
- •Introduction
- •1. Rectifiers
- •1.1 Employment, basic constituents
- •1.2. Technical and economic indexes of rectifier
- •1.3. Classification of rectifiers
- •1.4 Calculated basic parameters of designing
- •1.5 Some definitions
- •Thyristor as logical switch
- •1.7 A single-phase half-wave rectifier
- •1.7.1 Operation of single-phase half-wave rectifier with active load
- •For a secondary winding
- •For a primary winding
- •1.7.2. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with active - inductive load and limited inductance
- •1.7.3. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with resistive-capacitive load
- •1.8. A single-phase full-wave rectifier with a centre tap
- •1.8.1. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with a centre tap with an active load
- •1.7.2. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load and limitеd inductance
- •1.8.3. Operation of a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load with infinite inductance
- •1.8.4. Consideration of a stage of switching of thyristors for a full-wave rectifier with centre tap and active - inductive load with infinite inductance
- •1.8.5 An external characteristic in per unit values
- •1 .9 A single-phase bridge rectifier
- •Figure 1.18
- •From cathode group thyristors current is flowing through that the right one witch have anode voltage greater than other one.
- •From anode group thyristors current is flowing through that the right one witch have cathode voltage less than other one.
- •1.10 The three-phase rectifier with a centre tap
- •1.10.3 The controlled three-phase circuit with a centre tap
- •1.10.4 The account of a stage of switching for three phase rectifier with centre tap
- •1.10.5 External characteristic
- •1.11 Three-phase bridge rectifier
- •The external characteristic
- •1.12 The double three-phase rectifier with balancing reactor
- •1.12.2. Definition of parameters for a choice of thyristors, calculation of the transformer and the balancing reactor
- •1.12.3 Merits and demerits, conditions of application
- •1.13 Equivalent polyphase circuits
- •1.13.2. Parallel connection of double three-phase bridge rectifiers
- •Average value of the rectified voltage is
- •1.14 Operation of the rectifier with opposite- emf
- •1.14.1. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with center tap with opposite- emf and active load
- •1.14.2. Operation of the half-wave rectifier with center tap and opposite-emf and active-inductive load
- •2. Dependent inverters
- •2.1 Transition from a rectifying conditions to an inverting conditions
- •External characteristics
- •3. Equipment and characteristics
- •3.1 Transformers for converting sets
- •3.2 The higher harmonics of a current and a voltage
- •The higher harmonics in a curve of the rectified voltage
- •3.2.3 The higher harmonics in a curve of a prime current
- •3.3. Power characteristics of the converter
- •3.3.1. Efficiency
- •3.3.2 Power factor
1.4 Calculated basic parameters of designing
Basic parameters describing operating properties of rectifiers are:
- Average values of the rectified voltage and current Ud and Id;
- An EFFICIENCY;
- Power-factor Kp;
- An external characteristic – correlation between average rectified voltage and average rectified current of a load Ud=f (Id);
- Control characteristic – dependence between average rectified voltage and control angle Ud=f(α);
- Pulse factor- ratio of an RMS value of harmonic components of rectified voltage (current) to the average value of the rectified voltage (current):
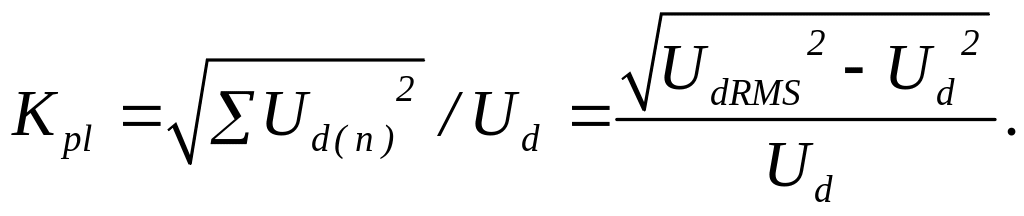
Distortion factor is equal to the ratio of an RMS value of a basic current harmonic to an RMS value of a complete primary winding current of transformer.
Power factor is equal to ratio of active power witch is carried by first harmonics of primary current and voltage to total power of those harmonics.
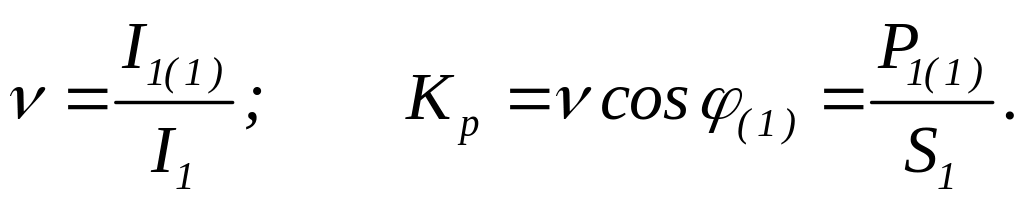
The parameters of individual elements of the rectifier are defined by the given operating conditions of a consumer of a direct current and possible anomalous duty of it (emergencies).
The main task of design calculations of the converters is that to definite the correlations enabling to find electrical parameters of the rectifiers, the transformer and also parameters of the filtering, stabilizing devices and regulating system account to the duty of the load, and then to choose these devices under the catalogue or, if it is necessary, to construct them.
Parameters describing operation of rectifiers:
- Average ITAV, root mean square ITRMS and maximum ITM values of a current flowing through a valve under rated duty of load and under possible overloads;
- Peak-inverse voltage of a valve if it is off-state URM;
- Peak-positive voltage of valve UDM (in the case of application of controlled rectifiers).
Parameters of power transformer:
- RMS values of voltage and current of a secondary (rectifier’s) winding of transformer U2 and I2;
- RMS value of a current of a primary winding of the transformer I1;
- Total powers of windings S1 and S2 and electrical rating (type power) of the transformer ST.
1.5 Some definitions
1). Let’s consider electromagnetic processes in the converter in angular coordinates
![]() ,
,
where ω- cyclic frequency, t- current time.
2). The angle, at which an uncontrolled rectifier is turned on, names as a point of natural turning on.
The angle when controlled rectifier is turned on just as a control pulse is applied names as a control angle (turning on, regulating, ignition angle). This angle is fixed concerning a point of natural turning on.
3). The average value, or direct component of a current (voltage) is a square between a current (voltage) waveform and abscissa axis averaged during of waveform period.
Figure 1.2
![]()
![]()
4). The root mean square value of periodical current is same value of a direct current, which flowing during of waveform period through the given part of a circuit, produces as amount of heat as considered alternating current.
Amount of heats is produced by the direct current is
Q==I2RMSּּRּT;
Amount of heat is produced by the alternating current is
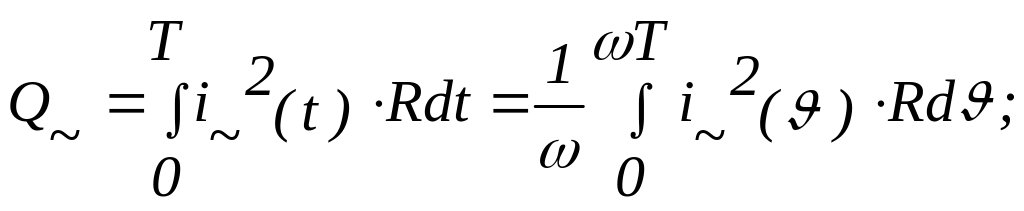
But the condition Q= = Q ~ must be executed.
From here

As U=IR, so
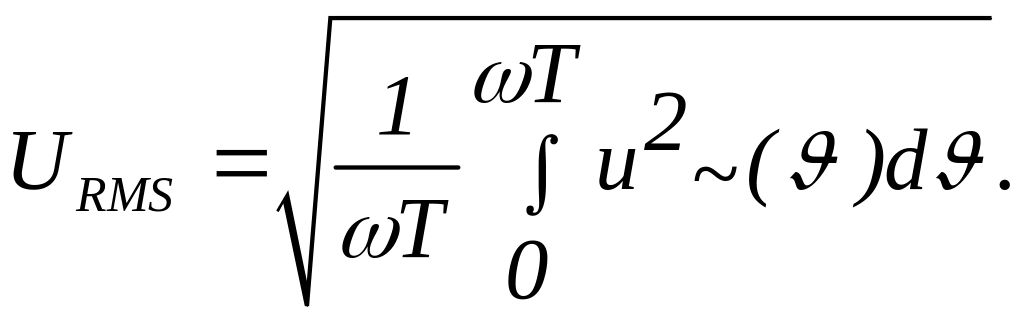
5). Let's suppose that the uncontrolled rectifier is a special case of controlled rectifier at
ά = 0.
6). Let’s consider thyristor as logical switch.
