
- •Acute kidney injury.
- •Relationships between AKI, AKD and CKD
- •Incidence of kidney pathology
- •Acute kidney injury
- •AKI criteria
- •AKI stages (KDIGO)
- •Classification of AKI
- •Common causes of AKI
- •Clinical Presentation of AKI
- •Diagnostic Approach in AKI
- •Prerenal AKI
- •Diagnosing pre-renal AKI
- •Renal AKI
- •Further lab evaluation for renal AKI
- •Postrenal AKI
- •Urine Output and AKI
- •Principles of AKI Management
- •Principles of AKI Management
- •Acute kidney disease
- •Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- •Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease
- •Conceptual model of CKD
- •Key questions in CKD
- •Assessment of renal function: estimation of GFR
- •Why CKD-EPI is the most appropriate estimation of GFR?
- •www.kidney.org
- •Assessment of renal function: GFR measurement
- •How to assess albuminuria?
- •GFR categories in CKD
- •Albuminuria categories in CKD
- •CKD causes
- •Risk factors of CKD
- •Каковы факторы прогрессирования ХБП
- •Prognosis of CKD by GFR and albuminuria categories
- •GFR and albuminuria grid to reflect the risk of progression by intensity of
- •How to formulate diagnosis in CKD?
- •Clinical case
- •Stratification by cardiovascular and renal risks
- •Clinical diagnosis
- •Treatment of CKD
- •Renal replacement therapy
- •Clinical examples
- •73-year old female
- •Physical examination
- •Blood chemistry:
- •Индексация ХБП по уровню альбуминурии
- •Сstratification by cardiovascular and renal risks
- •Recommended frequency of monitoring
- •Направление к нефрологу в зависимости от категории СКФ и альбуминурии
- •Diagnosis:
- •69-year old male
- •no abnormalities in physical examination at admission BP 167/80 mmHg
- •Blood chemistry
- •Diagnosis
CKD causes
•Primary nephropathy (chronic or rapidly progressive GN)
•Primary tubular-interstitial disorders (chronic pyelonephritis, interstitial and radiation nephritis)
•Urinary tract obstruction (kidney stones, hydronephrosis, tumors of urinary tract)
•Vascular diseases (malignant hypertension, renal artery stenosis, hypertension)
•Systemic autoimmune diseases (SLE, systemic sclerosis)
•Metabolic disorders (DM, amyloidosis, gout)
•Drugs
•Toxins
•Congenital disorders (polycystic kidney disease, renal hypoplasia, Alport syndrome)
Risk factors of CKD
Non-modifiable
Old age Male gender
Initial low amount of nephrons (low birth weight) Ethnic aspects
Genetic factors (including family history of CKD)
Модифицируемые
Артериальная гипертония Сахарный диабет Ожирение/метаболический синдром Дислипидемия Табакокурение Аутоиммунные заболевания
Хроническое воспаление/системные инфекции Инфекции и конкременты мочевых путей Обструкция нижних мочевых путей Лекарственная токсичность Высокое потребление белка Гипергомоцистеинемия Беременность
Каковы факторы прогрессирования ХБП
Modifiable Hypertension Diabetes
Obesity/metabolic syndrome Dyslipidemia
Smoking Autoimmune diseases
Chronic inflammation/systemic infection Infections and concrements of urinary tract Urinary tract obstruction
Drugs toxicity
High protein and sodium intake Hyperhomocysteinemia Pregnancy
Persistent activity of the disease
High proteinuria Anemia Metabolic acidosis
Ca/P disturbances (hyperparathyroidism)
Национальные рекомендации. Хроническая болезнь почек. Проект. http:// journal.nephrolog.ru/ckd/

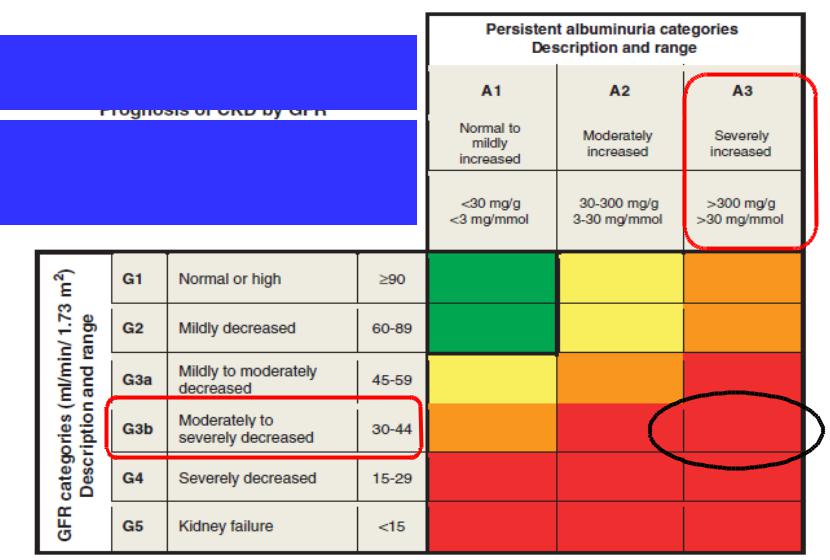
Prognosis of CKD by GFR and albuminuria categories
Green: low risk (if no other markers of kidney disease, no CKD); Yellow: moderately increased risk; Orange: high risk; Red, very high risk.

GFR and albuminuria grid to reflect the risk of progression by intensity of coloring (green, yellow, orange, red, deep red). The numbers in the boxes are a guide to the frequency of monitoring (number of times per year).

How to formulate diagnosis in CKD?
Describe the primary disease and its clinical presentation
Mention CKD GFR, albuminuria category and type of renal replacement therapy
Национальные рекомендации. Хроническая болезнь почек: основные положения, определение, диагностика, скрининг, подходы к профилактике и лечению. http://journal.nephrolog.ru/ckd/
Clinical case
•Female, 72 years
•DM, MI 4 years ago
•WC 108 cm
•HbA1c 7,3%, LDL 3,4 mmol/l
•BP 158/84 mmHg
•Creatinine 112 µmol/l, UACr 384 mg/g
•4 months ago
•UACr 350 mg/g
Stratification by cardiovascular and renal risks
eGFR 42 ml/min/1,73 m2 UACr 384 mg/g
Diabetic and hypertensive kidney diseases
CKD G3bА3.
http://www.kidney-international.org Kidney International 2013;3(1): S1-163
Clinical diagnosis
•Arterial hypertension, stage II, risk 3 (high). Left ventricular hypertrophy
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, target HbA1c <7,0%.
•Abdominal obesity. Dyslipidemia.
•Diabetic and hypertensive kidney disease. CKD G3b, А3.
Treatment of CKD
•Low-protein diet with sufficient amount of potassium and phosphorus
•BP control (target BP < 140/90 mmHg)
•Glycemia control
•Cholesterol control
•Correction of electrolyte and acid-base disturbances
•Anemia treatment (erythropoietin)
•Prevention of hyperparathyroidism
•Treatment of acute infections
