
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •About the Editors
- •Contributors
- •1: Tracheobronchial Anatomy
- •Trachea
- •Introduction
- •External Morphology
- •Internal Morphology
- •Mucous Layer
- •Blood Supply
- •Anatomo-Clinical Relationships
- •Bronchi
- •Main Bronchi
- •Bronchial Division
- •Left Main Bronchus (LMB)
- •Right Main Bronchus (RMB)
- •Blood Supply
- •References
- •2: Flexible Bronchoscopy
- •Introduction
- •History
- •Description
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Absolute Contraindications
- •Procedure Preparation
- •Technique of FB Procedure
- •Complications of FB Procedure
- •Basic Diagnostic Procedures
- •Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
- •Transbronchial Lung Biopsy (TBLB)
- •Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (TBNA)
- •Bronchial Brushings
- •Advanced Diagnostic Bronchoscopy
- •EBUS-TBNA
- •Ultrathin Bronchoscopy
- •Transbronchial Lung Cryobiobsy (TBLC)
- •Therapeutic Procedures Via FB
- •LASER Bronchoscopy
- •Electrocautery
- •Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC)
- •Cryotherapy
- •Photodynamic Therapy
- •Airway Stent Placement
- •Endobronchial Valve Placement
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Procedure Description
- •Procedure Planning
- •Target Approximation
- •Sampling
- •Complications
- •Future Directions
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •4: Rigid Broncoscopy
- •Innovations
- •Ancillary Equipment
- •Rigid Bronchoscopy Applications
- •Laser Bronchoscopy
- •Tracheobronchial Prosthesis
- •Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (TBNA)
- •Rigid Bronchoscope in Other Treatments for Bronchial Obstruction
- •Mechanical Debridement
- •Pediatric Rigid Bronchoscopy
- •Tracheobronchial Dilatation
- •Foreign Bodies Removal
- •Other Indications
- •Complications
- •The Procedure
- •Some Conclusions
- •References
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Preprocedural Evaluation and Preparation
- •Physical Examination
- •Procedure-Related Indications
- •Application of the Technique
- •Topical Anesthesia
- •Anesthesia of the Nasal Mucosa and Nasopharynx
- •Anesthesia of the Mouth and Oropharynx
- •Superior Laryngeal Nerve Block
- •Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Block (RLN)
- •Conscious Sedation
- •Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC)
- •General Anesthesia
- •Monitoring the Depth of Anesthesia
- •Interventional Bronchoscopy Suites
- •Airway Devices
- •Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
- •Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
- •Rigid Bronchoscope
- •Modes of Ventilation
- •Spontaneous Ventilation
- •Assisted Ventilation
- •Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIV)
- •Positive Pressure Controlled Mechanical Ventilation
- •Jet Ventilation
- •Electronic Mechanical Jet Ventilation
- •Postprocedure Care
- •Special Consideration
- •Anesthesia for Peripheral Diagnostic and Therapeutic Bronchoscopy
- •Anesthesia for Interventional Bronchoscopic Procedures During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Background
- •Curricular Structure and Delivery
- •What Is a Bronchoscopy Curriculum?
- •Tradition, Teaching Styles, and Beliefs
- •Using Assessment Tools to Guide the Educational Process
- •The Ethics of Teaching
- •When Learners Teach: The Journey from Novice to Mastery and Back Again
- •The Future Is Now
- •References
- •Interventional Procedure
- •Assessment of Flow–Volume Curve
- •Dyspnea
- •Analysis of Pressure–Pressure Curve
- •Conclusions
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Adaptations of the IP Department
- •Environmental Control
- •Personal Protective Equipment
- •Procedure Performance
- •Bronchoscopy in Intubated Patients
- •Other Procedures in IP Unit
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Safety
- •Patient Safety
- •Provider Safety
- •Patient Selection and Screening
- •Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Staging
- •Inpatients
- •COVID-19 Clearance
- •COVID Clearance: A Role for Bronchoscopy
- •Long COVID: A Role for Bronchoscopy
- •Preparing for the Next Pandemic
- •References
- •Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Clinical Presentation
- •Diagnosis
- •Treatment
- •History and Historical Perspectives
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Benign and Malignant Tumors
- •Tumors with Uncertain Prognosis
- •Application of the Technique
- •Evidence Based Review
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •12: Cryotherapy and Cryospray
- •Introduction
- •Historical Perspective
- •Equipment
- •Cryoadhesion
- •Indications
- •Cryorecanalization
- •Cryoadhesion and Foreign Body Removal
- •Cryoadhesion and Mucus Plugs/Blood Clot Retrieval
- •Endobronchial Cryobiopsy
- •Transbronchial Cryobiopsy for Lung Cancer
- •Safety Concerns and Contraindications
- •Cryoablation
- •Indications
- •Evidence
- •Safety Concerns and Contraindications
- •Cryospray
- •Indications
- •Evidence
- •Safety Concerns and Contraindications
- •Advantages of Cryotherapy
- •Limitations
- •Future Research Directions
- •References
- •13: Brachytherapy
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Application of the Technique
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Adjuvant Treatment
- •Palliative Treatment
- •Complications
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •14: Photodynamic Therapy
- •Introduction
- •Photosensitizers
- •First-Generation Photosensitizers
- •M-Tetrahidroxofenil Cloro (mTHPC) (Foscan®)
- •PDT Reaction
- •Tumor Damage Process
- •Procedure
- •Indications
- •Curative PDT Indications
- •Palliative PDT Indications
- •Contraindications
- •Rationale for Use in Early-Stage Lung Cancer
- •Rationale
- •PDT in Combination with Other Techniques for Advanced-Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- •Commentary
- •Complementary Endoscopic Methods for PDT Applications
- •New Perspectives
- •Other PDT Applications
- •Conclusions
- •References
- •15: Benign Airways Stenosis
- •Etiology
- •Congenital Tracheal Stenosis
- •Iatrogenic
- •Infectious
- •Idiopathic Tracheal Stenosis
- •Distal Bronchial Stenosis
- •Diagnosis Methods
- •Patient History
- •Imaging Techniques
- •Bronchoscopy
- •Pulmonary Function Test
- •Treatment
- •Endoscopic Treatment
- •Dilatation
- •Laser Therapy
- •Stents
- •How to Proceed
- •Stent Placement
- •Placing a Montgomery T Tube
- •The Rule of Twos for Benign Tracheal Stenosis (Fig. 15.23)
- •Surgery
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •16: Endobronchial Prostheses
- •Introduction
- •Indications
- •Extrinsic Compression
- •Intraluminal Obstruction
- •Stump Fistulas
- •Esophago-respiratory Fistulas (ERF)
- •Expiratory Central Airway Collapse
- •Physiologic Rationale for Airway Stent Insertion
- •Stent Selection Criteria
- •Stent-Related Complications
- •Granulation Tissue
- •Stent Fracture
- •Migration
- •Contraindications
- •Follow-Up and Patient Education
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Overdiagnosis
- •False Positives
- •Radiation
- •Risk of Complications
- •Lung Cancer Screening Around the World
- •Incidental Lung Nodules
- •Management of Lung Nodules
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Minimally Invasive Procedures
- •Mediastinoscopy
- •CT-Guided Transthoracic Biopsy
- •Fluoroscopy-Guided Transthoracic Biopsies
- •US-Guided Transthoracic Biopsy
- •Thoracentesis and Pleural Biopsy
- •Thoracentesis
- •Pleural Biopsy
- •Surgical or Medical Thoracoscopy
- •Image-Guided Pleural Biopsy
- •Closed Pleural Biopsy
- •Image-Guided Biopsies for Extrathoracic Metastases
- •Tissue Acquisition, Handling and Processing
- •Implications of Tissue Acquisition
- •Guideline Recommendations for Tissue Acquisition in Mediastinal Staging
- •Methods to Overcome Challenges in Tissue Acquisition and Genotyping
- •Rapid on-Site Evaluation (ROSE)
- •Sensitive Genotyping Assays
- •Liquid Biopsy
- •Summary, Recommendations and Highlights
- •References
- •History
- •Data Source and Methodology
- •Tumor Size
- •Involvement of the Main Bronchus
- •Atelectasis/Pneumonitis
- •Nodal Staging
- •Proposal for the Revision of Stage Groupings
- •Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- •Discussion
- •Methodology
- •T Descriptors
- •N Descriptors
- •M Descriptors
- •Summary
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Historical Perspective
- •Fluoroscopy
- •Radial EBUS Mini Probe (rEBUS)
- •Ultrasound Bronchoscope (EBUS)
- •Virtual Bronchoscopy
- •Trans-Parenchymal Access
- •Cone Beam CT (CBCT)
- •Lung Vision
- •Sampling Instruments
- •Conclusions
- •References
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Narrow Band Imaging (NBI)
- •Dual Red Imaging (DRI)
- •Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS)
- •Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy and Endocytoscopy
- •Raman Spectrophotometry
- •Application of the Technique
- •Supplemental Technology for Diagnostic Bronchoscopy
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Summary and Recommendations, Highlight of the Developments During the Last Three Years (2013 on)
- •References
- •Introduction
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Endoscopic AF-OCT System
- •Preclinical Studies
- •Clinical Studies
- •Lung Cancer
- •Asthma
- •Airway and Lumen Calibration
- •Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- •Future Applications
- •Summary
- •References
- •23: Endobronchial Ultrasound
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Equipment
- •Technique
- •Indication, Application, and Evidence
- •Convex Probe Ultrasound
- •Equipment
- •Technique
- •Indication, Application, and Evidence
- •CP-EBUS for Malignant Mediastinal or Hilar Adenopathy
- •CP-EBUS for the Staging of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- •CP-EBUS for Restaging NSCLC After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- •Complications
- •Summary
- •References
- •Introduction
- •What Is Electromagnetic Navigation?
- •SuperDimension Navigation System (EMN-SD)
- •Computerized Tomography
- •Computer Interphase
- •The Edge Catheter: Extended Working Channel (EWC)
- •Procedural Steps
- •Planning
- •Detecting Anatomical Landmarks
- •Pathway Planning
- •Saving the Plan and Exiting
- •Registration
- •Real-Time Navigation
- •SPiN System Veran Medical Technologies (EMN-VM)
- •Procedure
- •Planning
- •Navigation
- •Biopsy
- •Complications
- •Limitations
- •Summary
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Image Acquisition
- •Hardware
- •Practical Considerations
- •Radiation Dose
- •Mobile CT Studies
- •Future Directions
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •26: Robotic Assisted Bronchoscopy
- •Historical Perspective
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Diagnostic Yield
- •Monarch RAB
- •Ion Endoluminal Robotic System
- •Summary
- •References
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •General
- •Application of the Technique
- •Preoperative Care
- •Patient’s Position and Operative Field
- •Incision and Initial Dissection
- •Palpation
- •Biopsy
- •Control of Haemostasis and Closure
- •Postoperative Care
- •Complications
- •Technical Variants
- •Extended Cervical Mediastinoscopy
- •Mediastinoscopic Biopsy of Scalene Lymph Nodes
- •Inferior Mediastinoscopy
- •Mediastino-Thoracoscopy
- •Video-Assisted Mediastinoscopic Lymphadenectomy
- •Transcervical Extended Mediastinal Lymphadenectomy
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Case 1
- •Adrenal and Hepatic Metastases
- •Brain
- •Bone
- •Case 1 Continued
- •Biomarkers
- •Case 1 Concluded
- •Case 2
- •Chest X-Ray
- •Computerized Tomography
- •Positive Emission Tomography
- •Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- •Endobronchial Ultrasound with Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
- •Transthoracic Needle Aspiration
- •Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
- •Endoscopic Ultrasound with Needle Aspiration
- •Combined EUS-FNA and EBUS-TBNA
- •Case 2 Concluded
- •Case 3
- •Standard Cervical Mediastinoscopy
- •Extended Cervical Mediastinoscopy
- •Anterior Mediastinoscopy
- •Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery
- •Case 3 Concluded
- •Case 4
- •Summary
- •References
- •29: Pleural Anatomy
- •Pleural Embryonic Development
- •Pleural Histology
- •Cytological Characteristics
- •Mesothelial Cells Functions
- •Pleural Space Defense Mechanism
- •Pleura Macroscopic Anatomy
- •Visceral Pleura (Pleura Visceralis or Pulmonalis)
- •Parietal Pleura (Pleura Parietalis)
- •Costal Parietal Pleura (Costalis)
- •Pleural Cavity (Cavitas Thoracis)
- •Pleural Apex or Superior Pleural Sinus [12–15]
- •Anterior Costal-Phrenic Sinus or Cardio-Phrenic Sinus
- •Posterior Costal-Phrenic Sinus
- •Cost-Diaphragmatic Sinus or Lateral Cost-Phrenic Sinus
- •Fissures18
- •Pleural Vascularization
- •Parietal Pleura Lymphatic Drainage
- •Visceral Pleura Lymphatic Drainage
- •Pleural Innervation
- •References
- •30: Chest Ultrasound
- •Introduction
- •The Technique
- •The Normal Thorax
- •Chest Wall Pathology
- •Pleural Pathology
- •Pleural Thickening
- •Pneumothorax
- •Pulmonary Pathology
- •Extrathoracic Lymph Nodes
- •COVID and Chest Ultrasound
- •Conclusions
- •References
- •Introduction
- •History of Chest Tubes
- •Overview of Chest Tubes
- •Contraindications for Chest Tube Placement
- •Chest Tube Procedural Technique
- •Special Considerations
- •Pneumothorax
- •Empyema
- •Hemothorax
- •Chest Tube Size Considerations
- •Pleural Drainage Systems
- •History of and Introduction to Indwelling Pleural Catheters
- •Indications and Contraindications for IPC Placement
- •Special Considerations
- •Non-expandable Lung
- •Chylothorax
- •Pleurodesis
- •Follow-Up and IPC Removal
- •IPC-Related Complications and Management
- •Competency and Training
- •Summary
- •References
- •32: Empyema Thoracis
- •Historical Perspectives
- •Incidence
- •Epidemiology
- •Pathogenesis
- •Clinical Presentation
- •Radiologic Evaluation
- •Biochemical Analysis
- •Microbiology
- •Non-operative Management
- •Prognostication
- •Surgical Management
- •Survivorship
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •Evaluation
- •Initial Intervention
- •Pleural Interventions for Recurrent Symptomatic MPE
- •Especial Circumstances
- •References
- •34: Medical Thoracoscopy
- •Introduction
- •Diagnostic Indications for Medical Thoracoscopy
- •Lung Cancer
- •Mesothelioma
- •Other Tumors
- •Tuberculosis
- •Therapeutic Indications
- •Pleurodesis of Pneumothorax
- •Thoracoscopic Drainage
- •Drug Delivery
- •Procedural Safety and Contraindications
- •Equipment
- •Procedure
- •Pre-procedural Preparations and Considerations
- •Procedural Technique [32]
- •Medical Thoracoscopy Versus VATS
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Historical Perspective
- •Indications and Contraindications
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Endobronchial Valves
- •Airway Bypass Tracts
- •Coils
- •Other Methods of ELVR
- •Summary and Recommendations
- •References
- •36: Bronchial Thermoplasty
- •Introduction
- •Mechanism of Action
- •Trials
- •Long Term: Ten-Year Study
- •Patient Selection
- •Bronchial Thermoplasty Procedure
- •Equipment
- •Pre-procedure
- •Bronchoscopy
- •Post-procedure
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
- •Technical Aspects of BAL Procedure
- •ILD Cell Patterns and Diagnosis from BAL
- •Technical Advises for Conventional TLB and TLB-C in ILD
- •Future Directions
- •References
- •Introduction
- •The Pediatric Airway
- •Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- •Endobronchial Ultrasound
- •Virtual Navigational Bronchoscopy
- •Cryobiopsy
- •Therapeutic Procedures
- •Dilation Procedures
- •Thermal Techniques
- •Mechanical Debridement
- •Endobronchial Airway Stents
- •Metallic Stents
- •Silastic Stents
- •Novel Stents
- •Endobronchial Valves
- •Bronchial Thermoplasty
- •Discussion
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Etiology
- •Congenital ADF
- •Malignant ADF
- •Cancer Treatment-Related ADF
- •Benign ADF
- •Iatrogenic ADF
- •Diagnosis
- •Treatment Options
- •Endoscopic Techniques
- •Stents
- •Clinical Results
- •Stent Complications
- •Other Available Stents
- •Other Endoscopic Methods
- •References
- •Introduction
- •Anatomy and Physiology of Swallowing
- •Functional Physiology of Swallowing
- •Epidemiology and Risk Factors
- •Types of Foreign Bodies
- •Organic
- •Inorganic
- •Mineral
- •Miscellaneous
- •Clinical Presentation
- •Acute FB
- •Retained FB
- •Radiologic Findings
- •Bronchoscopy
- •Airway Management
- •Rigid Vs. Flexible Bronchoscopy
- •Retrieval Procedure
- •Instruments
- •Grasping Forceps
- •Baskets
- •Balloons
- •Suction Instruments
- •Ablative Therapies
- •Cryotherapy
- •Laser Therapy
- •Electrocautery and APC
- •Surgical Management
- •Complications
- •Bleeding and Hemoptysis
- •Distal Airway Impaction
- •Iron Pill Aspiration
- •Follow-Up and Sequelae
- •Conclusion
- •References
- •Vascular Origin of Hemoptysis
- •History and Historical Perspective
- •Diagnostic Bronchoscopy
- •Therapeutic Bronchoscopy
- •General Measures
- •Therapeutic Bronchoscopy
- •Evidence-Based Review
- •Summary
- •Recommendations
- •References
- •History
- •“The Glottiscope” (1807)
- •“The Esophagoscope” (1895)
- •The Rigid Bronchoscope (1897–)
- •The Flexible Bronchoscope (1968–)
- •Transbronchial Lung Biopsy (1972) (Fig. 42.7)
- •Laser Therapy (1981–)
- •Endobronchial Stents (1990–)
- •Electromagnetic Navigation (2003–)
- •Bronchial Thermoplasty (2006–)
- •Endobronchial Microwave Therapy (2004–)
- •American Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology (AABIP) and Journal of Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology (JOBIP) (1992–)
- •References
- •Index
516 |
J. A. Moya Amorós |
|
|
Pleural Cavity (Cavitas Thoracis)
It is a virtual slit-like space located between the parietal and visceral pleura that is 10–20 μm in size and contains few milliliters of serous fuid. The pleural serosa, by adapting to the anatomical elements that stand out inside the pleural cavity, forms depressions that are called sinuses or pleural recesses (recessus pleuralis). The most prominent and constant are as follows:
Pleural Apex or Superior Pleural Sinus [12–15]
It is a pleural cleft formed by the costal and mediastinal pleurae confuence. It occupies a cervical position forming the superior cone or dome, which is located above the clavicle, at the neck base.
To keep the pleural apex xed to the neck base, there are 3 ligaments that act as brous straps inserted through the external pleural face towards the neighboring bony structures, and which are collectively called the Sebileau suspensory apparatus (Fig. 29.11):
•\ Transverse-pleural ligament: It extends from the C7 vertebra transverse process to the pleural apex, and also emits an expansion towards the 1st rib. If it contains muscle bers it is called scalenus minimus muscle.
•\ Costo-pleural ligament: It extends from the neck and the 1st rib posteromedial border to the pleural apex.
•\ Vertebro-pleural ligament: It extends from the C7 vertebral body to the pleural apex.
Section of the three ligaments causes the pleural dome descent. This surgical maneuver called apicolysis was used in the past to carry out tuberculous cavern collapse therapy, when located in the upper lobe.
Anterior Costal-Phrenic Sinus or Cardio-Phrenic Sinus
Cleft that forms at the retrosternal level by the confuence or intersection between the costal, diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleurae. It has a trihedral angle appearance with some adipose content, with abundant lymphoid tissue from the thoracic and abdominal walls, as well as from the supramesocolic compartment. On the left side, it is located lateral to the heart up to 4 cm from the midsagittal line (Fig. 29.12).
Posterior Costal-Phrenic Sinus
Cleft is formed by the intersection of the diaphragmatic, costal and mediastinal pleurae, on the D11 vertebral body. It is the pleural cavity lowest point, and therefore the place where the fuid accumulated in the pleural cavity is deposited in pathological processes (Fig. 29.12).
Cost-Diaphragmatic Sinus or Lateral Cost-Phrenic Sinus
Pleural cleft is located between the diaphragm descending fanks and the chest wall. It is formed by the costal and diaphragmatic pleurae refection, adopting the appearance of a dihedral angle. It runs over the diaphragm costal insertions, surpassing them behind the arcuate ligament, with which it can go beyond the 12th rib lower border (Fig. 29.12).
Fissures18
They are depressions on the lung surface covered with visceral pleura, in the form of visceral pleura invaginations towards the lung parenchyma. They divide each lung into different lobes: three
Данная книга находится в списке для перевода на русский язык сайта https://meduniver.com/
29 Pleural Anatomy |
517 |
|
|
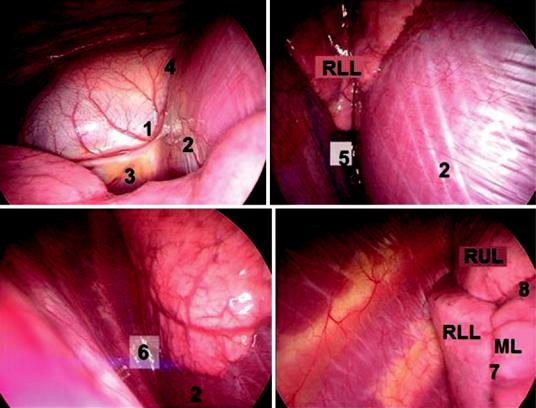
Fig. 29.12 Thoracoscopic view of the right pleural cavity, (1) Pericardium, (2) diaphragm, (3) phrenic nerve and pericardiophrenic vein, (4) cardiophrenic sinus, (5) poste-
rior costophrenic sinus, (6) lateral costophrenic sinus, (7) major ssure, (8) minor ssure, RUL right upper lobe, RLL right lower lobe, ML middle lobe
in the right lung and two in the left. There may be anomalies in the number of cracks, both due to excess and defect (Fig. 29.12).
•\ Major ssure, oblique: Presents an oblique trajectory, from the fourth dorsal vertebra level to the end of the fth intercostal space. In the right lung, it begins at fourth rib neck levels, follows an oblique path downwards and forwards to reach the fth intercostal space diaphragmatic face. In depth, it crosses from lateral to medial and reaches the pulmonary hilum anterior and inferior part.
At the posterior and superior part, it separates the superior lobe from the inferior lobe, while in the anterior and inferior part, it separates the inferior lobe from the middle lobe.
In the left lung, there is only a major s- sure, and it has a slightly different path as it descends in the form of an italic ʃ from its uppermost part to the anterior and lower part.
•\ Minor ssure, horizontal: It only exists on the right side , begins at the fourth intercostal space level, and ascends slightly until it ends at the third intercostal space level. It runs forward in depth and medially reaches the hilum anterior part, separating the upper lobe from the middle lobe.
•\ Superior and inferior accessory ssures: the superior or azygos ssure originates from the azygos vein arch, which, during its embryonic development, splits the upper lobe mesenchyme into two parts: a medial or Wrisberg azygos lobe and a lateral or superior lobe. Thisssural anomaly is often associated with the
