- •Introduction
- •1. Rectifiers
- •1.1 Employment, basic constituents
- •1.2. Technical and economic indexes of rectifier
- •1.3. Classification of rectifiers
- •1.4 Calculated basic parameters of designing
- •1.5 Some definitions
- •Thyristor as logical switch
- •1.7 A single-phase half-wave rectifier
- •1.7.1 Operation of single-phase half-wave rectifier with active load
- •For a secondary winding
- •For a primary winding
- •1.7.2. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with active - inductive load and limited inductance
- •1.7.3. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with resistive-capacitive load
- •1.8. A single-phase full-wave rectifier with a centre tap
- •1.8.1. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with a centre tap with an active load
- •1.7.2. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load and limitеd inductance
- •1.8.3. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load with infinite inductance
- •1.8.4. Consideration of a stage of switching of thyristors for a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load with infinite inductance
- •1.8.5 An external characteristic in per unit values
- •1 .9 A single-phase bridge rectifier
- •Figure 1.18
- •From cathode group thyristors current is flowing through that the right one witch have anode voltage greater than other one.
- •From anode group thyristors current is flowing through that the right one witch have cathode voltage less than other one.
- •1.10 The three-phase rectifier with a centre tap
- •1.10.3 The controlled three-phase circuit with a centre tap
- •1.10.4 The account of a stage of switching for three phase rectifier with centre tap
- •1.10.5 External characteristic
- •1.11 Three-phase bridge rectifier
- •The external characteristic
- •1.12 The double three-phase rectifier with balancing reactor
- •1.12.2. Definition of parameters for a choice of thyristors, calculation of the transformer and the balancing reactor
- •1.12.3 Merits and demerits, conditions of application
- •1.13 Equivalent polyphase circuits
- •1.13.2. Parallel connection of double three-phase bridge rectifiers
- •Average value of the rectified voltage is
- •1.14 Operation of the rectifier with opposite- emf
- •1.14.1. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with center tap with opposite- emf and active load
- •1.14.2. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with center tap and opposite-emf and active-inductive load
- •2. Dependent inverters
- •2.1 Transition from a rectifying conditions to an inverting conditions
- •External characteristics
- •3. Equipment and characteristics
- •3.1 Transformers for converting sets
- •3.2 The higher harmonics of a current and a voltage
- •The higher harmonics in a curve of the rectified voltage
- •3.2.3 The higher harmonics in a curve of a prime current
- •3.3. Power characteristics of the converter
- •3.3.1. Efficiency
- •3.3.2 Power factor
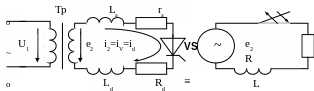
1.7.2. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with active - inductive load and limited inductance
Conditions: =0, ra=0, La=0, 0 < Ld < ∞
|
Figure 1.5
Ld is connected in series with a load for smoothing a rectified current.
Equivalent resistance and inductance of a circuit are
![]()
According to second Kirchhoff’s law
![]()
where
![]()
Characteristic equation is
![]()
From
here
![]()
We should search out solution as i=iss+ifr; where ifr – a free component, iss - a steady state component.
![]()
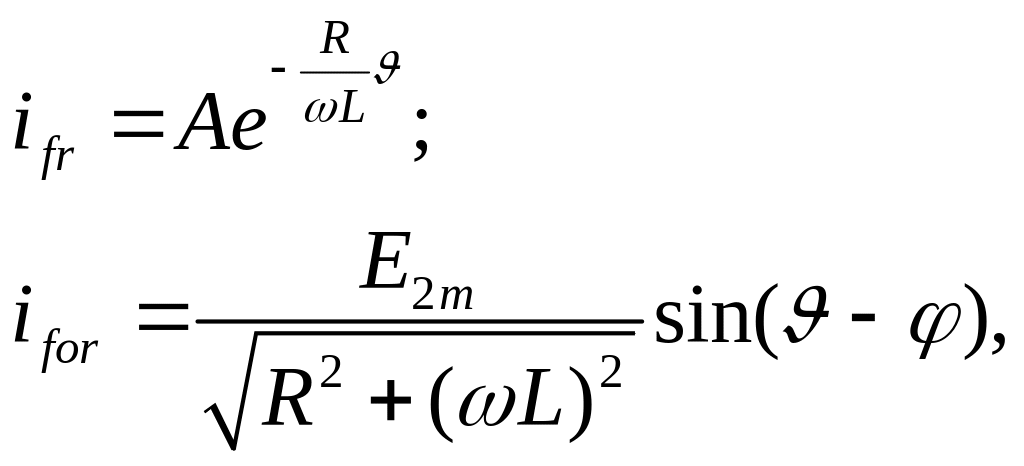
Where
![]()
Constant A we could be found from initial conditions:
At
![]()
Then
![]()
from here
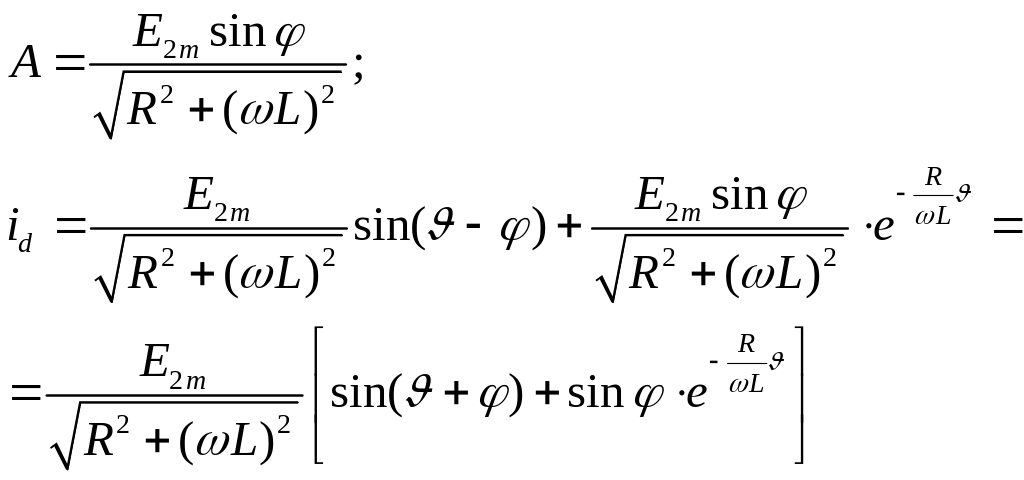
Let's designate
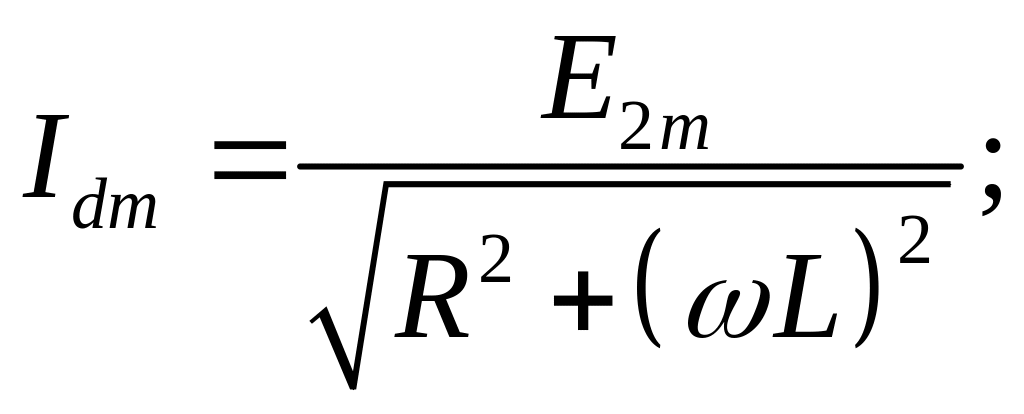
Then
![]()
|
U, I |
Figure 1.6
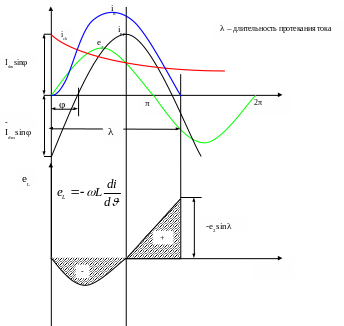
Let's find the energy reserved in inductance L by period
![]()
Energy which inductance accumulates
![]()
Energy which inductance takes out
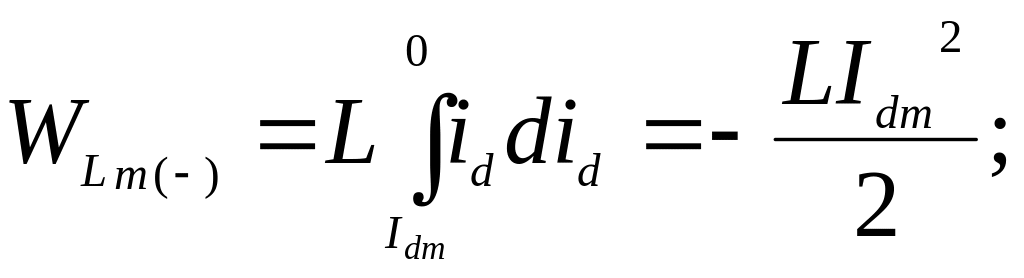
Thus, in the time of period
![]()
A direct component of the rectified voltage is
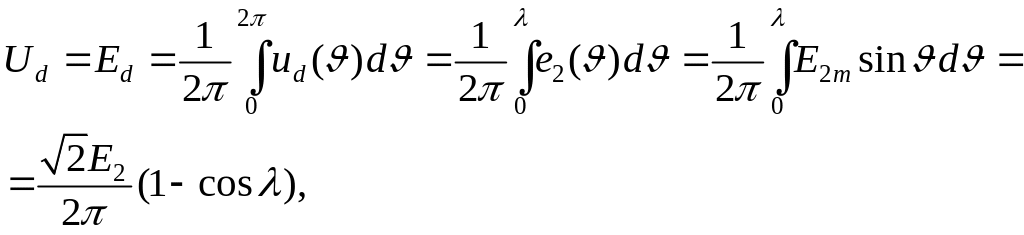
where - a pulse load current duration.
A direct component of a rectified current is
![]()
It is possible to determine λ from the condition: at = λ id =0
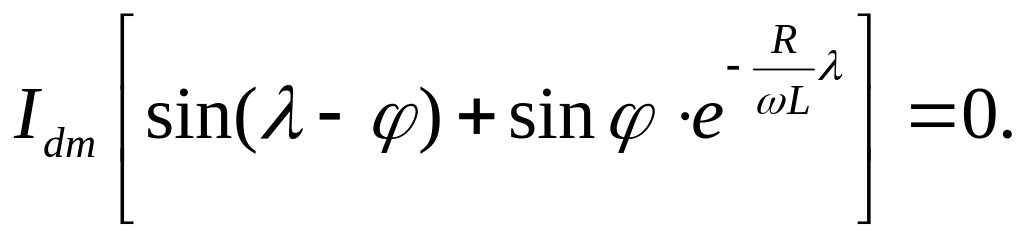
If Ld would increase, λ also increases and Idm goes down, hence, Kr decreases. Thus, it is possible to use Ld as the filter of a load current.
1.7.3. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with resistive-capacitive load
Conditions: α=0, ra=0,
Ld=0,
0 < C <
![]()
|
Figure 1.7
The equations describing electric processes in the circuit are
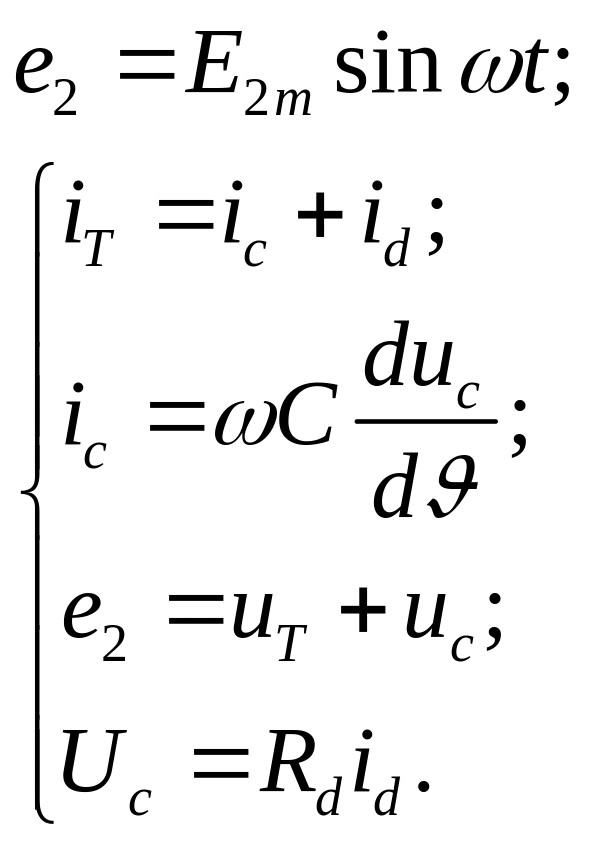
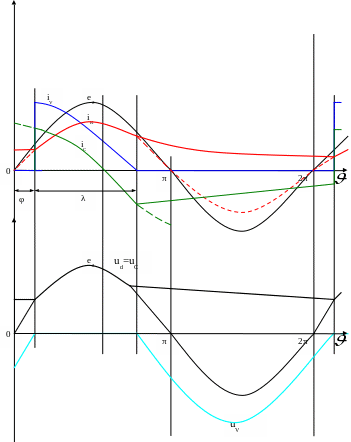
Let's designate:
λ - a pulse thyristor current duration,
φ – a delay angle of the thyristor switching on is fixed concerning a point of natural switching on.
Let's consider intervals:
1)
![]()
The thyristor is on-state:
UT=0;
Let's find IT.

2)
![]() -
-
The thyristor is off-state:
![]() .
.
According to second Kirchhoff’s law
![]()
Characteristic equation is
![]() .
.
Root of this equation is
![]() .
.
Then a voltage across the condenser is
![]() .
.
Current through the load is
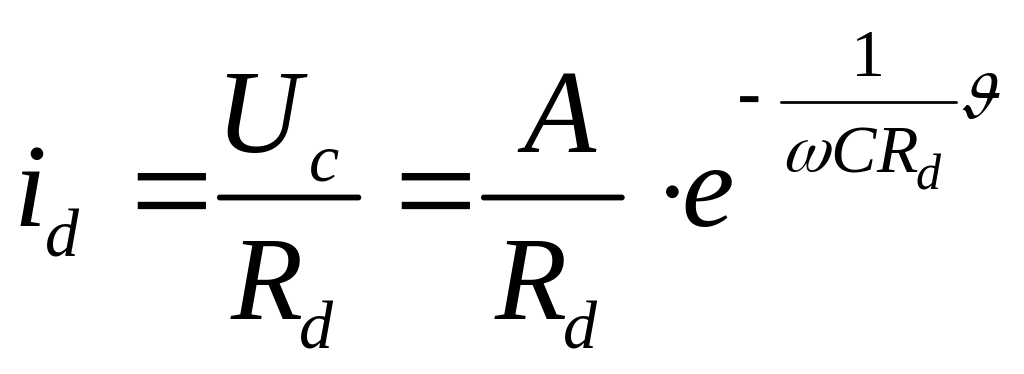 .
.
Current of the condenser is
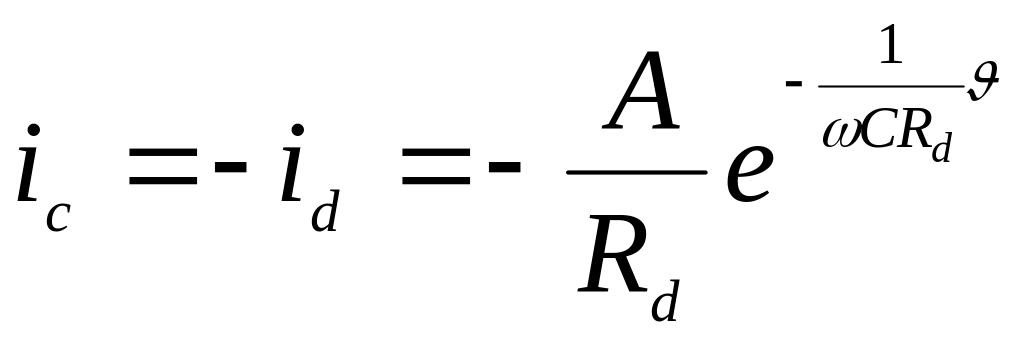 .
.
Voltage across the thyristor is
![]() .
.
Constant A we could be defound from the condition:
At
![]()
Then
![]() .
.
Let's define
![]()
At
![]()

|
Figure 1.7
According to the diagram of changing the function tg()
![]() limits by
limits by
![]() .
.
For active load:
![]()
for the capacitive load:
![]() ,
,
From the condition of the no interrupted process, i.e. periodicity of electromagnetic processes in the circuit, we could find φ:
![]()
This transcendental equation can be solved graphically or by numerical methods by computer.
e,u
e,i |
Fig. 1.8 – The diagram of electric processes in a single-phase half-wave circuit of the rectifier with resistive-capacitive load.
1.8. A single-phase full-wave rectifier with a centre tap
The single-phase full-wave rectifier with a centre tap is in fact two-phase one because the secondary winding of the transformer with a centre tap creates two EMF which are equal by module, but are in opposite directions.
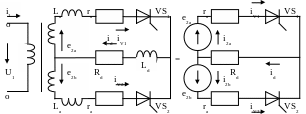
Figure 1.9