
- •2 Discuss in pairs professional responsibilities of mentioned above jobs.
- •3 Make a small speech supporting the statement “The Modern World Needs Packaging Development Engineers”. Produce at least five arguments proving this point of view.
- •If you want to become a packaging development engineer …
- •5 Answer the questions below
- •6 Find the words in the text that have such meanings as:
- •7 Match the words to the definitions.
- •8 Make up collocations matching the words from the box to the words below.
- •9 Explain meanings of the following words from the text.
- •10 Make up a dialogue.
- •11 Read the text below and use the word given in capitals at the end of each line to form a word that fits in the space in the same line.
- •12 Read the description of a Packaging Engineer job and fill in the correct preposition from the box. Each preposition should be used once.
- •13 Work individually. Study the information below. Grammar tenses Present Tenses
- •14 Read the description of the Present Tenses and do exercises afterwards. Present simple
- •Present continuous
- •Present perfect
- •Present perfect continuous
- •15 Using the words in parentheses, complete the sentences below with the appropriate tenses of Simple Present or Present Continuous.
- •16 Using the words in parentheses, complete the sentences below with the appropriate tenses of Present Perfect or Present Continuous or Present Perfect Continuous.
- •17 Read the description of the Past Tenses and do exercises afterwards. Past Tenses
- •Past simple
- •Past continuous
- •Past perfect
- •Past perfect continuous
- •18 Using the words in parentheses, complete the sentences below with the appropriate tense of Past Simple, Past Perfect, Past Continuous or Past Perfect Continuous.
- •19 Using the words in parentheses, complete the text below with the appropriate tenses Past Perfect or Past Perfect Continuous
- •20 Read the description of the Future Tenses and do exercises afterwards. Future Tenses
- •Future simple
- •Future continuous
- •Future perfect
- •Future perfect continuous
- •21 Using the words in parentheses, complete the sentences below with the appropriate Future Tense (in several cases you’ll have to use one of Present Tenses).
- •22 Look through the tables of grammar tenses and find the common features in structure of all a) Simple Tenses, b) Continuous Tenses, c) Perfect-Continuous Tenses, d) Perfect Tenses.
- •23 Below you can see the list of words. Group them according to the Grammar Tense and fill in the Table 1.
- •24 Define what Grammar Tense the description belongs to.
- •25 Analyze the following sentences and define their Grammar Tenses. The first is done for you.
- •26 Circle the letters of the correct verb forms the complete the sentences.
- •27 Using the words in parentheses, complete the sentences below with the appropriate Grammar Tense.
- •28 Compose sentences out of the words from the columns. Use as many Grammar Tenses as you can.
- •Introduction
- •9 You are going to read the text and make up a dispute afterwards.
- •30 Discuss in pairs such an opinion:
- •31 Role-play.
- •32 Role-play.
- •33 Look at the questions concerning work experience. Compare ideas in pairs or small groups within 5 minutes.
- •37 In paragraph
- •4 Explain meanings of these word and phrases in English.
- •Origin of Modern Packaging and Canning
- •6 Retell the text using the diagram below.
- •7 Match the words from the list to the definitions. Consult with a dictionary if it is necessary.
- •8 Explain meanings of these phrases in English and compose your own sentences using them.
- •9 Read the text and fill in the missed prepositions. Canning
- •10 Look through the text one more time and find the information required in the diagram below.
- •11 Scan the text once again and answer the questions.
- •12 Read the descriptions. What is the word for each one? The first letter is already there. There is one space for each other letter in the word. For questions 1-10, write the words.
- •Use the word given in capitals at the end of each line to form a word that fits in the space in the same line.
- •15 Decide whether the statements are true or false. Correct the sentence if it’s wrong.
- •16 After reading the following text say if you share the enthusiasm about the new package with it's creators.
- •17 Complete the sentence with the right variant.
- •18 Fill the correct word from the box below. Use the words only once.
- •19 Find as many antonyms to the listed words as you can in the text.
- •20 Match the words from the list to the definitions. Consult with a dictionary if it is necessary.
- •21 Match the words in list a with their synonyms in list b. Then choose any two words in list a and explain them for other students to guess.
- •22 Explain meanings of these word and phrases in English.
- •23 Work individually. Study the information about the Passive Voice and do exercises afterwards. The passive voice
- •Verbs with two objects have two possible passive structures.
- •24 Fill in the table with the sentences below.
- •25 Make simple past passive negatives and questions.
- •26 Ask questions with Who ……….By?
- •Ex: Contracts are being signed.
- •31 Fill in the gaps with the form of the verb given in the right column. You should choose between Passive Voice and Active Voice. You can use the preposition «by» in the Passive Voice sentences.
- •32 Play the game.
- •33 Remake the story, turning all sentences into the Passive.
- •34 You are going to take part in a conference. The subject of you report is “Food Packaging Revolution.” Sum up all the information from this unit and make the report.
- •35 Role-Play.
- •36 Comment on such statements as:
- •37 Discuss these questions in your group.
- •38 Make a survey and write a composition describing the future of packaging. Support your ideas with the facts concerning modern tendencies.
- •Word list
- •6 Say if the following sentences are true or false according to the text.
- •7 Read the text once again and find all necessary information to complete the diagram: write the missed words and answer the questions.
- •8 Match the words 1-7 from the text to their definitions a-g.
- •9 Explain meanings of the following words in English:
- •10 Make up collocations matching the words from the box to the words below, translate them into Russian, make up a number of sentences using all of them.
- •11 You are going to read the text about strategies that help Packaging Development Engineers to assure successful package development. Before reading work in pairs and discuss the questions below.
- •In what spheres of life do people have strategies?
- •12 Now read the text and check if you were right. While reading, fill in the gaps with the most appropriate word (a, b, c or d). Think carefully about both meaning and grammar.
- •13 Say if the following sentences are true or false according to the text.
- •14 Read the text again. Then, working with a partner, retell it to each other in your own words.
- •15 Match the phrases from the left list to their definitions on the right.
- •16 Match the words to their opposites, as in the example.
- •17 Make up collocations matching the words from the box to the words below.
- •18 Explain meanings of the following words from the text.
- •19 Write the missing words. The first letters are done for you as hints.
- •20 Study the information about participle in the table below. Do the grammar activities following this table. P articiples
- •24 Rewrite these sentences using a present participle or a past participle.
- •26 Read the jokes and comment on them using as many participles as you can. Choose any joke and paraphrase it using the Present and the Past Participle.
- •29 Role-play. You are a Project Team. Discuss the main parameters of the future package. Use suitable phrases from the boxes below.
- •30 Comment on the pictures.
- •31 Discuss these questions in your group.
- •33 Look carefully at the sample below and find such elements as:
- •Word list
- •Lead-in
- •1 Discuss in groups the following questions:
- •2 Complete each sentence with a word from the list. Say to what sphere of life this definition of label belongs to.
- •3 There are many types of labels. Here are the most common ones.
- •4 Explain the meanings of the words in English
- •5 Read the descriptions. What is the word for each one? The first letter is already there. There is one space for each other letter in the word. For questions 1-17, write the words.
- •6 You are going to read a text about textile labels. Before you read, check that you understand these important words. Match the words to the definitions.
- •7 Read the following text and decide which answer (a, b, c or d) best fits each gap. Think carefully about both meaning and grammar.
- •8 Discuss these questions in pairs.
- •9 Read the text again. Then, working with a partner, retell it to each other in your own words.
- •10 Make up collocations matching the words from the box to the words below, translate them into Russian, make up a number of sentences using all of them.
- •11 Match the phrases from the list to the label instruction describing their meaning.
- •12 Read the Label (Picture b) and point out as much information as possible. You may use decryption of symbols (Picture a) as a hint.
- •13 Work individually. Study the information about the article and do exercises afterwards. The Article
- •14 Study these sentences and explain the use of the article.
- •15 Use this map to answer the questions in the way shown. Write the name of the place and the place it is in. On maps we do not normally use the, but in your sentences, use the if necessary.
- •16 Complete the sentences with the where necessary.
- •17 Work individually. Study the information about the Indefinite Article (a/an)
- •18 Study these sentences and explain the use of a /an article.
- •19 Compare and contrast these labels paying special attention to the articles a/ an and the.
- •20 Work individually. Study the information about the cases of Zero Article
- •21 Study these sentences and explain the use of the zero article.
- •22 Read these texts and decide if you need to add nothing (the zero article), a/an or the.
- •23 Explain the use of articles (including the zero article) in these sentences.
- •24 Choose the correct form.
- •25 Read this text and decide if you need to add a/an / the or nothing (the zero article).
- •25 Work in pairs and work out custom labels for such kinds of products as:
- •27 Make up a dialogue.
- •28 Comment on one of the following extract and discuss with your group questions below.
- •W ord list
- •It starts with design
- •Wow! what a package! An Austrian Treat Creates Allure with a Hand-Made Touch
- •Take mascara for a spin
- •Allure increasingly luscious standpoint coated
- •Demystifying icon design
- •Conditionals
- •In pairs ask and answer questions about what you would do in each of the following situations, as in the example. Use your own ideas.
- •Past/present, present/past
- •Past/future, future/past
- •Present/future, future/present
- •Food Packaging
- •Food packaging
- •Food labelling
- •New package for new consumers
- •Complex object / complex subject
- •It says ‘An honest product from an honest company…
- •100% Artificial’
- •How packaging can influence consumer buying behaviour
- •Successful packaging
- •Effective package design
- •Package scent as product preference driver
- •Rules to remember:
- •In your opinion, does packaging affect the environment? If yes, in what way?
- •How do you understand the term ‘sustainable packaging’? What properties should it have?
- •Look at the pictures. Are there any products which have a sustainable package? What are the things made from?
- •Sustainable packaging
- •What’s the deal with biodegradable packaging?
- •Emphasis
Food labelling
1. Food labels, especially those used on processed and prepared foods, need to convey a great deal of information to consumers. Labels need to tell the consumer what they're buying, how healthy it is, if it contains any ingredient that might affect people with allergies, and how to store and cook it safely.
Prepared and packaged food should list all ingredients in order of weight, including water. Additives must be listed and identified as colourings, preservatives or flavourings. Colourings and preservatives must be listed by their full name, or E-number, or both. Flavourings don't need to be individually named.
The amount of significant ingredients included in a product (for instance the chicken content of a chicken pie, or the amount of strawberries in strawberry yoghurt) must be given as a percentage of the total.
By law all allergens (any ingredient that may cause an allergic reaction, including celery, eggs, milk, peanuts and sulphur dioxide) must be clearly marked.
Although genetically modified (GM) ingredients have to be specified on labels, there is no requirement for ingredients that may be derived from GM-linked sources to be stated. For instance, the GM link to meat, eggs or milk used from animals that are given GM feed, or lecithin (often used in cakes) derived from GM soya would not have to be declared on the label.
2. Knowing the calorie, fat, sugar and salt content of food can help consumers to make healthier food choices. Manufacturers have been reducing the amount of salt, use of trans-fats and sugar in products, but beware misleading claims on the packaging. The term 'No added sugar' could mean sweeteners are used instead of sugar and the food could be high in saturated fat. A low-fat product could still have a high sugar content.
M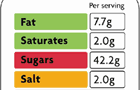 ost
foods include a nutritional breakdown of the amount of energy such
as calories (kcal), fats (including saturated), carbohydrates,
fibre, salt, sugar and so on, per serving and per 100g, on the pack.
This breakdown is only mandatory if the food makes a nutritional
claim such as low-fat or reduced salt. In practice, however, most
foods carry this breakdown.
ost
foods include a nutritional breakdown of the amount of energy such
as calories (kcal), fats (including saturated), carbohydrates,
fibre, salt, sugar and so on, per serving and per 100g, on the pack.
This breakdown is only mandatory if the food makes a nutritional
claim such as low-fat or reduced salt. In practice, however, most
foods carry this breakdown.
The Food Standards Agency has devised a traffic lights system to help shoppers see the levels of fat, sugar and salt that are contained in ready-made foods more easily. Red denotes a high salt, sugar or fat content, green represents low and amber a moderate content. This colour code can be presented as a wheel or a row of lights.
3. Food must carry the name and address of the manufacturer, packer or retailer. However, these details might be misleading because if the main ingredients are imported, a manufacturer does not have to state where these have been sourced from. They can get around this requirement by describing the product as 'produced in the UK'.
A steak and stout pie or a chilled chicken tikka masala could have been made in the UK (and state this on the label), but the meat might have come from Brazil or Thailand.
4. It’s common sense to follow storage instructions to keep food bought in a freezer or fridge for the period advised on the label.
Use-by dates are put on perishable foods such as ready meals, dairy produce and smoked fish. These dates are intended to inform the consumer of the period after which the foods are unsafe to eat. If a product is not eaten by the specified date, they could be unsafe to eat. Once a packet or jar has been opened, follow storage instructions and don't risk keeping the product for longer than advised.
The sell-by or display-until date information is aimed at the shop or retailer. The purpose of these labels is to tell shop workers and managers when the food is approaching its use-by date. The best-before date is a recommendation applied to preserved or longer-lasting foods. Dried or tinned foods are usually not unsafe to eat after the date given, but they may be stale or may have deteriorated in quality after that time.
Ex.12. Read the text then answer the following questions:
What information does a label need to convey to consumers?
In what way must ingredients be listed on the food label?
What can nutritional information tell us about?
When nutritional breakdown is necessary to be printed on the package?
How does a traffic lights system work?
What information do storage instructions include?
Ex.13. Look at the picture and find the items on the label that are required by law.
1)Manufacturer's name and contact details, 2)name of the product, 3)description of the product, 4)weight (NB - some foods are exempt, for example bread), 5)ingredients (listed in descending order of weight), 6)cooking/heating instructions, 7)storage instructions, 8)best-before date, 9)the process used for manufacture.

Ex.14. Explain meanings of these word and phrases in English.
Processed foods
prepared foods
perishable foods
additives
allergens
genetically modified ingredients
nutritional breakdown
storage instructions
use-by dates
the sell-by or display-until date
the best-before date
Ex.15. Find the following words or expressions in the text about food labelling. Two definitions are given below for each of them. Study the context in which they occur in the text and decide in each case which is the best definition a) or b).
1. to convey |
a) to take or carry from one place to another; transport b) to communicate or make known
|
2. to specify |
a) to name or state explicitly or in detail b) to include as an item in a specification |
3. to derive |
a) to arrive at by reasoning; deduce or infer b) to obtain or receive from a source
|
4. mandatory |
a)required or commanded by authority; obligatory b) of, having the nature of, or containing a mandate
|
5. to devise |
a) to form, plan, or arrange in the mind; design or contrive b) to transmit or give (real property) by will
|
6. stale |
a) having lost freshness, effervescence or palatability b) lacking originality or spontaneity
|
7. to deteriorate |
a) to weaken or disintegrate; decay b) to grow worse; degenerate |
Ex.16. Use the words and expressions from ex.15 to complete the following sentences.
The importance of food packaging is to _______ a brand identity, to facilitate product use, and to modify the material properties of foods.
Packagers can ______ end caps, trays, cushions, and clamshell packaging that best fit their product and shipping methods.
If one has knowledge of specific sensitivities of a food or the properties of another product, one can _____ the necessary packaging requirements.
_______ labelling is the requirement of consumer products to state their ingredients or components.
Food technologists _____ new and improved techniques for the processing, conservation and preservation of food items.
Because of constantly changing consumer demands and Food and Drug Administration requirements, things rarely get _____ in the food packaging industry.
An understanding of the various factors that cause food to _______ is helpful to ensure that the correct packaging is selected.
Ex.17. Read the following extract and fill each of the gaps with one suitable word. There is an example at the beginning.
