
- •Acute kidney injury.
- •Relationships between AKI, AKD and CKD
- •Incidence of kidney pathology
- •Acute kidney injury
- •AKI criteria
- •AKI stages (KDIGO)
- •Classification of AKI
- •Common causes of AKI
- •Clinical Presentation of AKI
- •Diagnostic Approach in AKI
- •Prerenal AKI
- •Diagnosing pre-renal AKI
- •Renal AKI
- •Further lab evaluation for renal AKI
- •Postrenal AKI
- •Urine Output and AKI
- •Principles of AKI Management
- •Principles of AKI Management
- •Acute kidney disease
- •Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- •Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease
- •Conceptual model of CKD
- •Key questions in CKD
- •Assessment of renal function: estimation of GFR
- •Why CKD-EPI is the most appropriate estimation of GFR?
- •www.kidney.org
- •Assessment of renal function: GFR measurement
- •How to assess albuminuria?
- •GFR categories in CKD
- •Albuminuria categories in CKD
- •CKD causes
- •Risk factors of CKD
- •Каковы факторы прогрессирования ХБП
- •Prognosis of CKD by GFR and albuminuria categories
- •GFR and albuminuria grid to reflect the risk of progression by intensity of
- •How to formulate diagnosis in CKD?
- •Clinical case
- •Stratification by cardiovascular and renal risks
- •Clinical diagnosis
- •Treatment of CKD
- •Renal replacement therapy
- •Clinical examples
- •73-year old female
- •Physical examination
- •Blood chemistry:
- •Индексация ХБП по уровню альбуминурии
- •Сstratification by cardiovascular and renal risks
- •Recommended frequency of monitoring
- •Направление к нефрологу в зависимости от категории СКФ и альбуминурии
- •Diagnosis:
- •69-year old male
- •no abnormalities in physical examination at admission BP 167/80 mmHg
- •Blood chemistry
- •Diagnosis
Acute kidney injury.
Chronic kidney disease
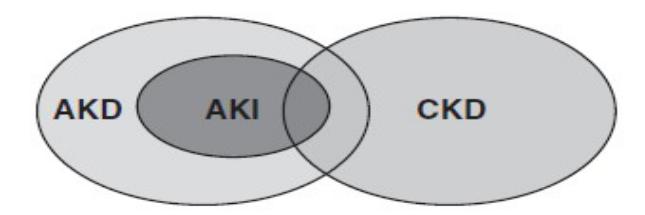
Relationships between AKI, AKD and CKD
•AKD – acute kidney disease (duration <3 months)
•AKI – acute kidney injury (subset of AKD)
•CKD – chronic kidney disease
•AKI and AKD may be superimposed upon CKD
Incidence of kidney pathology
AKI
Incidence
•20-200 cases per 1 million of general population
•7-18% hospitalized patients
•≥50% of intensive care department patients
High mortality
•5-10% in uncomplicated AKI
•50-70% in AKI secondary to other organ failure( intensive care)
•> 50% in dialysis requiring AKI
CKD
•CKD - a candidate for the 5th "killer disease"
•CKD is widespread (10-13% of the adult population)
•CKD is a lethal disease (only 1 out of 30 CKD patients survives to receive RRT, the rest die from CV complications)
•CKD is treatable (screening in risk groups, renoprotective strategy, fighting with vascular calcification)
Lewington, A. J. et al. Kidney Int. 84, 457–467 (2013) Hoste, E. A. et al. Intensive Care Med. 41, 1411–1423 (2015)
Selby NM et al CJASN 2012; 7(4): 533-40
Acute kidney injury
AKI as an abrupt decrease in kidney function that occurs over a period of 7 days or less. May be accompanied by electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalance
The cause of AKI should be determined if possible. The most important thing is to detect reversible causes
AKI criteria
•Increase in SCr of ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 µmol/l) in 48 h; OR
•Increase in SCr ≥ 1.5 fold from baseline in 7 days OR
•Oliguria< 0.5 ml/kg/h x 6 h
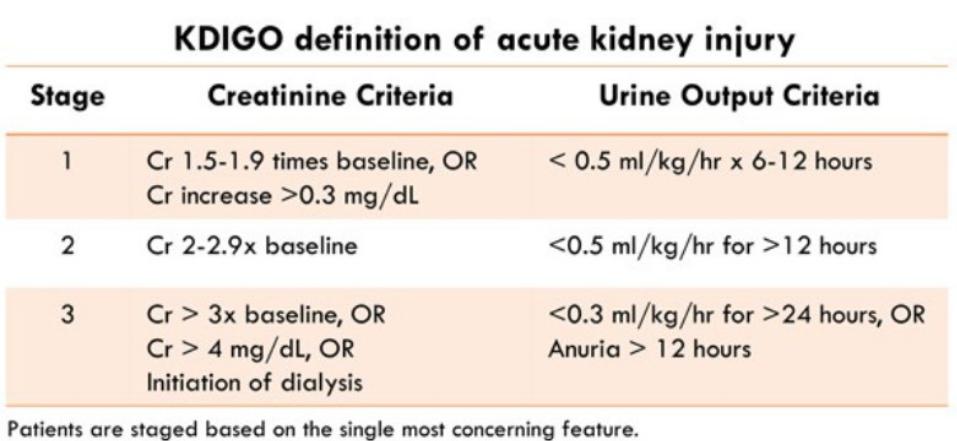
AKI stages (KDIGO)
Classification of AKI
•Prerenal
•Renal
•Postrenal
Risk factors of AKI
•Age (new-born, >60 years), pregnancy, delivery,
•Metabolic (gout, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus)
•Haemodynamic (heart failure, liver cirrhosis)
•Drugs (sulfonamides, antibiotics, etc.)
•Toxic (alcohol, narcotics)
•Traumatic (polytrauma, massive burns, cardiac surgery)
•Renal (obstructive kidney disease, nephrotic syndrome, toxemia of pregnancy, chronic renal failure)
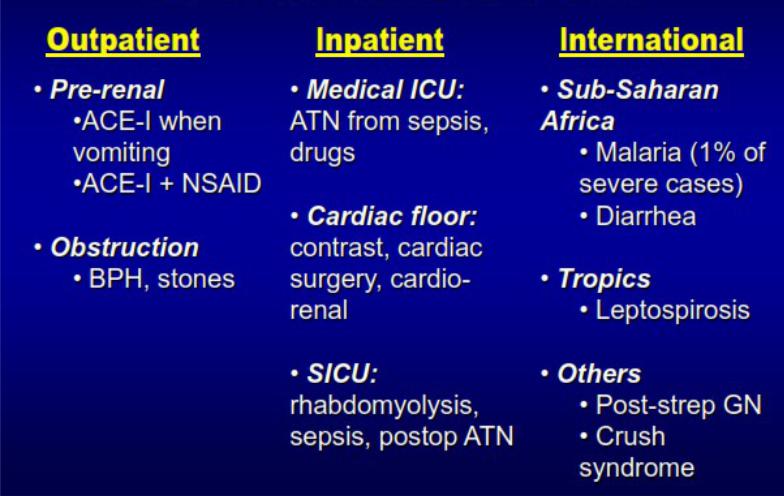
Common causes of AKI
Clinical Presentation of AKI
•Symptoms
•Malaise
•Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting
•Pruritus
•Dehydration
•Confusion, convulsions
•Signs
•Hypertension
•Fluid overload: peripheral oedema, SOB/ bibasal crackles/raised JVP
•Dehydration: postural hypotension, poor urine output (palpable bladder)
Diagnostic Approach in AKI
•Time of onset – prior serum creatinine
•Careful review of history and physical exam
•Comorbidities
•Medications
•Current illness (vomiting, diarrhea, blood loss, etc)
•BP, volume status, skin lesions, flank/abdominal signs
