
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS
- •MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL
- •ABS BRAKES
- •ADJUSTING REAR SERVICE BRAKES
- •TESTING APPLICATION ADJUSTER OPERATION
- •BLEEDING BRAKE SYSTEM
- •PRESSURE BLEEDING
- •BLEEDING WITHOUT A PRESSURE BLEEDER
- •TEST FOR FLUID CONTAMINATION
- •WHEEL STUD NUT TIGHTENING
- •BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
- •INSPECTION OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
- •FIG. 10 BRAKE LINE ROUTING NON ABS BRAKES
- •INSTALLATION OF BRAKE HOSE
- •TYPES OF TUBING FLARES
- •TO REPAIR OR FLARE TUBING
- •ISO TUBING FLARES
- •BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
- •BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
- •BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
- •BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
- •BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
- •REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES
- •DESCRIPTION
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •REAR BRAKE DRUM REMOVAL
- •BRAKE DRUM INSTALLATION
- •BRAKE SHOE ASSEMBLIES
- •REMOVAL
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •BRAKE SHOE INSTALLATION
- •KELSEY HAYES REASSEMBLE
- •VARGA REASSEMBLE
- •BRAKE DRUM REFACING
- •WHEEL CYLINDERS
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •REMOVING WHEEL CYLINDERS FROM BRAKE SUPPORT PLATES
- •DISASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
- •ASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
- •INSTALLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
- •BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY
- •REMOVAL
- •INSTALLATION
- •HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT SWITCH
- •ABS BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE OPERATION
- •HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
- •PROPORTIONING VALVES
- •PROPORTIONING VALVE APPLICATIONS
- •TESTING ABS PROPORTIONING VALVES
- •FRONT DISC BRAKES
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •SHOE AND LINING WEAR
- •SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER
- •BRAKE SHOE SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •REMOVAL
- •INSTALLATION
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •BRAKE SHOES REMOVE
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •BRAKE SHOES INSTALL
- •DISC BRAKE CALIPER DISASSEMBLY
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION OF BRAKE CALIPER
- •ASSEMBLING DISC BRAKE CALIPER
- •REAR DISC BRAKES
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •LINING WEAR
- •SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •BRAKE SHOE REMOVAL
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •BRAKE SHOE INSTALLATION
- •DISASSEMBLING REAR CALIPER ASSEMBLY
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •CLEANING AND INSPECTION
- •ASSEMBLING REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER
- •BRAKE DISC (ROTOR)
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •INSPECTION DIAGNOSIS
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •CHECKING BRAKING DISC FOR RUNOUT AND THICKNESS
- •BRAKING DISC REMOVAL
- •INSTALLING BRAKING DISC
- •REFINISHING BRAKING DISC
- •REFACING BRAKING DISC
- •RESURFACING BRAKING DISC
- •BRAKING DISC (ROTOR) REFINISHING LIMITS
- •PARKING BRAKES
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •ADJUSTING PARKING BRAKE
- •FIG. 2 PARKING BRAKE CABLE ROUTING AA AND AP BODY
- •FIG. 4 PARKING BRAKE CABLE ROUTING AG AND AJ BODY
- •SELF ADJUSTING PROCEDURES
- •TO RELOAD SELF ADJUSTER
- •ADJUST PARKING BRAKE
- •REAR PARKING BRAKE CABLE REMOVAL
- •DRUM BRAKES
- •DISC BRAKES
- •INSTALLING PARKING BRAKE REAR CABLE
- •DRUM BRAKES
- •DISC BRAKES ALL
- •REMOVING PARKING BRAKE FRONT CABLE
- •INSTALLING PARKING BRAKE FRONT CABLE
- •REMOVAL AG AND AJ BODY
- •INSTALLATION AG AND AJ BODY
- •REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION PARKING BRAKE SHOES
- •ALL WITH REAR DISC BRAKES
- •INSTALLING PARKING BRAKE SHOES
- •MASTER CYLINDER
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
- •TESTING THE MASTER CYLINDER
- •MASTER CYLINDER SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL
- •BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR REPLACEMENT
- •BLEEDING MASTER CYLINDER
- •INSTALLING MASTER CYLINDER
- •POWER BRAKES
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •SERVICE PROCEDURES
- •POWER BRAKE BOOSTER ASSEMBLY
- •WHEEL BEARINGS
- •FRONT WHEEL BEARINGS
- •REAR WHEEL BEARINGS
- •NORMAL SERVICE
- •INSPECTION
- •REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
- •MAJOR ABS COMPONENTS
- •HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
- •PEDAL FEEL
- •TIRE NOISE & MARKS
- •ABS EQUIPPED VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
- •ABS WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
- •RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP
- •NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMPS
- •HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
- •HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR
- •DUAL FUNCTION PRESSURE SWITCH
- •PRESSURE TRANSDUCERS
- •DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
- •PROPORTIONING VALVES
- •FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
- •DUAL FUNCTION PRESSURE SWITCH WIRING DIAGRAM
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •PRESSURE SWITCH AND PRESSURE TRANSDUCER WIRING
- •ABS SYSTEM WIRING SCHEMATIC
- •ABS SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
- •SYSTEM RELAY
- •ABS HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
- •NORMAL BRAKING
- •ABS BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •DEFINITIONS
- •ABS SYSTEM GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES
- •SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS
- •INTERMITTENT FAULTS
- •ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
- •SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
- •BENDIX ABS SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
- •ON CAR HYDRAULIC ABS COMPONENT SERVICE
- •GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
- •BLEEDING ABS BRAKE SYSTEM
- •BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE AND RETURN HOSES (FIG. 6)
- •INSTALL
- •HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
- •BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR
- •HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR
- •PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 17)
- •ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
- •REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIGS. 13 AND 15)
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
- •MAJOR COMPONENTS
- •MASTER CYLINDER AND VACUUM BOOSTER
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •PEDAL FEEL
- •TIRE NOISE & MARKS
- •VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
- •WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
- •NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP
- •MODULATOR ASSEMBLY
- •ISOLATION VALVES
- •SHUTTLE ORIFICE
- •FLUID SUMPS
- •HYDRAULIC SPRING ACCUMULATOR
- •PROPORTIONING VALVES
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
- •SYSTEM RELAY
- •HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
- •NORMAL BRAKING
- •ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
- •GENERAL INFORMATION
- •DEFINITIONS
- •ABS COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •ABS GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
- •ABS BRAKE SYSTEM ON VEHICLE SERVICE
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES
- •SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
- •INTERMITTENT FAULTS
- •ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
- •ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
- •BENDIX ABS SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
- •GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
- •CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
- •MODULATOR ASSEMBLY (FIG. 2)
- •MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER
- •PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 5)
- •ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
- •WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
- •FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIG. 12)
- •REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIGS. 13 AND 14)
- •SPECIFICATIONS
- •SPECIFICATIONS METRIC
- •BRAKE ACTUATION SYSTEM
- •TIGHTENING REFERENCE
5 - 68 BRAKES |
|
|
Ä |
|
|
||
Remove bleeding tubes from cylinder, plug outlets |
Remove master cylinder from vise and install on |
||
and install caps. |
power brake vacuum booster. |
||
|
|
It is not necessary to bleed the entire hydrau- |
|
|
|
lic system after replacing the master cylinder, |
|
|
|
providing that the master cylinder has been |
|
|
|
bled and filled upon installation. |
|
|
|
INSTALLING MASTER CYLINDER |
|
|
|
Position master cylinder over studs of power brake |
|
|
|
unit, align push rod with master cylinder piston. |
|
|
|
Install the master cylinder to power brake unit |
|
|
|
mounting nuts (Fig. 4) and tighten to 28 NIm (250 in. |
|
|
|
lbs.) torque. |
|
|
|
Connect brake tubes to master cylinder primary |
|
|
|
and secondary ports. Tighten fittings to 17 NIm (145 |
|
|
|
in. lbs.) torque. |
|
Fig. 6 Bleeding Master Cylinder
POWER BRAKES
GENERAL INFORMATION
All vehicles, except non turbo charged AP bodies, equipped with manual transmissions use a 205 mm tandem booster. The non turbo charged manual transmission equipped AP body application use a 230 mm non-tandem booster.
The purpose of the vacuum operated power brake booster. Is to reduce the amount of force applied to the brake pedal by the drivers foot. To obtain the required hydraulic pressure in the brake system to stop the vehicle.
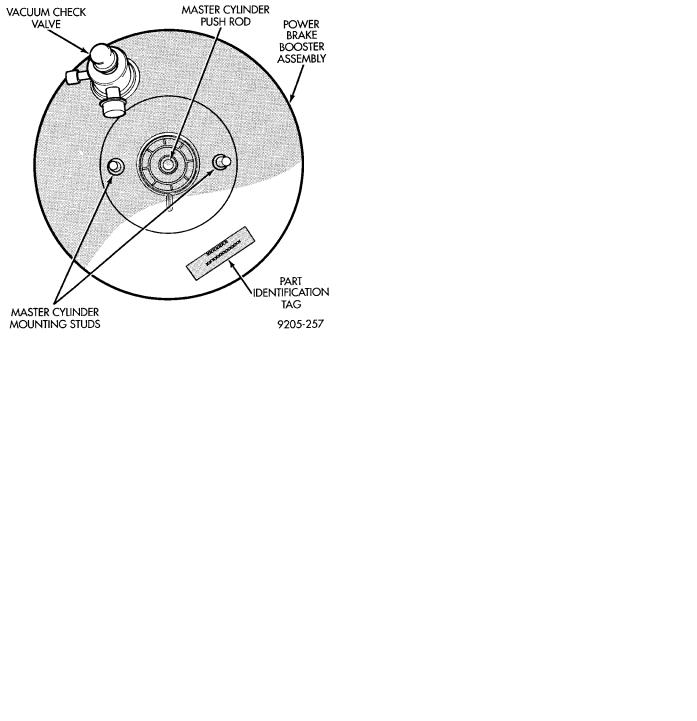
The power brake booster can be identified if required, by the tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig. 1). This tag contains the following information. The production part number of the power booster assembly, the date it was built and who manufactured it.
The power brake booster assembly is not a repairable part and must be replaced as a complete unit if it is found to be faulty in any way. The power booster vacuum check valve is not repairable but can be replaceable as an assembly.
The power brake booster in vacuum operated. The vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the engine through the power brake booster check valve (Fig. 2).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power boosters input rod moves forward. This opens and closes valves in the power booster, creating a vacuum on one side of a diaphragm and allowing atmospheric
Fig. 1 Power Brake Booster Identification
pressure to enter on the other. This difference in pressure forces the output rod of the power booster out against the primary piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons in the master cylinder move forward this creates the hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
