
- •Харків. Вид. Хнеу, 2010
- •Харків. Вид. Хнеу, 2010
- •Introduction
- •Module 1. Basics of market economy Lecture 1. Basic economic terminology
- •1. Terminology
- •Economic resources
- •2. Economic reasoning
- •Choices made at the margin(край)
- •Three basic economic decisions
- •5. Economic forces
- •6. The role of theory in economics
- •Value judgments
- •Microeconomics and macroeconomics
- •8. Economics and other subjects
- •Lecture 2. Economic systems: capitalism, socialism and mixed economy
- •1. Evolving развитие Economic Systems
- •2. Socialism
- •3. Capitalism
- •Figure 2.1. The circular of income and expenditure in a market economy:
- •Specialization and Exchange обмен
- •4. Differences between soviet-style socialism and capitalism
- •Table 2.1 Capitalism’s and soviet-style socialism’s solutions to the three economic problems
- •5. Mixed Economy
- •Government and the Economy
- •Some modern models of mixed economy
- •6. Transition economy
- •Government price setting.
- •Passive macroeconomic policies.
- •7. Other classifications of economic systems
- •Lecture 3. Supply спрос and demand требование
- •1. Markets: purposes and functions
- •2. Demand
- •The Market Demand Curve and the Law of Demand
- •Table 3.1 a demand schedule for grade a eggs
- •Foundation for the law of demand:
- •Figure 3.2. Changes in demand
- •Figure 3.3. Changes in quantity demanded
- •3. Supply
- •The market supply curve and the law of supply
- •Table 3.2 a supply schedule for a eggs
- •4. The marriage of supply and demand (market equilibrium)
- •Lecture 4. Elasticity of supply and demand
- •1. Price elasticity of demand.
- •2. Price elasticity of supply.
- •1. Price elasticity of demand
- •Determinants of price elasticity of demand
- •3. The proportion of income consumers spend on the good.
- •2. Price elasticity of supply
- •Determinants of price elasticity of supply
- •Perfectly inelastic and perfectly elastic supply
- •Module 2. Basics of micro and macroeconomics Lecture 5. Business firm
- •3. Functions of business firms.
- •1. Terminology
- •Scale of production
- •2. Basic types of business enterprise
- •Pros and cons of corporate business
- •Other types of enterprises
- •3. Functions of business firms
- •4. Management
- •Lecture 6. Production, cost and profit
- •3. Variable costs, fixed costs, and total costs.
- •1. Production relationships
- •Period of Production
- •2. The law of diminishing marginal returns
- •Total product curve and marginal product curve
- •Average Product
- •3. Variable costs, fixed costs, and total costs
- •4. Measuring cost and profit
- •5. Normal profit and economic profit
- •Theories of profit
- •Profit as a pay for input
- •Table 7.1 Annual production possibilities for food and clothing
- •3. Law of increasing opportunity cost
- •4. Economic growth: expanding production possibilities
- •Lecture 8: Macroeconomics: economic growth, business cycles, unemployment, and inflation
- •2. Business cycles.
- •4. Inflation.
- •1. Economic growth and living standards
- •Productivity
- •2. Business cycles
- •Leading Indicators
- •3. Unemployment
- •Types of unemployment
- •4. Inflation
- •Types of inflation
- •Relationship between inflation and unemployment
- •Economic interdependence among nations
- •5. Macroeconomic policy
- •Types of macroeconomic policy
- •Lecture 9. Monopoly, oligopoly and competition
- •1. Monopoly
- •How monopoly is maintained: barriers to entry
- •2. Perfect competition
- •3. Monopolistic competition
- •Product differentiation
- •Price discrimination
- •4. Oligopoly
- •Concentration ratios
- •The competitive spectrum
- •1) Cartel.
- •Forming a cartel: directions and difficulties
- •2) Implicit Price Collusion.
- •3) Price war.
- •4) The Contestable Market Model.
- •5) Price leadership.
- •6) Price rigidity: the kinked demand curve model.
- •7) Entry-limit pricing.
- •A Comparison of Various Market Structures
- •Lecture 10. Money, banking and financial sector
- •2. The definition and functions of money.
- •1. Financial sector
- •Institutions and financial markets
- •Financial institutions
- •Types of financial Institutions
- •Financial Markets
- •Differences among Money Market Assets
- •The role of interest rates in the financial sector
- •References
- •Contents
2. The law of diminishing marginal returns
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that the extra production obtained from increases in a variable input will eventually decline as more of the variable input is used together with the fixed inputs.
Total product curve and marginal product curve
A total product curve describes how output varies in the short run as more of any one input is used together with fixed amounts of other inputs under current technology. Points on a total product curve give the output that's obtainable, given current technology, from any quantity of the variable input used with the fixed inputs.
The total product of a variable input such as labor services, is the amount of output produced over any given period when that input is used along with other fixed inputs (fig. 6.1).
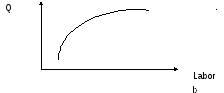
Figure 6.1. Total product of labor
The marginal product of an input is the increase in output from one more unit of that input when the quantity of all other inputs is unchanged. Marginal product (MPL) is:
MPL=ΔTotalP/ΔLabor,
where ΔTP – the change in the total product of labor;
ΔL – the increase number of workers hired per week.
When the marginal product of labor is zero, total product is at its maximum value per period.
This is because at the point where MPL is zero, hiring another worker doesn't add to production anymore, and hiring still one more worker would begin to reduce output.
When marginal product is negative, additional workers decrease weekly production (figure 6.2).
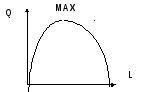
Figure 6.2. Marginal product of labor
Average Product
The average product of an input is the total output produced over a given period divided by the number of units of that input used.
The average product labor is therefore total product (TP) divided by the number of workers (L):
Average product of labor = TP/L.
The average product measures output per worker, which is an indication of the productivity of workers in a plant (figure 6.3).

Figure 6.3. Average product of labor
Remember: when the marginal product falls below the average product of an input, the average product declines уменьшатся. This means the law of diminishing marginal returns also implies that the average product of a variable input will eventually decline as more of that input is used together with fixed inputs.
3. Variable costs, fixed costs, and total costs
In the short run, costs are divided into two basic categories:
1) Fixed costs (FC) are those that do not vary as a firm varies its output. Managers often refer to their fixed costs as over headed costs. These are costs that must be incurred подвергается in the short run even if the firm doesn't produce anything.
2) Variable costs (VC) are those that change with output. These are the costs variable inputs.
Total cost (TC) is the sum of the value of all inputs used over any given period to produce goods. Total cost is the sum of fixed costs and variable costs:
TC = VC + FC
Average cost (AC) is total cost divided by the number of units of output produced over a given period. It's also called average total cost. Managers often refer average cost as their unit cost:
AC=TC/Q
Average variable cost (AVC) is variable cost divided by the number of units of output produced over a given period:
AVC= VC/Q
Average fixed cost (AFC) is fixed cost divided by the number of units of output produced over a given period:
AFC=FC/Q
It's easy to show that average cost is the sum of average variable cost and average fixed cost. Remember that total cost is the sum of variable cost and fixed cost. It follows that:
TC/Q=VC/Q+FC/Q
The two terms on the other side of the equal sign are AVC and AFC, respectively. It follows that:
AC = AVC + AFC
Marginal cost (MC) is the extra cost of producing one more unit of output. There is no accounting concept that parallels marginal cost. However, all good business managers have an idea of their marginal cost and use their estimates of marginal cost of production to make decisions:
MC=ΔTC/ΔQ,
where ΔTC is the change in total cost associated with any given change output, ΔQ.
