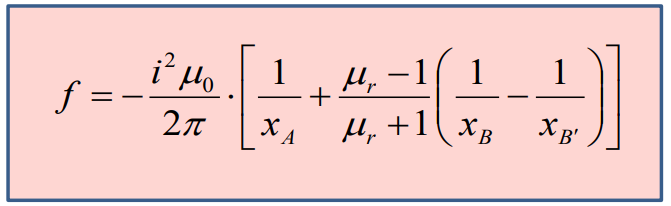- •Лекция 1. Fundamental concepts of electromagnetics. Electrostatics. (Начало электростатики)
- •Vectors and scalar fields. (Векторные и скалярные поля)
- •Electrostatic field. (Электростатическое поле)
- •Coulomb’s Law. (Закон Кулона)
- •Electric Field Strength e and Displacement Field d. (Напряжённость и смещение электрического поля)
- •Gauss’ Law. (Закон Гаусса)
- •Electric Potential. (Электрический потенциал)
- •Work in the electric field. (Работа в электрическом поле)
- •Dielectric polarization. (Диэлектрическая поляризация)
- •Dielectric material characteristics. (Характеристики диэлектриков)
- •Properties of dielectric materials. (Свойства диэлектрических материалов)
- •Poisson’s and Laplace’ s equations. (Уравнения Пуассона и Лапласа)
- •Лекция 2. Boundary conditions for the Laplace or Poisson equations (Граничные уравнения для уравнений Лапласа и Пуассона)
- •Electrostatic Energy (Электростатическая энергия)
- •Virtual experiment. (Эксперимент по нахождению энергии системы)
- •Consequences (Следствия)
- •Continuity Equation (Уравнение непрерывности)
- •Лекция 3. Static magnetic field (Статическое магнитное поле)
- •Variables and units (Переменные и единицы измерения)
- •Main Relations (Основные соотношения)
- •Magnetic flux density (Индукция магнитного поля)
- •Biot-Savart’s law (Закон Био-Савара)
- •Ampere’s law (Закон полного тока)
- •Scalar magnetic potential (Скалярный магнитный потенциал)
- •The cut in the space (Разрез в пространстве)
- •Laplace equation for the scalar magnetic potential (Уравнение Лапласа для скалярного магнитного потенциала)
- •Vector magnetic potential (Векторный магнитный потенциал)
- •Magnetic flux (Магнитный поток)
- •Differential equation for the vector magnetic potential (Дифференциальное уравнение для векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Gauging of the vector magnetic potential (Калибровка векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Integral presentation of the vector magnetic potential (Интегральное представление векторного потенциала)
- •Inductance (Индуктивность)
- •Mutual inductance (Взаимная индуктивность)
- •Inductance of thin contours (Индуктивность тонких контуров)
- •Field intensity inside a cylindrical conductor (Напряжённость поля внутри цилиндрического проводника)
- •Лекция 4. Method of images (метод зеркальных изображений)
- •Equivalent charge density (эквивалентная плотность заряда)
- •Method of images for cylindrical boundaries between dielectrics (метод изображений цилиндрических границ между диэлектриками) Problem formulation (постановка задачи)
- •The inverse point (обратная точка)
- •Normal component of the field intensity (нормальная составляющая напряжённости поля)
- •Geometrical relations (геометрические соотношения)
- •Angles (углы)
- •Field induced by the line sources (поле, индуцированное линейными источниками)
- •The field sources for the external domain (источники полей для внешней области)
- •The field sources for the internal domain (источники полей для внутренней области)
- •Image method for the flat boundary between magnetic media (Метод изображений для плоской границы между магнитными носителями)
- •Equivalent magnetic charge density (Эквивалентная плотность магнитного заряда)
- •Dependence of the field intensity on the coordinate (Зависимость напряжённости поля от координаты)
- •Inductance of the two-wire transmission line per unit length (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии передачи на единицу длины)
- •Total inductance (Общая индуктивность)
- •Forces. The first line. (Силы. 1ая линия)
- •Forces. The second line. (Силы. 2ая линия)
- •Лекция 5. Solution of Laplace’s equation by separation of variables. (Решение уравнения Лапласа методом разделения переменных) Application of Laplace’s equation (Применение уравнения Лапласа).
- •Choice of a coordinate system (Выбор системы координат)
- •Variable separation in cylindrical coordinates (Разделение переменных в цилиндрических координатах)
- •Angular function (Угловая функция)
- •Radial function (Радиальная функция)
- •General solution of the Laplace’s equation in a cylindrical coordinate system (Общее решение уравнения Лапласа в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •Application of the variable separation method for the magnetic field modeling (Применение метода разделения переменных для моделирования магнитного поля)
- •Reduced scalar magnetic potential (Редуцированный скалярный магнитный потенциал)
- •Combination of scalar magnetic potential and reduced magnetic potential (Комбинация скалярного магнитного потенциала и редуцированного магнитного потенциала)
- •The scalar potential induced by the current line (Скалярный потенциал, индуцируемый линией тока)
- •The current potential in the cylindrical coordinate system (Потенциал от линии с током в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •The current potential in the complex plane (Потенциал от линии с током в комплексной плоскости)
- •Expansion of the current potential in the cylindrical coordinate system (Разложение потенциала от линии с током в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •Potentials in the problem domain (Потенциалы в проблемной области)
- •Inductance of the two-wire transmission line per unit length (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии передачи на единицу длины)
- •The flux induced by the magnetized cylinder (Поток, индуцируемый намагниченным цилиндром)
- •Лекция 6. Time dependent electromagnetic fields (Зависящие от времени электрические поля)
- •Faraday’s Law (Закон электромагнитной индукции)
- •Lenz’s Law (правило Ленца)
- •Induction by a temporal change of b (Индукция за счёт временного изменения b)
- •Induction through the motion of the conductor (Индукция за счёт движения проводника)
- •Induction by simultaneous temporal change of b and motion of the conductor (Индукция одновременным изменением во времени b и движением проводника)
- •Unipolar generator (Униполярный генератор)
- •Hering’s paradox (Парадокс Геринга)
- •Periodic electromagnetic field in the conductors. (Периодическое электромагнитное поле в проводниках)
- •Penetration of the electromagnetic field into a conductor. (Проникновение электромагнитного поля в проводник)
- •The skin effect. (Скин-эффект)
- •Poynting’s Theorem. (Теорема Пойнтинга) Electromagnetic Field Energy. (Энергия электромагнитного поля)
- •The rate of decrease of the electromagnetic field energy in a closed volume. (Скорость уменьшения энергии электромагнитного поля в замкнутом объёме)
- •Energy flows in the electromagnetic field (Поток энергии в электромагнитном поле)
- •Transmission of energy in a dc line (Передача энергии в линиях постоянного тока)
- •Transmission of energy in a dc line (Передача энергии в линиях постоянного тока)
- •The field picture near the wires with current (Картина поля вблизи провода с током)
- •Energy flows in static fields (Поток энергии в статических полях)
- •The momentum of the electromagnetic field (Момент электромагнитного поля)
- •The momentum of the electromagnetic field (Момент электромагнитного поля)
- •Лекция 8. Numerical Methods of the Electromagnetic Field Modeling. (Численные методы моделирования электромагнитного поля) Classification of the numerical methods (Классификация численных методов)
- •Classification of the problems (Классификация проблем)
- •Classification of the methods (Классификация методов)
- •Method of moments (Метод моментов)
- •Discretization of the problem domain (Дискретизация проблемной области)
- •Algebraic equation system (Алгебраическая система уравнений)
- •Finite element method (Метод конечных элементов)
- •Discretization (Дискретизация)
- •Finite functions (Ограниченная функция – отлична от нуля только в пределах треугольника)
- •Approximation of functions inside triangles (Аппроксимация функций внутри треугольника)
- •Approximation of the equation (Аппроксимация уравнения)
- •Weighted residual method (метод взвешенных невязок)
- •Galerkin method (метод Бубнова-Галеркина)
- •Weak formulation (ослабленная формулировка)
- •First type boundary conditions (Первый тип граничных условий)
- •The potential and field intensity (Потенциал и напряжённость поля)
Inductance of the two-wire transmission line per unit length (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии передачи на единицу длины)
The
total inductance is infinitely big because line is infinitely big,
that’s why we should find the inductance per unit length. First of
all, we have to define inductance of the two-wire line itself without
influence of the cylinder. Then we add the additional flux which is
induced by ferromagnetic cylinder. As usual the total inductance in
such line (diameter of each wire is much less than the distance
between this two wires and much less than the distance between wire
and ferromagnetic cylinder) may be splitted in two parts:
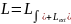 ,
where
,
where
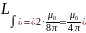 (cause we have 2 wires)
(cause we have 2 wires)

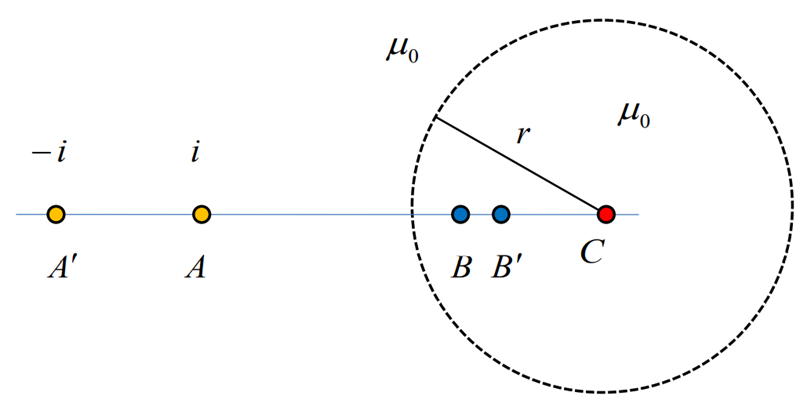
External fluxes (Внешние потоки)
Our
system of two wire lines and ferromagnetic cylinder may be replaced
by four long wires. Two of them are exactly the same as initial wires
(A’ A), but there are two mirror images (B B’), they have
current, that differs from the current in primary wires and these
currents are defined by this expression:
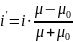 .
We want to find a flux which is coupled with two wire lines (A’
A). That means the flux which crosses the line which connects centers
of wires (A’ A). The most important part of this flux is the flux
which is induced by the line itself.
.
We want to find a flux which is coupled with two wire lines (A’
A). That means the flux which crosses the line which connects centers
of wires (A’ A). The most important part of this flux is the flux
which is induced by the line itself.
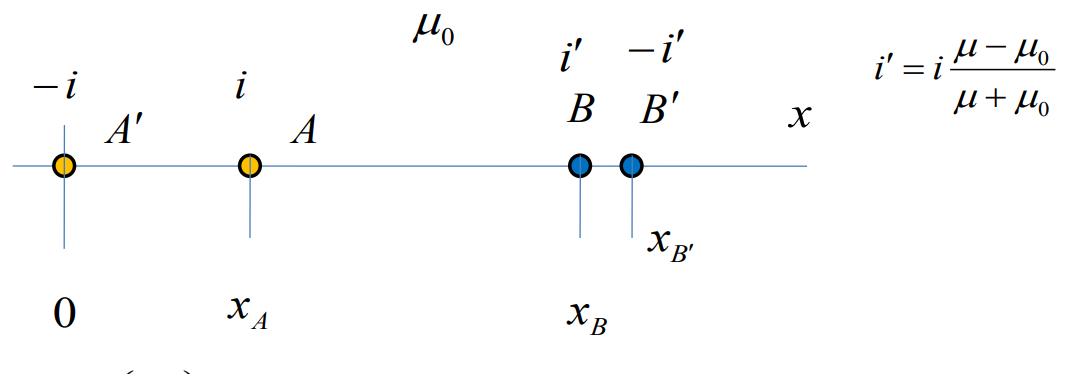
![]() , ФA
– flux which is induced by the wire A; xA
– the distance between A’ and A; ФA=
ФA’
(absolutely symmetrical system), R – radius of wire.
, ФA
– flux which is induced by the wire A; xA
– the distance between A’ and A; ФA=
ФA’
(absolutely symmetrical system), R – radius of wire.
The
magnetic field which is induced by the mirror image B also has a form
of
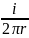 ,
where r – distance between the center of the wire and the point of
interest. This magnetic field should be integrated over segment A’
A (really we should integrate over the area, but we consider a
two-wire line with the length of one unit, so area is simply a
product of this one unit and the distance between the centers of
wires A’ A). We should integrate the flux density which is induced
by the wire B and will get exactly the same expression but the limits
will be different:
,
where r – distance between the center of the wire and the point of
interest. This magnetic field should be integrated over segment A’
A (really we should integrate over the area, but we consider a
two-wire line with the length of one unit, so area is simply a
product of this one unit and the distance between the centers of
wires A’ A). We should integrate the flux density which is induced
by the wire B and will get exactly the same expression but the limits
will be different:
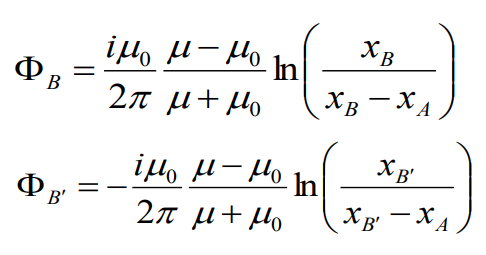 ФB – flux
which is induced by the wire B; xB
– the distance between wires A’ and B;
ФB – flux
which is induced by the wire B; xB
– the distance between wires A’ and B;
![]() ФB’ –
flux which is induced by the wire B’; ФB’=
-ФB
(opposite currents)
ФB’ –
flux which is induced by the wire B’; ФB’=
-ФB
(opposite currents)
For
simplicity we should use
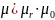 (relative magnetic permeability and magnetic permeability of vacuum)
so we have such expressions:
(relative magnetic permeability and magnetic permeability of vacuum)
so we have such expressions:
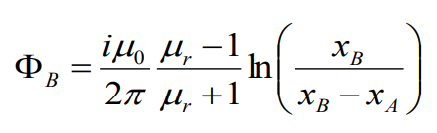
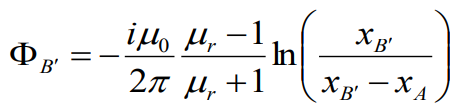
Total inductance (Общая индуктивность)
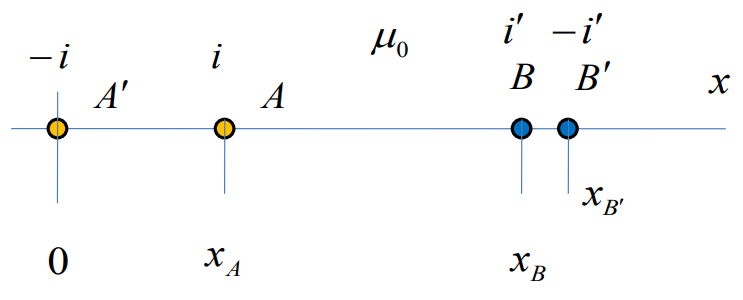
We
should summarize all the fluxes, after that we divided it by the
current:
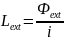
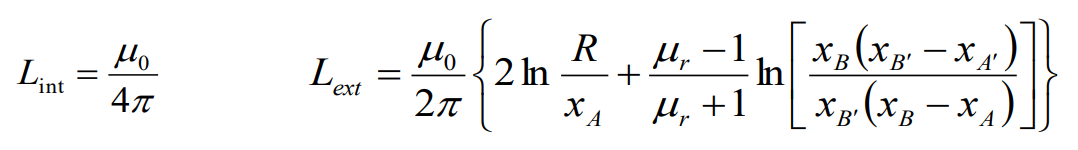
Finally we have:
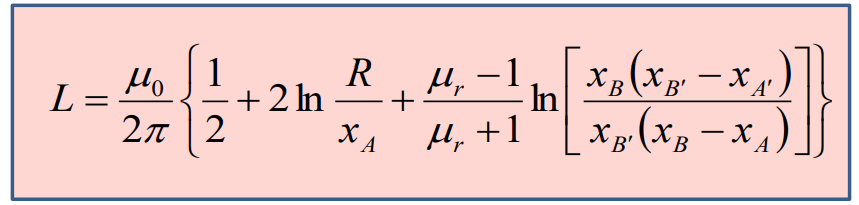
Forces. The first line. (Силы. 1ая линия)
 We
can consider the force which is applied to the left wire with the
coordinates of zero (A’), may be calculated as a sum of three
components:
We
can consider the force which is applied to the left wire with the
coordinates of zero (A’), may be calculated as a sum of three
components:
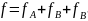 ,
where
,
where
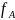 - the force from the sight of a second wire;
- the force from the sight of a second wire;
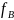 – the force from the sight of first image;
– the force from the sight of first image;
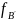 - the force from the sight of second image. If we have two wires with
the same directions of the current the force will be attractive. And
if we have two wires with the opposite directions of the current the
force will be repulsive. According to these principles we have such
expressions:
- the force from the sight of second image. If we have two wires with
the same directions of the current the force will be attractive. And
if we have two wires with the opposite directions of the current the
force will be repulsive. According to these principles we have such
expressions:
![]() ,
it has minus because force is repulsive
,
it has minus because force is repulsive
![]() , it has minus because force is repulsive
, it has minus because force is repulsive
![]() ,
it has positive sign because force is attractive
,
it has positive sign because force is attractive
Finally: