
- •Advanced chapters of theoretical electro-engineering. Lecture 3
- •Static magnetic field.
- •Variables and units
- •Main Relations
- •Magnetic flux density
- •Biot–Savart’s Law
- •Ampere’s Law
- •Scalar magnetic potential
- •The cut in the space
- •Laplace equation for the scalar magnetic potential
- •Vector magnetic potential
- •Magnetic flux
- •Differential equation for the
- •Gauging of the vector magnetic potential
- •Integral presentation of the vector magnetic potential
- •Integral presentation of the vector magnetic potential
- •Inductance.
- •Mutual inductance.
- •Inductance of thin contours
- •Field intensity inside a cylindrical conductor
- •Flux linkage of a thin current layer
- •Flux linkage of a thin current layer
- •Internal inductance of a thin conductor
- •External inductance of two-wire transmission line
- •Inductance of a two-wire transmission line
Advanced chapters of theoretical electro-engineering. Lecture 3
SPbTU, IE, Prof. A.G. Kalimov 2022 |
1 |
Static magnetic field.
2
Variables and units
Variable |
symbol |
Units |
|
Flux density |
B |
Tesla |
[T] |
Field intensity |
H |
Ampere/ meter |
[A/m] |
Magnetic permeability |
μ |
Henry/meter |
[H/m] |
Inductance |
L |
Henry |
[H] |
Flux |
Φ |
Weber |
[Wb] |
Flux linkage |
ψ |
Weber |
[Wb] |
Scalar magnetic potential |
Um |
Ampere |
[A] |
Vector magnetic potential |
A |
T· m (Wb/m) |
[T·m] |
Magnetization |
M |
Ampere/ meter |
[A/m] |
3

Main Relations
B H
B 0 H 0 M
M H ( r 1)
r 0
4
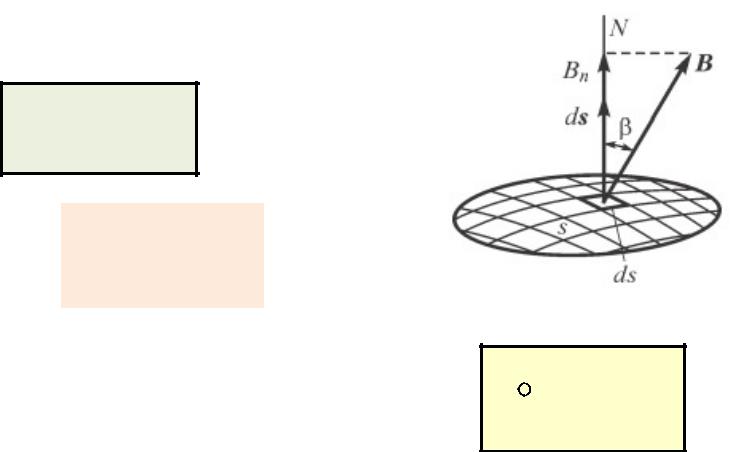
Magnetic flux density
Definition of the flux density vector
F Q B v
Flux |
B dS |
B d |
|
S |
ds |
|
|
There are no magnetic charges in the nature |
B ds 0 |
|
S |
5
Biot–Savart’s Law
Due to Biot-Savart’s law the flux density induced by the current sources may be expressed as:
|
|
|
|
|
0dV |
J r |
|
|
|
dB |
|
|
||
|
J |
|||
|
4 r3 |
|||
r
For the line current: |
|
dS |
dl |
|
|
|
|
0i |
dl r |
|
|
dB |
|
||
|
|
||
|
4 r3 |
|
|
6
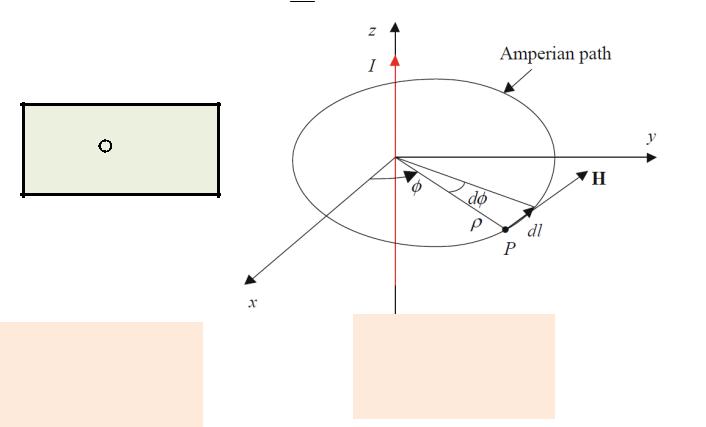
Ampere’s Law
(закон полного тока)
The magnetic field intensity
- magnetic permeability
Integral |
form of |
I H dl |
the |
Ampere’s |
|
Law |
|
l |
|
|
I is the current crossing the surface limited by the contour
B H
|
|
|
J curl H |
Differential form |
J H |
or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7
Scalar magnetic potential
Main relations: |
|
|
curl H J |
divB 0 |
B H |
In general case the H – field is not potential:
H dl i
|
l |
Nevertheless outside the space with currents: |
curl H 0 |
It is possible to introduce the scalar potential: |
H Um |
Um |
- the unit is – А (Ampere) |
8

The cut in the space
I |
H dl 0 |
|
l |
H Um
Um
9
Laplace equation for the scalar magnetic potential
Basic equations: |
|
|
divB 0 |
B H |
H grad(Um ) |
In general case:
Um 0
For the medium with the constant magnetic permeability:
Um 0 - Laplace equation
10
