
- •Лекция 1. Fundamental concepts of electromagnetics. Electrostatics. (Начало электростатики)
- •Vectors and scalar fields. (Векторные и скалярные поля)
- •Electrostatic field. (Электростатическое поле)
- •Coulomb’s Law. (Закон Кулона)
- •Electric Field Strength e and Displacement Field d. (Напряжённость и смещение электрического поля)
- •Gauss’ Law. (Закон Гаусса)
- •Electric Potential. (Электрический потенциал)
- •Work in the electric field. (Работа в электрическом поле)
- •Dielectric polarization. (Диэлектрическая поляризация)
- •Dielectric material characteristics. (Характеристики диэлектриков)
- •Properties of dielectric materials. (Свойства диэлектрических материалов)
- •Poisson’s and Laplace’ s equations. (Уравнения Пуассона и Лапласа)
- •Лекция 2. Boundary conditions for the Laplace or Poisson equations (Граничные уравнения для уравнений Лапласа и Пуассона)
- •Electrostatic Energy (Электростатическая энергия)
- •Virtual experiment. (Эксперимент по нахождению энергии системы)
- •Consequences (Следствия)
- •Continuity Equation (Уравнение непрерывности)
- •Лекция 3. Static magnetic field (Статическое магнитное поле)
- •Variables and units (Переменные и единицы измерения)
- •Main Relations (Основные соотношения)
- •Magnetic flux density (Индукция магнитного поля)
- •Biot-Savart’s law (Закон Био-Савара)
- •Ampere’s law (Закон полного тока)
- •Scalar magnetic potential (Скалярный магнитный потенциал)
- •The cut in the space (Разрез в пространстве)
- •Laplace equation for the scalar magnetic potential (Уравнение Лапласа для скалярного магнитного потенциала)
- •Vector magnetic potential (Векторный магнитный потенциал)
- •Magnetic flux (Магнитный поток)
- •Differential equation for the vector magnetic potential (Дифференциальное уравнение для векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Gauging of the vector magnetic potential (Калибровка векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Integral presentation of the vector magnetic potential (Интегральное представление векторного потенциала)
- •Inductance (Индуктивность)
- •Mutual inductance (Взаимная индуктивность)
- •Inductance of thin contours (Индуктивность тонких контуров)
- •Field intensity inside a cylindrical conductor (Напряжённость поля внутри цилиндрического проводника)
- •Лекция 4. Method of images (метод зеркальных изображений)
- •Equivalent charge density (эквивалентная плотность заряда)
- •Method of images for cylindrical boundaries between dielectrics (метод изображений цилиндрических границ между диэлектриками) Problem formulation (постановка задачи)
- •The inverse point (обратная точка)
- •Normal component of the field intensity (нормальная составляющая напряжённости поля)
- •Geometrical relations (геометрические соотношения)
- •Angles (углы)
- •Field induced by the line sources (поле, индуцированное линейными источниками)
- •The field sources for the external domain (источники полей для внешней области)
- •The field sources for the internal domain (источники полей для внутренней области)
- •Image method for the flat boundary between magnetic media (Метод изображений для плоской границы между магнитными носителями)
- •Equivalent magnetic charge density (Эквивалентная плотность магнитного заряда)
- •Dependence of the field intensity on the coordinate (Зависимость напряжённости поля от координаты)
- •Inductance of the two-wire transmission line per unit length (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии передачи на единицу длины)
- •Total inductance (Общая индуктивность)
- •Forces. The first line. (Силы. 1ая линия)
- •Forces. The second line. (Силы. 2ая линия)
- •Лекция 5. Solution of Laplace’s equation by separation of variables. (Решение уравнения Лапласа методом разделения переменных) Application of Laplace’s equation (Применение уравнения Лапласа).
- •Choice of a coordinate system (Выбор системы координат)
- •Variable separation in cylindrical coordinates (Разделение переменных в цилиндрических координатах)
- •Angular function (Угловая функция)
- •Radial function (Радиальная функция)
- •General solution of the Laplace’s equation in a cylindrical coordinate system (Общее решение уравнения Лапласа в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •Application of the variable separation method for the magnetic field modeling (Применение метода разделения переменных для моделирования магнитного поля)
- •Reduced scalar magnetic potential (Редуцированный скалярный магнитный потенциал)
- •Combination of scalar magnetic potential and reduced magnetic potential (Комбинация скалярного магнитного потенциала и редуцированного магнитного потенциала)
- •The scalar potential induced by the current line (Скалярный потенциал, индуцируемый линией тока)
- •The current potential in the cylindrical coordinate system (Потенциал от линии с током в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •The current potential in the complex plane (Потенциал от линии с током в комплексной плоскости)
- •Expansion of the current potential in the cylindrical coordinate system (Разложение потенциала от линии с током в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •Potentials in the problem domain (Потенциалы в проблемной области)
- •Inductance of the two-wire transmission line per unit length (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии передачи на единицу длины)
- •The flux induced by the magnetized cylinder (Поток, индуцируемый намагниченным цилиндром)
- •Лекция 6. Time dependent electromagnetic fields (Зависящие от времени электрические поля)
- •Faraday’s Law (Закон электромагнитной индукции)
- •Lenz’s Law (правило Ленца)
- •Induction by a temporal change of b (Индукция за счёт временного изменения b)
- •Induction through the motion of the conductor (Индукция за счёт движения проводника)
- •Induction by simultaneous temporal change of b and motion of the conductor (Индукция одновременным изменением во времени b и движением проводника)
- •Unipolar generator (Униполярный генератор)
- •Hering’s paradox (Парадокс Геринга)
- •Periodic electromagnetic field in the conductors. (Периодическое электромагнитное поле в проводниках)
- •Penetration of the electromagnetic field into a conductor. (Проникновение электромагнитного поля в проводник)
- •The skin effect. (Скин-эффект)
- •Poynting’s Theorem. (Теорема Пойнтинга) Electromagnetic Field Energy. (Энергия электромагнитного поля)
- •The rate of decrease of the electromagnetic field energy in a closed volume. (Скорость уменьшения энергии электромагнитного поля в замкнутом объёме)
- •Energy flows in the electromagnetic field (Поток энергии в электромагнитном поле)
- •Transmission of energy in a dc line (Передача энергии в линиях постоянного тока)
- •Transmission of energy in a dc line (Передача энергии в линиях постоянного тока)
- •The field picture near the wires with current (Картина поля вблизи провода с током)
- •Energy flows in static fields (Поток энергии в статических полях)
- •The momentum of the electromagnetic field (Момент электромагнитного поля)
- •The momentum of the electromagnetic field (Момент электромагнитного поля)
- •Лекция 8. Numerical Methods of the Electromagnetic Field Modeling. (Численные методы моделирования электромагнитного поля) Classification of the numerical methods (Классификация численных методов)
- •Classification of the problems (Классификация проблем)
- •Classification of the methods (Классификация методов)
- •Method of moments (Метод моментов)
- •Discretization of the problem domain (Дискретизация проблемной области)
- •Algebraic equation system (Алгебраическая система уравнений)
- •Finite element method (Метод конечных элементов)
- •Discretization (Дискретизация)
- •Finite functions (Ограниченная функция – отлична от нуля только в пределах треугольника)
- •Approximation of functions inside triangles (Аппроксимация функций внутри треугольника)
- •Approximation of the equation (Аппроксимация уравнения)
- •Weighted residual method (метод взвешенных невязок)
- •Galerkin method (метод Бубнова-Галеркина)
- •Weak formulation (ослабленная формулировка)
- •First type boundary conditions (Первый тип граничных условий)
- •The potential and field intensity (Потенциал и напряжённость поля)
Electrostatic Energy (Электростатическая энергия)
The force in electric field:
![]()
The work (from mechanics):
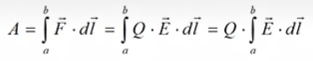
Definition of the potential difference:
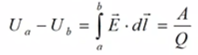
For infinitely remote point "a":
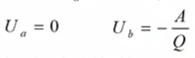
The work is done by the electric field without any external force. This is insolated system.
Energy conservation law (total energy can't be
changed):
![]()
(W – potential, A – work).
But what exactly work do? This work in insulated system (where only charges and electric field exist) transformed into kinetic energy if there no other participles of all this event. (честно, я не понял, почему он тут вдруг начал говорить про кинетическую энергию, хотя до этого всё время говорил про потенциальную)
So, we have got:
![]()
But if there external force which moves a charge and moves so that velocity of charge is constant (or velocity at the start = velocity at the finish point), so there is no change of kinetic energy. In this case, the external force applied to electric charge look like that (equal but with the opposite sign): . And after all we get the same relation: .
Virtual experiment. (Эксперимент по нахождению энергии системы)
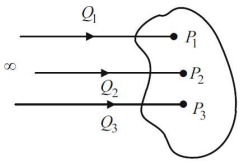
Consider three points P1, P2, and P3 in a charge free space. The point charges Q1 ,Q2 , and Q3 are brought from infinity to those points, respectively and in turn (соответственно и по очереди).
![]()
No work is done in bringing point charge Q1 from infinity to point P1 (because there wasn't electric field in the beginning). Then we have
![]()
U21 is the potential induced at point P2 due to Q1,
U31 is the potential induced at point P3 due to Q1 ,
U32 is the potential induced at point P3 due to Q2.
If we want to find a potential in any point, we need to summarize the potentials, which induced by all charges.
Now we reverse this experiment and we move at the beginning charge Q3, then Q2, then Q1.
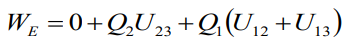
U23 is the potential induced at point P2 due to Q3,
U12 is the potential induced at point P1 due to Q2 ,
U13 is the potential induced at point P1 due to Q3.
And if we add two equation we get:
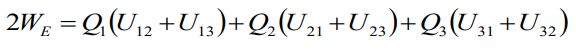
or
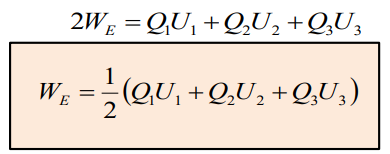
U1 is the potential induced at point P1 due to Q2 and Q3,
U2 is the potential induced at point P2 due to Q1 and Q3 ,
U3 is the potential induced at point P3 due to Q1 and Q2.
Consequences (Следствия)
In general case:
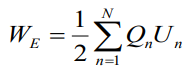
If the charges are distributed over the space:
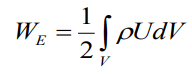 for the space charges (U – function because it
distributed somehow over the space, where we do integrate). These
charges really may exist.
for the space charges (U – function because it
distributed somehow over the space, where we do integrate). These
charges really may exist.
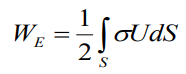 for the surface charges (for example –
conducting electrode)
for the surface charges (for example –
conducting electrode)
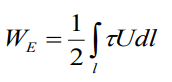 for the line charges (it doesn't exist in our
world, because we can't compress the charges into infinitely thin
line, but in practice we can have ALMOST linear charges (energy
transfer lines – wires) and we can approximate it as a thin line?
but bad consequences may happen because of approximation – it may
give us an infinite WE
and we can't to calculate it)
for the line charges (it doesn't exist in our
world, because we can't compress the charges into infinitely thin
line, but in practice we can have ALMOST linear charges (energy
transfer lines – wires) and we can approximate it as a thin line?
but bad consequences may happen because of approximation – it may
give us an infinite WE
and we can't to calculate it)
Substituting in the expression for the energy of charges distributed in the volume (now it's not only electrostatic field, but in electric field this consequence work too):
![]() (for any field)
(for any field)
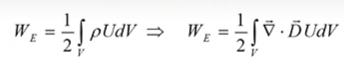
![]()
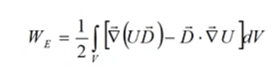
Applying the Gauss theorem (not Gauss law for field! по-русски это формула Остроградского - Гаусса) to the first term:
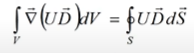
We have static system, which is limited (not infinitely). So, we have a point, which is very far from system. So far, that system may seemed like a point (may be charge point, may be not). And if we are going to infinity our potential and displacement induced by this point are inversed proportional to the radius.
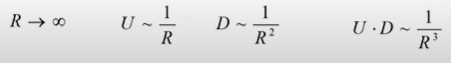
Area of a spherical surface
![]()
Energy:
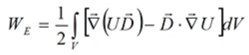
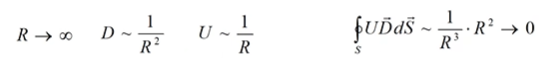
Finally, we get:

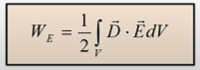
Also, we can conclude something (but it is a kind of a sumption [предположение]). Нельзя говорить, что мы выделим в области объём, и там будет какая-то энергия. Энергия WE=Q*U говорит нам, что на самом деле энергия концентрируется в заряде, а через объёмную плотность энергии формула говорит, что энергия концентрируется вокруг заряда. Что из этого правильно и нет – может быть потом он расскажет, а может и нет.
Energy per unit volume (volume density of electric
energy):
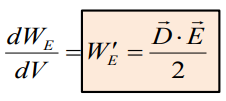
For isotropic medium:
![]()
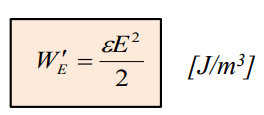
Electric currents. (Электрический ток)
Just now we consider only constant currents. But we expand our result on all current.
Variables and units. (Переменные)
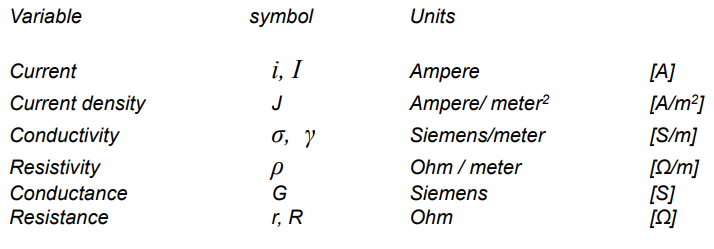
Basic definitions (Основные понятия)
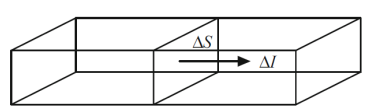
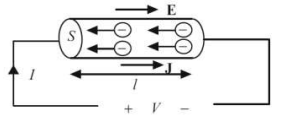
Current – is the charge which cross some area
over time unit:
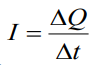
Current density:
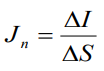 and
and
![]()
How current density induce in the beginning? There should be some current carrier. In our usual material (metals) usual carries part are electrons. So
current density depends on the velocity and
density of moving charges:
![]()
Conductivity and resistance (Проводимость и сопротивление)
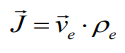
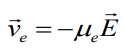 where
where
![]() is the mobility of electrons (electrons often hits ions and they are
stopped by them)
is the mobility of electrons (electrons often hits ions and they are
stopped by them)
Ne – concentration of electrons.
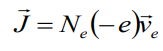
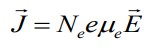
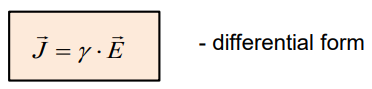
conductivity:
![]()
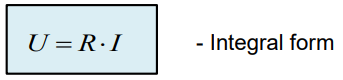
Ohm’s law:
Resistance:
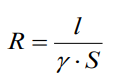
Power and Joule’s Law (Мощность и закон Джоуля)
Consider a charge Q moves at a velocity v by an electric field E to a distance l. In this case, the expression of the work done is:
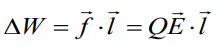
Power – is the energy, which dissipated
(рассеянный) or consumed or
generated over time unit:
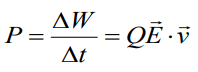
Total charge:
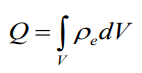
So
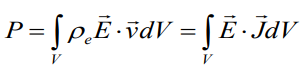 Joule’s law in differential form
Joule’s law in differential form
For a constant cross-section conductor, the
expression of the volume is:
![]()
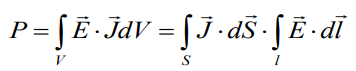
Expression for the power:
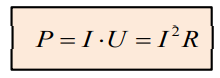 (Joule’s law in integral form)
(Joule’s law in integral form)
