
- •LIVER DISEASES
- •LIVER DISEASES
- •Do you know that …
- •Liver structure v. portae system
- •Liver
- •Liver functions
- •Major risk factors for liver disease
- •Symptoms of liver disorders
- •Fatigue
- •Jaundice
- •Jaundice or icterus
- •Jaundice: major types
- •Causes of jaundice
- •Darkening of the Urine
- •Pale (light) Stools
- •Liver Pain
- •Ascites
- •Ascites, umbilical hernia
- •Ascites
- •Симптомы и синдромы заболеваний печени
- •ПОРТАЛЬНАЯ ГИПЕРТЕНЗИЯ
- •Possible levels of block in portal hypertension
- •Hepatocellular cytolisis
- •Stigmata of chronic liver disease
- •Cholestasis syndrom
- •CHOLESTASIS
- •Etiology of Dupuitren contracture
- •Etiologic factors of gynecomastia
- •polyneuropathia
- •ПРИЧИНЫ ПОРТАЛЬНОЙ ГИПЕРТЕНЗИИ
- •Расширенные вены передней стенки живота, асцит
- •ЭГДС.
- •Расширение v. рortae и vv. hepaticae
- •ПЕЧЕНОЧНОКЛЕТОЧНАЯ
- •ПРИЧИНЫ ПЕЧЕНОЧНОЙ НЕДОСТАТОЧНОСТИ
- •Синдром печеночно-клеточной недостаточности
- •Печеночная энцефалопатия
- •ГЕПАТОРЕНАЛЬНЫЙ СИНДРОМ I и II тип
- •Патогенеза гепаторенального синдрома
- •Типы гепаторенального синдрома
- •ФАКТОРЫ, ПРОВОЦИРУЮЩИЕ РАЗВИТИЕ ГЕПАТОРЕНАЛЬНОГО СИНДРОМА (на фоне поражения печени)
- •Желтуха, ксантелазмы
- •ГИПЕРСПЛЕНИЗМ
- •Маркеры хронической алкогольной интоксикации
- •Классификация тяжести поражения печени по Чайлд-Пью
- •ЭГДС – расширенные вены пищевода
- •Пункционная биопсия печени под контролем УЗИ (цирроз)
- •Мелкоочаговое поражение печени при остром гепатите
- •Асцит, расширенная v.portae, неровность контуров при циррозе печени
- •Сцинтиграфия печени с метастазами
- •Сцинтиграфия мелкоузлового цирроза
- •Лапароскопия – крупноузловой цирроз
- •Передняя стенка живота при синдроме портальной гипертензии
- •Компьютерная томография
- •FibroScan®
- •Выраженность фиброза при фибросканировании печени
- •Stages of Liver Disease
- •Progression of Hepatitis B Infection
- •Healthy Liver
- •Healthy Liver
- •Types of Hepatitis
- •Hepatitis B is a Devastating Global Healthcare Issue
- •Hepatitis – Disease Terminology
- •How Hepatitis B is Acquired?
- •How the Infection is Acquired in the West?
- •Hepatitis B – Diagnosis Terminology
- •Diagnosis of Chronic Hepatitis B
- •Signs and Symptoms of HBV Infection
- •Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination
- •Global Control of Hepatitis B
- •Types of viral Hepatitis
- •Healthy Liver
- •Liver biopsy
- •Detection of serologic markers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, as a function
- •Lamivudine is a Potent Inhibitor of HBV Replication
- •Lamivudine has an Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profile
- •Patient Entry Criteria
- •One Year of Lamivudine - Conclusions
- •Resistance to Anti-Viral Drugs
- •Prevention of Hepatitis B
- •Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination
- •Recommendations for Pre-exposure Vaccination
- •Recommendations for Post-exposure Vaccination
- •Global Control of Hepatitis B
- •Concurrent immunologic diseases in type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Probabilities of clinical, biochemical, and histologic remission during corticosteroid therapy.
- •Clinical features of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Survival expectations and probability of developing cirrhosis during and after corticosteroid treatment.
- •liver biopsy
- •Detection of serologic markers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, as a function
- •The Efficacy and Safety of Lamivudine in HBeAg-positive Chronic Hepatitis B
- •Lamivudine is a Potent Inhibitor of HBV Replication
- •Lamivudine has an Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profile
- •What Patient Populations Have Been Studied
- •Key Lamivudine Clinical Studies (1)
- •Key Lamivudine Clinical Studies (2)
- •Patient Entry Criteria
- •Lamivudine Rapidly Suppresses
- •One Year of Lamivudine - Conclusions
- •Resistance to Anti-Viral Drugs
- •Concurrent immunologic diseases in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Probabilities of clinical, biochemical, and histologic remission during corticosteroid therapy.
- •Clinical features of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Survival expectations and probability of developing cirrhosis during and after corticosteroid treatment.
- •ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE
- •Principal alcohol-induced hepatic lesions
- •Alcohol-induced hepatic lesions
- •Pathogenesis of liver injury secondary to chronic ethanol ingestion
- •Equivalents of pure alcohol
- •Alcoholic fatty liver
- •Two-Hit Model of the Progression of Fatty Liver Disease
- •Alcoholic fatty liver
- •Similarities between Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
- •Alcoholic hepatitis
- •This figure depicts a laparoscopic view of a patient with chronic active hepatitis
- •Percutaneous liver biopsy with or without ultrasonic guidance
- •Alcoholic hepatitis: liver biopsy
- •Treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis
- •Причины смерти при алкогольном гепатите
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis: clinical manifestations

Percutaneous liver biopsy with or without ultrasonic guidance
•standard diagnostic approach for establishing the presence of chronic hepatitis
•Laparoscopic liver biopsy, which is used in large referral centers, has the advantage of minimizing the sample error by facilitating gross inspection of the liver and thus ensuring an adequate biopsy sample size.

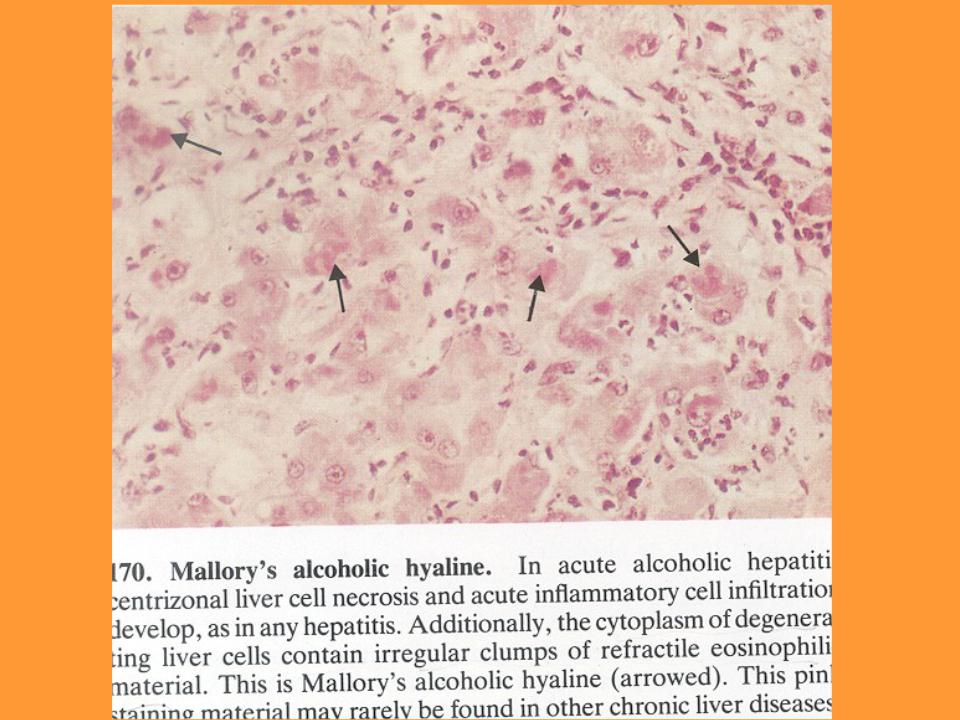
Alcoholic hepatitis: liver biopsy
•Major features found include
–marked variation in cell size
–evidence of cell necrosis and variable inflammation with a mixture of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cell
–there is evidence of variable sinusoidal compression
–pericellular fibrosis is an important feature
–In many pts eosinophilic inclusions (Mallory bodies) are found
–Often the most intense alcoholic-induced injury is in Zone III (centrilobular)


Treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis
•Administration of prednisolone in moderately large doses may be helpful in patients with encephalopathy
•However, the use of glucocorticoids in acute alcoholic hepatitis remains controversial and should probably be reserved
•Maintenance therapy with colchicine (0.6 mg PO bid) has been shown to slow disease progression and increase longevity of the patient with alcoholic liver disease in one long-term study.

Причины смерти при алкогольном гепатите
• |
Печеночная недостаточность (кома) 56% |
|
• |
Кровотечение |
31% |
• |
Гепаторенальный синдром |
28% |
• |
Инфекция |
15% |

Alcoholic cirrhosis
•The typical alcoholic patient with cirrhosis has had a daily consumption of a pint or more of whiskey, several quarts of wine, or an equivalent amount of beer for at least 10 years.
•The amount and duration of ethanol ingestion, rather than the type of alcoholic beverage or the pattern of ingestion, appear to be the important determinants

Alcoholic cirrhosis
•historically referred to as Laennec's cirrhosis
•is the most common type of cirrhosis in North and South America and in western Europe
•It is characterized by diffuse fine scarring, fairly uniform loss of liver cells, and small regenerative nodules
•may be clinically silent and 10 to 40% cases are discovered incidentally at laparotomy or autopsy
•In many cases symptoms are insidious in onset, occurring usually after 10 or more years of excessive alcohol use and progressing slowly over subsequent weeks and months

Alcoholic cirrhosis: clinical manifestations
•Easy bruising
•Increasing weakness and fatigue
•Hepatocellular dysfunction and portal hypertension
•Anorexia and malnutrition lead to weight loss and a reduction in skeletal muscle mass
•Progressive jaundice
•Bleeding from gastroesophageal varices, ascites
•Encephalopathy
•Progressive renal dysfunction often complicates the terminal phase of the illness.
