
- •Харків. Вид. Хнеу, 2010
- •Харків. Вид. Хнеу, 2010
- •Introduction
- •Module 1. Basics of market economy Lecture 1. Basic economic terminology
- •1. Terminology
- •Economic resources
- •2. Economic reasoning
- •Choices made at the margin(край)
- •Three basic economic decisions
- •5. Economic forces
- •6. The role of theory in economics
- •Value judgments
- •Microeconomics and macroeconomics
- •8. Economics and other subjects
- •Lecture 2. Economic systems: capitalism, socialism and mixed economy
- •1. Evolving развитие Economic Systems
- •2. Socialism
- •3. Capitalism
- •Figure 2.1. The circular of income and expenditure in a market economy:
- •Specialization and Exchange обмен
- •4. Differences between soviet-style socialism and capitalism
- •Table 2.1 Capitalism’s and soviet-style socialism’s solutions to the three economic problems
- •5. Mixed Economy
- •Government and the Economy
- •Some modern models of mixed economy
- •6. Transition economy
- •Government price setting.
- •Passive macroeconomic policies.
- •7. Other classifications of economic systems
- •Lecture 3. Supply спрос and demand требование
- •1. Markets: purposes and functions
- •2. Demand
- •The Market Demand Curve and the Law of Demand
- •Table 3.1 a demand schedule for grade a eggs
- •Foundation for the law of demand:
- •Figure 3.2. Changes in demand
- •Figure 3.3. Changes in quantity demanded
- •3. Supply
- •The market supply curve and the law of supply
- •Table 3.2 a supply schedule for a eggs
- •4. The marriage of supply and demand (market equilibrium)
- •Lecture 4. Elasticity of supply and demand
- •1. Price elasticity of demand.
- •2. Price elasticity of supply.
- •1. Price elasticity of demand
- •Determinants of price elasticity of demand
- •3. The proportion of income consumers spend on the good.
- •2. Price elasticity of supply
- •Determinants of price elasticity of supply
- •Perfectly inelastic and perfectly elastic supply
- •Module 2. Basics of micro and macroeconomics Lecture 5. Business firm
- •3. Functions of business firms.
- •1. Terminology
- •Scale of production
- •2. Basic types of business enterprise
- •Pros and cons of corporate business
- •Other types of enterprises
- •3. Functions of business firms
- •4. Management
- •Lecture 6. Production, cost and profit
- •3. Variable costs, fixed costs, and total costs.
- •1. Production relationships
- •Period of Production
- •2. The law of diminishing marginal returns
- •Total product curve and marginal product curve
- •Average Product
- •3. Variable costs, fixed costs, and total costs
- •4. Measuring cost and profit
- •5. Normal profit and economic profit
- •Theories of profit
- •Profit as a pay for input
- •Table 7.1 Annual production possibilities for food and clothing
- •3. Law of increasing opportunity cost
- •4. Economic growth: expanding production possibilities
- •Lecture 8: Macroeconomics: economic growth, business cycles, unemployment, and inflation
- •2. Business cycles.
- •4. Inflation.
- •1. Economic growth and living standards
- •Productivity
- •2. Business cycles
- •Leading Indicators
- •3. Unemployment
- •Types of unemployment
- •4. Inflation
- •Types of inflation
- •Relationship between inflation and unemployment
- •Economic interdependence among nations
- •5. Macroeconomic policy
- •Types of macroeconomic policy
- •Lecture 9. Monopoly, oligopoly and competition
- •1. Monopoly
- •How monopoly is maintained: barriers to entry
- •2. Perfect competition
- •3. Monopolistic competition
- •Product differentiation
- •Price discrimination
- •4. Oligopoly
- •Concentration ratios
- •The competitive spectrum
- •1) Cartel.
- •Forming a cartel: directions and difficulties
- •2) Implicit Price Collusion.
- •3) Price war.
- •4) The Contestable Market Model.
- •5) Price leadership.
- •6) Price rigidity: the kinked demand curve model.
- •7) Entry-limit pricing.
- •A Comparison of Various Market Structures
- •Lecture 10. Money, banking and financial sector
- •2. The definition and functions of money.
- •1. Financial sector
- •Institutions and financial markets
- •Financial institutions
- •Types of financial Institutions
- •Financial Markets
- •Differences among Money Market Assets
- •The role of interest rates in the financial sector
- •References
- •Contents
Financial Markets
A financial market is a market where financial assets and financial liabilities are bought and sold. The stock market, the bond market, and bank activities are all examples of financial markets (fig. 10.1).
A primary financial market is a market in which newly issued financial assets are sold. These markets transfer savings to borrowers who want to invest (buy real assets). Sellers in this market include venture capital firms (which sell part ownerships to new companies) and investment banks (which sell new stock and new bonds for existing companies). Where investment banks only assist firms in selling their stock venture capital firms often are partnerships that invest their own money in return for part ownership of a new firm.
A secondary financial market is a market in which previously issued financial assets can he bought and sold.
Differences among Money Market Assets
Money market assets differ slightly from each other.
A stock is a partial ownership right to a company. The stock owner has the right to vote on company policy, although generally, for smaller shareholders, this right doesn't convey much power.
The financial sector is important in macroeconomics because of its role in channeling flows out of the circular flow – such as savings – back into the circular flow, either in the form of consumer loans (such as you get when you buy something with your credit card), business loans (loans that finance business investment), or loans to government.
The role of interest rates in the financial sector
Price is the mechanism that equilibrates supply and demand in the real sector. Interest rates are the mechanism that equilibrates supply and demand in the financial sector. The channeling of savings into financial assets and the willingness of individuals to incur financial liabilities is strongly influenced by the interest rate on those financial assets and liabilities.
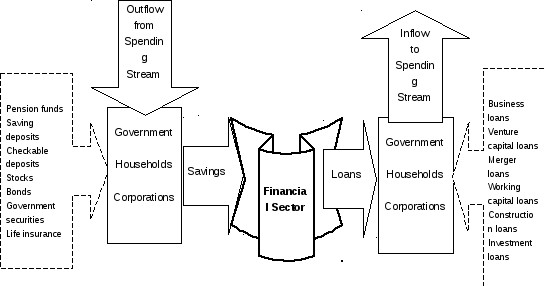
Figure 10.1. Financial sector
-
The definition and functions of money
Money is a highly liquid financial asset that s generally accepted in exchange for other goods, and is used as a reference in valuing other goods and can be stored as wealth.
Functions of money.
-
Money as a medium of exchange.
-
Money as a unit of account.
-
Money as a store of wealth.
Central bank
A bank is a financial institution whose primary function is holding money for and lending money to individuals and firms.
The Central bank is a bank that has the right to issue notes (IOUs). By law these Central bank notes are acceptable payment of one’s taxes and by convention these notes are acceptable payment to all people in the country.
Alternative definitions of money
To handle this ambiguity, economists have defined different concepts of money and have called them M1, M2, and L. Each is a reasonable concept of money. Let's consider their components:
1) M1 consists of currency in the hands of the public, checking account balances and traveler’s checks;
2) M2 is made up of M1 plus savings deposits, small-denomination time deposits, and money market mutual fund shares, along with some esoteric financial instruments that won't concern us here;
3) L is an even wider variety of short-term financial assets (assets whose maturity is less than one year) also have some of the attributes of money. They're liquid and can be "spent" relatively easily. For that reason they're included in some definitions of money.
