY 1.0MHz INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR
0.35
0.3
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
65
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 40. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by External 32kHz Crystal
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc DEVICE CLOCKED BY 32KHz CRYSTAL
25
(μA) cc
I
20
TA = 25˚C
TA = 85˚C
15
10
5
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
Figure 41. Power-down Supply Current vs. VCC
POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μA) |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
VCC (V) |
|
|
|
|
|
66 ATtiny11/12 
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 42. Power-down Supply Current vs. VCC
POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
WATCHDOG TIMER ENABLED
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(μ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC (V)
Figure 43. Analog Comparator Current vs. VCC
ANALOG COMPARATOR CURRENT vs. Vcc
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
(mA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC (V)
67
1006F–AVR–06/07

Analog comparator offset voltage is measured as absolute offset.
Figure 44. Analog Comparator Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Voltage
ANALOG COMPARATOR OFFSET VOLTAGE vs.
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE Vcc = 5V
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mV) |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
Voltage |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Offset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
Common Mode Voltage (V)
Figure 45. Analog Comparator Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Voltage
Offset Voltage (mV)
ANALOG COMPARATOR OFFSET VOLTAGE vs. COMMON MODE VOLTAGE Vcc = 2.7V
10
TA = 25˚C
8
6
TA = 85˚C
4
2
0
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
Common Mode Voltage (V)
68 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 46. Analog Comparator Input Leakage Current
ANALOG COMPARATOR INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
= 6V |
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(nA) |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
6.5 |
7 |
VIN (V)
Figure 47. Watchdog Oscillator Frequency vs. VCC
WATCHDOG OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY vs. Vcc
|
1600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
(kHz) |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC(V)
69
1006F–AVR–06/07

Sink and source capabilities of I/O ports are measured on one pin at a time.
Figure 48. Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Input Voltage
PULL-UP RESISTOR CURRENT vs. INPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
|
|
|
V |
= 5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120 |
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μA) |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OP |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
VOP (V)
Figure 49. Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Input Voltage
PULL-UP RESISTOR CURRENT vs. INPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
|
|
VCC = 2.7V |
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μA) |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
VOP (V)
70 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 50. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. Output Voltage
I/O PIN SINK CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
|
|
VCC = 5V |
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
OL |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
VOL (V)
Figure 51. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage
I/O PIN SOURCE CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
= 5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
|
VOH (V)
71
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 52. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. Output Voltage
I/O PIN SINK CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
V |
= 2.7V |
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
(mA) |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL |
|
|
|
|
|
I |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
VOL (V)
Figure 53. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage
I/O PIN SOURCE CURRENT vs. OUTPUT VOLTAGE
|
|
|
V |
|
= 2.7V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
(mA) |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
|
VOH (V)
72 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 54. I/O Pin Input Threshold Voltage vs. VCC
I/O PIN INPUT THRESHOLD VOLTAGE vs. Vcc
|
|
T = 25˚C |
|
|
|
A |
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
(V) |
1.5 |
|
|
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threshold |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
VCC
Figure 55. I/O Pin Input Hysteresis vs. VCC
I/O PIN INPUT HYSTERESIS vs. Vcc
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
0.18 |
|
|
|
0.16 |
|
|
(V) |
0.14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hysteresis |
0.12 |
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.06 |
|
|
|
0.04 |
|
|
|
0.02 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
VCC
73
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny12 Typical
Characteristics
The following charts show typical behavior. These data are characterized, but not tested. All current consumption measurements are performed with all I/O pins configured as inputs and with internal pull-ups enabled. A sine wave generator with rail-to-rail output is used as clock source.
The power consumption in Power-down Mode is independent of clock selection.
The current consumption is a function of several factors such as: operating voltage, operating frequency, loading of I/O pins, switching rate of I/O pins, code executed and ambient temperature. The dominating factors are operating voltage and frequency.
The current drawn from capacitive loaded pins may be estimated (for one pin) as CL*VCC*f where CL = load capacitance, VCC = operating voltage and f = average switching frequency of I/O pin.
The parts are characterized at frequencies higher than test limits. Parts are not guaranteed to function properly at frequencies higher than the ordering code indicates.
The difference between current consumption in Power-down Mode with Watchdog Timer enabled and Power-down Mode with Watchdog Timer disabled represents the differential current drawn by the Watchdog timer.
Figure 56. Active Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by Internal Oscillator
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
DEVICE CLOCKED BY 1.2MHz INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR
|
1.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Α) |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cc |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
74 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

 ATtiny11/12
ATtiny11/12
Figure 57. Active Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by External 32kHz Crystal
ACTIVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
DEVICE CLOCKED BY 32KHz CRYSTAL
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
(μΑ) |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cc |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
Figure 58. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by Internal Oscillator
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
DEVICE CLOCKED BY 1.2MHz INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mΑ) |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
75
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 59. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC, Device Clocked by External 32kHz Crystal
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. Vcc
DEVICE CLOCKED BY 32KHz CRYSTAL
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μΑ) |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
Vcc(V)
Analog Comparator offset voltage is measured as absolute offset.
Figure 60. Analog Comparator Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Voltage
ANALOG COMPARATOR OFFSET VOLTAGE vs.
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE VCC = 5V
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mV) |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
Voltage |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Offset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
Common Mode Voltage (V)
76 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

ATtiny11/12
Figure 61. Analog Comparator Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Voltage
Offset Voltage (mV)
ANALOG COMPARATOR OFFSET VOLTAGE vs.
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE |
V = 2.7V |
|
CC |
10 |
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
8 |
|
6 |
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
0
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
Common Mode Voltage (V)
Figure 62. Analog Comparator Input Leakage Current
ANALOG COMPARATOR INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
= 6V |
T = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(nA) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACLK |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
6.5 |
7 |
VIN (V)
77
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 63. Calibrated RC Oscillator Frequency vs. VCC
CALIBRATED RC OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY vs.
OPERATING VOLTAGE
|
1.22 |
|
|
|
|
|
TA |
= 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 45˚C |
||
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 70˚C |
|
1.18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MHz) |
1.14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC |
1.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.06 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC(V)
Figure 64. Watchdog Oscillator Frequency vs. VCC
WATCHDOG OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY vs. Vcc
|
1600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
(kHz) |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
6 |
VCC (V)
78 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

 ATtiny11/12
ATtiny11/12
Sink and source capabilities of I/O ports are measured on one pin at a time.
Figure 65. Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Input Voltage (VCC = 5V)
|
120 |
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μA) |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OP |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
VOP (V)
Figure 66. Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Input Voltage (VCC = 2.7V)
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(μA) |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
VOP (V)
79
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 67. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. Output Voltage (VCC = 5V)
|
70 |
|
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
VOL (V)
Figure 68. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage (VCC = 5V)
|
20 |
|
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
VOH(V)
80 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07

 ATtiny11/12
ATtiny11/12
Figure 69. I/O Pin Sink Current vs. Output Voltage (VCC = 2.7V)
OL
I (mA)
25
TA = 25˚C
20
TA = 85˚C
15
10
5
0
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
VOL (V)
Figure 70. I/O Pin Source Current vs. Output Voltage (VCC = 2.7V)
|
6 |
|
TA = 25˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
TA = 85˚C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mA) |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
VOH (V)
81
1006F–AVR–06/07

Figure 71. I/O Pin Input Threshold Voltage vs. VCC (TA = 25°C)
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
(V) |
1.5 |
|
|
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threshold |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
VCC
Figure 72. I/O Pin Input Hysteresis vs. VCC (TA = 25°C)
|
0.18 |
|
|
|
0.16 |
|
|
(V) |
0.14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hysteresis |
0.12 |
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.06 |
|
|
|
0.04 |
|
|
|
0.02 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
VCC
82 ATtiny11/12
1006F–AVR–06/07
