
- •Leukemia
- •Normal haemopoiesis
- •Hemoblastosis
- •Haemopoiesis
- •Leukemia
- •Types of leukemia
- •Classification of leukemia
- •Classification of AML
- •Pictures of blood
- •Myeloid Maturation
- •Lymphoblast/Myeloblast
- •Epidemiology of acute leukemia
- •Etiology
- •Two-hit model of leukemogenesis
- •Clinical presentation
- •Stages of acute leukemia
- •Extramedullar clinical presentation of acute leukemia
- •Leukemia cutis and chloroma
- •Gum hyperplasia
- •Diagnostics of leukemia
- •Morphological method
- •Normal bone marrow
- •Acute leukemia
- •Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- •Hodjkin`s lymphoma
- •Immunophenotyping
- •Cytochemical study
- •Cytogenetics and molecular genetics (FISH)
- •Prognosis in acute leukemia
- •Treatment of leukemia
- •Male patient., 85 years old
- •Physical examination at admission
- •Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- •Mechanism of formation of Philadelphia chromosome
- •Epidemiology оf CML
- •Phases of CML
- •Diagnostics of CML
- •Blood smear in CML
- •Bone marrow in CML
- •Blastic crisis
- •Cytogenetics
- •Treatment targets
- •Principles of treatment
- •Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- •Epidemiology and etiology of CLL
- •Clinical presentation
- •Classification of CLL (Binet) (1989)
- •Diagnostic criteria
- •Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- •Mature lymphocytes with normal structure. Gumprecht shadows
- •Bone marrow in CLL
- •Principles of treatment
- •Lymphomas
- •Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- •Clinical presentation
- •Stages of Hodgkin Lymphoma
- •Morphological classification
- •Diagnosis
- •Reed-Sternberg cells
- •Treatment
- •Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- •Hodgkin’s vs

Myeloid Maturation
myeloblast |
|
promyelocyte myelocyte metamyelocyteband |
|
neutrophil |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MATURATION 

Lymphoblast/Myeloblast
Epidemiology of acute leukemia
•2-3% of all malignancies.
•Morbidity: 3-5 per 100 000
•Diagnosis: 75% - in adults, 25% - in children
•In general myelo/lympho = 6:1
•In adults >40 years old = 4:1
•In children: 1:9
•Median age for AML = 60-65 years, for ALL = 10 years
Etiology
•Genetics
•Unstable genome in congenital disorders
•Radiation
•Chemicals
•Viruses (HLTV-1, EBV, HCV, HIV)
•Smoking (AML)

Two-hit model of leukemogenesis
Loss of function of transcription factors needed for differentiation
eg. AML1-ETO CBFb-SMMHC PML-RARa
Gain of function mutations of tyrosine kinases
eg. FLT3, c-KIT mutations
N- and K-RAS mutations
BCR-ABL TEL-PDGFbR
differentia |
+ |
enhanced |
Acute |
|
tion |
proliferati |
|||
Leukemia |
||||
block |
|
on |
|
Clinical presentation
•Anemic syndrome
•Infections and intoxication
•Haemorrhagic syndrome
•Lymphoprolipherative syndrome
•Syndrome of tumor toxicity
•Syndrome of tumor progression
•Leukostasis
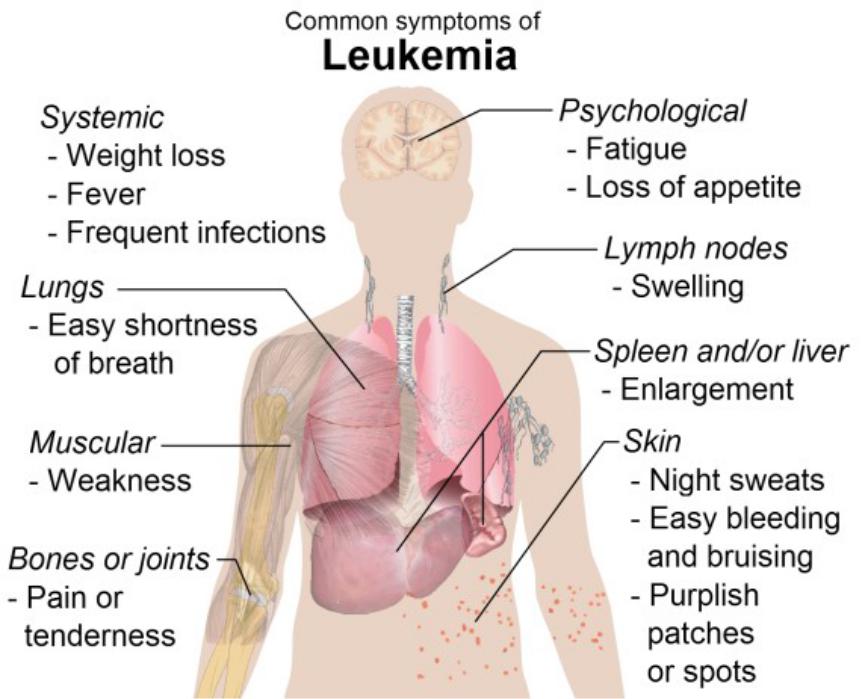
Stages of acute leukemia
•Onset
-Systemic inflammatory syndrome (fever, fatigue, intoxication)
-Symptoms associated with supression of normal hemopoiesis (anemia, haemorrhages, infections)
•Remission
•Partial
•Total (≤5% of blasts in bone marrow, normal hemopoiesis, normal general overall health, normal CBC, regression of organomegaly)
•Resistant form (no effect after 2 months of therapy)
•Minimal residual disease (residual population of leukemic cells, detected by highly sensitive methods)
•Relapse (>5% of blasts in bone marrow)
Extramedullar clinical presentation of acute leukemia
•Gum hyperplasia – infiltration of gums with blasts (specific for myeloid leukemia)
•Leukemia cutis – infiltration of the skin with blasts (formation of сyanotic lesions)
•Chloroma – solid extramedullary myeloid tumor composed of myeloblasts
•Involvement of the central nervous system -Meningeal symptoms
-Arterial hypertension -Papilledema -Nystagmus, squinty eyes -Paresthesia
•Leukemic infiltration of the organs: lungs, gut, myocardium

Leukemia cutis and chloroma
Chloroma in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Christian Sauter, M.D., and Emanuel Jacky, M.D. N Engl J Med 1998; 338:969
