
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •IX Congenital Malformations of the CNS
- •Objectives
- •VI Regeneration of Nerve Cells
- •Objectives
- •VI Venous Dural Sinuses
- •VII Angiography
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •IV Location of the Major Motor and Sensory Nuclei of the Spinal Cord
- •Case 6-1
- •Case 6-2
- •VII Conus Medullaris Syndrome (Cord Segments S3 to C0)
- •Objectives
- •Lesions of the Brainstem
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •VII The Facial Nerve (CN VII)
- •Objectives
- •IV Trigeminal Reflexes
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •IV Auditory Tests
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •VI Cortical and Subcortical Centers for Ocular Motility
- •VII Clinical Correlation
- •Objectives
- •IV Clinical Correlations
- •Objectives
- •Objectives
- •VI Cerebellar Syndromes and Tumors
- •Objectives
- •Objective
- •Objectives
- •I Major Neurotransmitters

C H A P T E R 6
Spinal Cord
Objectives
1.Describe the structure of the adult spinal cord; compare and contrast the adult structure with the spinal cord of the newborn.
2.Describe the structure of and modalities carried by each of the major spinal cord pathways: anterolateral system; posterior columns; spinocerebellars; corticospinals.
3.Describe classic lesions of the spinal cord, including Brown-Séquard syndrome, anterior spinal artery occlusion, vitamin B12 neuropathy, syringomyelia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
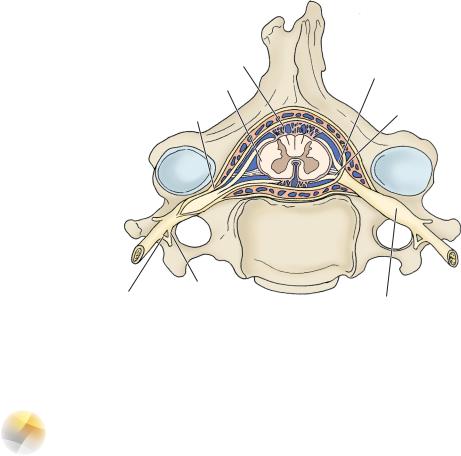
Structure—lies within the subarachnoid space and is held in place by two pial specializations: A pair of toothed denticulate ligaments and the filum terminale (Figure 6-1).
I Gray and White Rami Communicans (Figure 6-1)
A.Gray rami communicans contain unmyelinated postganglionic sympathetic fibers. They are found at all levels of the spinal cord.
B.White rami communicans contain myelinated preganglionic sympathetic fibers. They are found from T1 to L2 (the extent of the lateral horn and the intermediolateral cell column which forms it).
IISpinal Nerves
A.31 pairs: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal (Figures 6-1 and 6-2)
B.Contain preganglionic general visceral efferent (between T1 and L2 sympathetic and between S2 and S4 parasympathetic), general visceral afferent, general somatic efferent, and general somatic afferent fibers
C.Formed by the junction of anterior (motor) and posterior (sensory) roots, the posterior root is the site of the spinal ganglion (dorsal or posterior root ganglion), which contain all afferent cell bodies for the body (somatic and visceral)
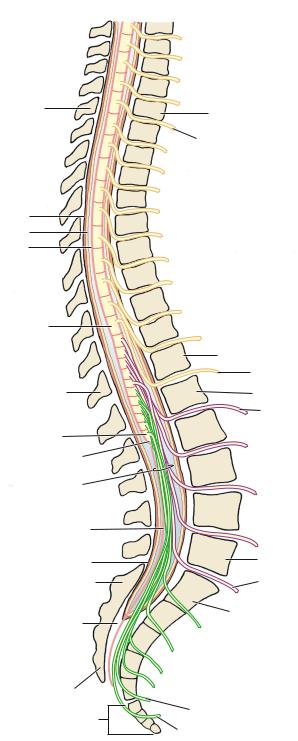
III Conus Medullaris (Figure 6-2), the tapering inferior end of the spinal cord, occurs in the newborn at the level of the body of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). In the adult, it occurs at the level of the inferior border of the first lumbar vertebra (L1). This is clinically relevant in determining the appropriate position for performing lumbar puncture in children and adults.
44
Spinal Cord |
45 |
Arachnoid mater
|
Posterior root |
Pia mater |
|
Dura mater |
Anterior root |
Gray ramus
White ramus
Spinal ganglion (dorsal root ganglion)
Figure 6-1 The spinal nerve.
IV Location of the Major Motor and Sensory Nuclei of the Spinal Cord
A.The ciliospinal center of Budge, from C8 to T2, contains the preganglionic sympathetic neurons that innervate the superior cervical ganglion to provide sympathetic innervation of the eye.
B.The intermediolateral cell column, of the lateral horn, from T1 to L2, contains all of the preganglionic sympathetic cell bodies in the body.
C.The posterior thoracic nucleus (nucleus dorsalis of Clarke), from C8 to L2, gives rise to the posterior spinocerebellar tract.
D.The sacral parasympathetic nucleus, from S2 to S4
E.The spinal accessory nucleus, from C1 to C6
F.The phrenic nucleus, from C3 to C5
G.Substantia gelatinosa and nucleus proprius, found at all spinal cord levels, contain neurons that mediate light touch, pain, and temperature.
46 |
Chapter 6 |
Posterior side |
Anterior side |
T2 vertebra |
T2 vertebra |
|
T2 nerve |
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
T12 spinal segment
|
T12 vertebra |
|
T12 nerve |
T12 vertebra |
L1 vertebra |
Coccygeal |
L1 nerve |
|
|
segment |
|
Conus medullaris |
|
Cauda equina |
|
Filum terminale |
|
internum |
|
Dural sac |
L5 vertebra |
|
|
S1 vertebra |
L5 nerve |
Vertebral canal |
S1 vertebra |
|
Filum terminale  externum
externum
S5 vertebra  S5 vertebra
S5 vertebra
S5 nerve
Coccyx
Coccygeal nerve
Figure 6-2 The spinal cord.
Spinal Cord |
47 |
H.Spinal Border Cells, found between L2 and S3, mediate unconscious (reflex) proprioception.
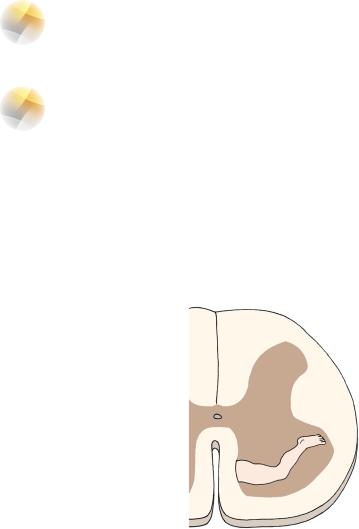
I.Somatic Motor Nuclei, found at all levels, somatotopically organized—medial group innervates more medial musculature, while the lateral group innervates appendicular musculature (Figure 6-3).
VThe Cauda Equina. Anterior and posterior roots that are found in the subarachnoid
space below the conus medullaris form the cauda equina.
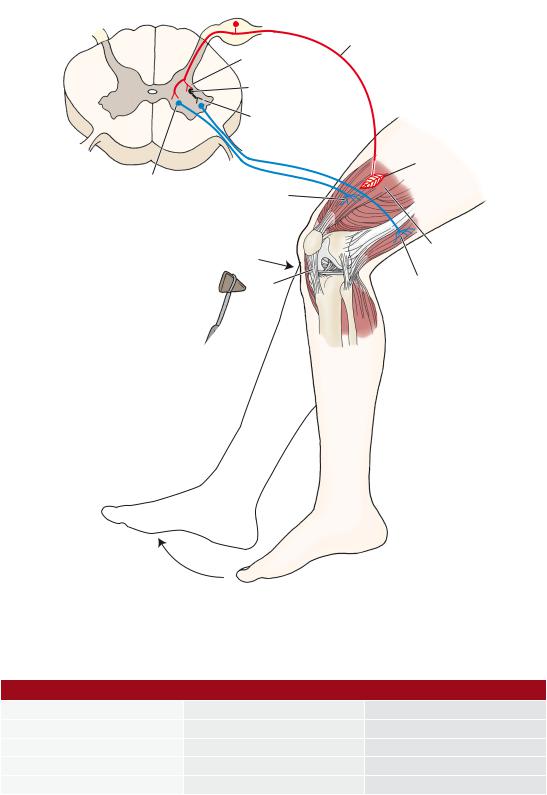
VI The Myotatic Reflex (Figure 6-4) is a monosynaptic and ipsilateral muscle stretch reflex (MSR). Like all reflexes, the myotatic reflex has an afferent and an efferent limb. Interruption of either limb results in areflexia.
A.The afferent limb includes a muscle spindle (receptor) and a spinal ganglion neuron and its Ia fiber.
B.The efferent limb includes an anterior horn motor neuron that innervates the striated muscle (effector).
C.The five most commonly tested MSRs are listed in Table 6-1.
Flexors
Extensors
Lumbar enlargement
Figure 6-3 Somatotopic organization of the motoneurons of the anterior horn.
48 |
Chapter 6 |
Ia afferent
Excitatory
synapse
|
Inhibitory |
|
|
neuron |
|
|
Inhibitory |
|
|
synapse |
|
|
|
Muscle |
Alpha motor |
Alpha motor |
spindle |
|
||
neuron |
neuron projection to |
|
|
homonymous muscle |
|
Tap stimulus |
|
|
to knee joint |
Quadriceps |
|
|
|
muscle |
|
Patellar |
Alpha motor neuron |
|
ligament |
projection to antagonistic |
|
|
(heteronymous muscle) |
Figure 6-4 Myotatic reflex.
Table 6-1: The Five Most Commonly Tested Muscle Stretch Reflexes
Muscle Stretch Reflex |
Cord Segment |
Muscle |
Ankle jerk |
S1 |
Gastrocnemius |
Knee jerk |
L2–L4 |
Quadriceps |
Biceps jerk |
C5 and C6 |
Biceps brachii |
Forearm jerk |
C5 and C6 |
Brachioradialis |
Triceps jerk |
C7 and C8 |
Triceps brachii |
