
11020
.pdf
Fig.1. The location of the school in the district Fig.2.The location of the school in the district
The recreational zone is represented by the park in the ravine and it adjoins the school. On the other side it is surrounded by high-rise residential houses.
Master plan of the school itself includes different playgrounds (fig. 3), utility zone, sport core according to the Code 42.13330.2011 “Urban Planning”.
One of the important question in design of educational buildings is insolation. Insolation requirements provide comfortable use of the building; it influences the mood of people, their health. (fig.4). Thus, classrooms, laboratories, computer classes are oriented to the south and east points. As a result, there is a convenient location of these premises, because sun light gets into them from the morning till the afternoon.
Fig.3. Master plan |
Fig.4. Insolation |
Direct sunlight is not necessary in drafting and drawing classrooms during studying process, that is why they have north-facing and west-facing windows.
As for the appearance of the building, there was an idea to design a school with the technical bies. Therefore the concept of the project is a cable with white cover and colorful wires inside. (fig.5) Gable facades, as a wire section, have an elaborate structure that can be seen in a big amount of extruded planes of
541


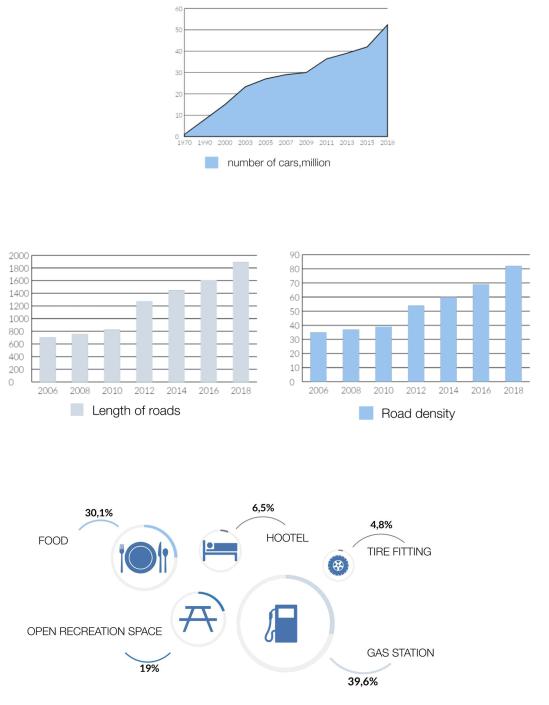

Pic.2 Roadside complex
Multifunctional roadside complexes are special areas containing all types of road service facilities providing a wide range of customer services such as repair and maintenance of motor vehicles, services connected with accommodation, dining, relaxation etc.
It should be noted, however, that in the recent years, objects of roadside clusters in scientific publications have not been seen as independent architectural objects. Specific relevant studies are absent. In addition, there are no special mechanisms or tools for finding universal architectural and planning solutions applicable to the objects. There is not any methodology for comprehensive assessment of objects. There is also no RA development strategy.
The aim of the research is to analyze the formation of the roadside architecture, to develop typological and methodological models based on the generalization of foreign and domestic experience.
Tasks of the research:
-to study the formation and evolution of the RA environment
-to develop the system of type-forming factors with regard to spaceplanning solutions
-to classify the RA structures according to their typological characteristics.
It should be noted, however, that in the recent years, objects of roadside clusters in scientific publications have not been seen as independent architectural objects. Specific relevant studies are absent. In addition, there are no special mechanisms or tools for finding universal architectural and planning solutions applicable to the objects. There is not any methodology for comprehensive assessment of objects. There is also no RA development strategy.
The formation of the RA environment is one of the key national objectives in the 20th century.
546


